Abstract
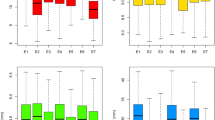
Maize (Zea mays L.) is one of the most important crops throughout the world. In this study, three agronomic traits related to kernel morphology of a recombinant inbred line (RIL) population derived from the cross between Mo17 and Huangzao4 were selected to be investigated, including kernel length, kernel width and kernel height. Furthermore, the descriptive statistics and correlation analysis were performed using SPSS 11.5 software in the three traits. The results are useful for further quantitative trait locus mapping and molecular marker-assisted selection for the three kernel morphology traits in maize breeding program.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bouchez A, Hospital F, Causse M, Gallais A, Charcosset A (2002) Marker-assisted introgression of favorable alleles at quantitative trait loci between maize elite lines. Genetics 162:1945–1959
Cao Y, Li C, Yan J, Jiao F, Liu X, Hasty KA, Stuart JM, Gu W, Jiao Y (2012) Analysis of candidate genes of spontaneous arthritis in mice deficient for interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Genes Genet Syst 87:107–113
Chardon F, Virlon B, Moreau L, Falque M, Joets J, Decousset L, Murigneux A, Charcosset A (2004) Genetic architecture of flowering time in maize as inferred from quantitative trait loci meta-analysis and synteny conservation with the rice genome. Genetics 168:2169–2185
Conti V, Roncallo PF, Beaufort V, Cervigni GL, Miranda R, Jensen CA, Echenique VC (2011) Mapping of main and epistatic effect QTLs associated to grain protein and gluten strength using a RIL population of durum wheat. J Appl Genet 52:287–298
Ding AM, Li J, Cui F, Zhao CH, Ma HY, Wang HG (2011) QTL mapping for yield related traits using two associated RIL populations of wheat. Acta Agronomica Sinica 37(9):1511–1524
Ding JQ, Wang XM, Chander S, Li JS (2008) Identification of QTL for maize resistance to common smut by using recombinant inbred lines developed from the Chinese hybrid Yuyu22. J Appl Genet 49:147–154
Ding D, Li WH, Song GL, Qi HY, Liu JB, Tang JH (2011) Identification of QTLs for arsenic accumulation in maize (Zea mays L.) Using a RIL Population. PLoS ONE 6:e25646
Dobón A, Canet JV, Perales L, Tornero P (2011) Quantitative genetic analysis of salicylic acid perception in Arabidopsis. Planta 234:671–684
Fu S, Zhan Y, Zhi H, Gai J, Yu D (2006) Mapping of SMV resistance gene Rsc-7 by SSR markers in soybean. Genetica 128:63–69
Guo JF, Su GQ, Zhang JP, Wang GY (2008) Genetic analysis and QTL mapping of maize yield and associate agronomic traits under semiarid land condition. Afr J Biotechnol 7:1829–1838
Hatakeyama K, Horisaki A, Niikura S, Narusaka Y, Abe H, Yoshiaki H, Ishida M, Fukuoka H, Matsumoto S (2010) Mapping of quantitative trait loci for high level of self-incompatibility in Brassica rapa L. Genome 53:257–265
Li M, Sun P, Zhou H, Chen S, Yu S (2011) Identification of quantitative trait loci associated with germination using chromosome segment substitution lines of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 123:411–420
Liu QM, Jiang JH, Niu FA, He YJ, Hong DL (2013) QTL analysis for seven quality traits of RIL population in Japonica rice based on three genetic statistical models. Rice Sci 20:31–38
Liu R, Wang B, Guo W, Wang L, Zhang T (2011) Differential gene expression and associated QTL mapping for cotton yield based on a cDNA-AFLP transcriptome map in an immortalized F2. Theor Appl Genet 123:439–454
Liu XH, Zheng ZP, Tan ZB, Li Z, He C, Liu DH, Zhang GQ, Luo YC (2010) QTL mapping for controlling anthesis-silking interval based on RIL population in maize. Afr J Biotechnol 9:950–955
Ma Z, Zhao D, Zhang C, Zhang Z, Xue S, Lin F, Kong Z, Tian D, Luo Q (2007) Molecular genetic analysis of five spike-related traits in wheat using RIL and immortalized F2 populations. Mol Genet Genomics 277:31–42
Ordas B, Malvar RA, Hill WG (2008) Genetic variation and quantitative trait loci associated with developmental stability and the environmental correlation between traits in maize. Genet Res 90:385–395
Pilet ML, Duplan G, Archipiano M, Barret P, Baron C, Horvais R, Tanguy X, Lucas MO, Renard M, Delourme R (2001) Stability of QTL for field resistance to blackleg across two genetic backgrounds in oilseed rape. Crop Sci 41:197–205
Ribaut JM, Jiang C, Gonzales-de-Leon D, Edmeades GO, Hosington D (1997) Identification of quantitative trait loci under drought trait loci under drought conditions in tropical maize. 2. Yield components and marker-assisted selection strategies. Theor Appl Genet 94:887–896
Salomé PA, Bomblies K, Laitinen RA, Yant L, Mott R, Weigel D (2011) Genetic architecture of flowering-time variation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 188:421–433
Sandal N, Jin H, Rodriguez-Navarro DN, Temprano F, Cvitanich C, Brachmann A, Sato S, Kawaguchi M, Tabata S, Parniske M, Ruiz-Sainz JE, Andersen SU, Stougaard J (2012) A set of Lotus japonicus Gifu x Lotus burttii recombinant inbred lines facilitates map-based cloning and QTL mapping. DNA Res 19:317–323
Takagi H, Abe A, Yoshida K, Kosugi S, Natsume S, Mitsuoka C, Uemura A, Utsushi H, Tamiru M, Takuno S, Innan H, Cano LM, Kamoun S, Terauchi R (2013) QTL-seq: rapid mapping of quantitative trait loci in rice by whole genome resequencing of DNA from two bulked populations. Plant J 74:174–183
Wan X, Weng J, Zhai H, Wang J, Lei C, Liu X, Guo T, Jiang L, Su N, Wan J (2008) Quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis for rice grain width and fine mapping of an identified QTL allele gw-5 in a recombination hotspot region on chromosome 5. Genetics 179:2239–2252
Wan XY, Wan JM, Jiang L, Wang JK, Zhai HQ, Weng JF, Wang HL, Lei CL, Wang JL, Zhang X, Cheng ZJ, Guo XP (2006) QTL analysis for rice grain length and fine mapping of an identified QTL with stable and major effects. Theor Appl Genet 112:1258–1270
Wang HL, Yu DY, Wang YJ, Chen SY, Gai JY (2004) Mapping QTL of soybean root weight with RIL population NJRIKY. Yi Chuan 26:333–336
Wang L, Wang AH, Huang XH, Zhao Q, Dong GJ, Qian Q, Sang T, Han B (2011) Mapping 49 quantitative trait loci at high resolution through sequencing-based genotyping of rice recombinant inbred lines. Theor Appl Genet 122:327–340
Xu P, Wang H, Li Q, Gai JY, Yu DY (2007) Mapping QTLs related to oil content of soybeans. Yi Chuan 29:92–96
Yang XJ, Lu M, Zhang SH, Zhou F, Qu YY, Xie CX (2008) QTL mapping of plant height and ear position in maize (Zea mays L.). Yi Chuan 30:1477–1486
Zhang Z, Liu Z, Cui Z, Hu Y, Wang B, Tang J (2013) Genetic analysis of grain filling rate using conditional QTL mapping in maize. PLoS ONE 8(2):e56344
Zheng ZP, Liu XH (2013) Genetic analysis of agronomic traits associated with plant architecture by QTL mapping in maize. Genet Mol Res 12:1243–1253
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Scientific Research Fund of the Sichuan Provincial Education Department (13ZA0012) of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this paper
Cite this paper
Liao, C., He, D., Liu, X. (2014). Descriptive Statistics and Correlation Analysis of Three Kernel Morphology Traits in a Maize Recombinant Inbred Line Population. In: Li, S., Jin, Q., Jiang, X., Park, J. (eds) Frontier and Future Development of Information Technology in Medicine and Education. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 269. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-7618-0_78
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-7618-0_78
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-007-7617-3
Online ISBN: 978-94-007-7618-0
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)