Abstract
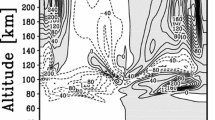
Vertical coupling by atmospheric waves is essential for the wind and temperature structure of the middle atmosphere. In particular, momentum carried by atmospheric gravity waves (GWs) governs the global circulation in the mesosphere and is for instance the reason for the cold summer mesopause. However, the small horizontal scales of GWs (tens to thousands of km) are challenging both global modeling and observations from satellite. Further, due to the small scales involved, there is a severe lack of understanding about GWs themselves, as well as dynamical phenomena involving GWs. Until recently, global observations of GWs were sparse and little was known about the global distribution of GWs, as well as their seasonal variation. Therefore, several projects in the priority program Climate And Weather of the Sun-Earth System (CAWSES) of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) have addressed a number of the most pressing problems. Global distributions of GW activity and momentum fluxes have been derived from observations with number of satellite instruments, resulting in the first multi-year global data sets of GW parameters, covering time scales from seasonal variations up to the duration of almost a full 11-year solar cycle. In addition, seasonal and tidal variations of sporadic E layers in the ionosphere were studied in Global Positioning System (GPS) radio occultation data. Satellite observations of GWs and sporadic E layers were complemented by ground-based observations (radar and low-frequency (LF) drift measurements). All these observations, as well as accompanying modeling activities provided important constraints for GW parameterizations. Further activities addressed important aspects of GW propagation usually neglected in global modeling: GW ray tracing studies revealed the importance of non-vertical propagation of GWs and first steps were undertaken to develop an improved GW parameterization based on GW ray tracing techniques.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, M. J., Gille, J. C., Cavanaugh, C., Coffey, M., Craig, C., Eden, T., Francis, G., Halvorson, C., Hannigan, J., Khosravi, R., Kinnison, D., Lee, H., Massie, S., Nardi, B., Barnett, J. J., Hepplewhite, C., Lambert, A., & Dean, V. (2008). Global estimates of gravity wave momentum flux from High Resolution Dynamics Limb Sounder observations. Journal of Geophysical Research, 113, D15S18. doi:10.1029/2007JD008807.
Alexander, M. J., Geller, M., McLandress, C., Polavarapu, S., Preusse, P., Sassi, F., Sato, K., Eckermann, S., Ern, M., Hertzog, A., Kawatani, Y., Pulido, M., Shaw, T. A., Sigmond, M., Vincent, R., & Watanabe, S. (2010). Recent developments in gravity-wave effects in climate models and the global distribution of gravity-wave momentum flux from observations and models. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 136, 1103–1124. doi:10.1002/qj.637.
Arras, C., Wickert, J., Beyerle, G., Heise, S., Schmidt, T., & Jacobi, C. (2008). A global climatology of ionospheric irregularities derived from GPS radio occultation. Geophysical Research Letters, 35, L14809. doi:10.1029/2008GL034158.
Arras, C., Jacobi, C., & Wickert, J. (2009). Semidiurnal tidal signature in sporadic E occurrence rates derived from GPS radio occultation measurements at higher midlatitudes. Annales Geophysicae, 27, 2555–2563.
Baldwin, M. P., & Dunkerton, T. J. (2001). Stratospheric harbingers of anomalous weather regimes. Science, 294, 581–584.
Charron, M., & Manzini, E. (2002). Gravity waves from fronts: parameterization and middle atmosphere response in a general circulation model. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 59, 923–941.
de la Torre, A., Schmidt, T., & Wickert, J. (2006a). A global analysis of wave potential energy in the lower stratosphere derived from 5 years of GPS radio occultation data with CHAMP. Geophysical Research Letters, 33, L24809. doi:10.1029/2006GL027696.
de la Torre, A., Alexander, P., Llamedo, P., Menéndez, C., Schmidt, T., & Wickert, J. (2006b). Gravity waves above the Andes detected from GPS radio occultation temperature profiles: jet mechanism? Geophysical Research Letters, 33, L24810. doi:10.1029/2006GL027343.
de la Torre, A., Llamedo, P., Alexander, P., Schmidt, T., & Wickert, J. (2010). Estimated errors in a global gravity wave climatology from GPS radio occultation temperature profiles. Advances in Space Research, 46, 174–179. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2010.02.033.
Dunkerton, T. J. (1997). The role of gravity waves in the quasi-biennial oscillation. Journal of Geophysical Research, 102, 26053–26076.
Ern, M., & Preusse, P. (2009a). Wave fluxes of equatorial Kelvin waves and QBO zonal wind forcing derived from SABER and ECMWF temperature space-time spectra. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 9, 3957–3986. doi:10.5194/acp-9-3957-2009.
Ern, M., & Preusse, P. (2009b). Quantification of the contribution of equatorial Kelvin waves to the QBO wind reversal in the stratosphere. Geophysical Research Letters, 36, L21801. doi:10.1029/2009GL040493.
Ern, M., Preusse, P., Alexander, M. J., & Warner, C. D. (2004). Absolute values of gravity wave momentum flux derived from satellite data. Journal of Geophysical Research, 109, D20103. doi:10.1029/2004JD004752.
Ern, M., Preusse, P., & Warner, C. D. (2005). A comparison between CRISTA satellite data and Warner and McIntyre gravity wave parameterization scheme: Horizontal and vertical wavelength filtering of gravity wave momentum flux. Advances in Space Research, 35, 2017–2023. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2005.04.109.
Ern, M., Preusse, P., & Warner, C. D. (2006). Some experimental constraints for spectral parameters used in the Warner and McIntyre gravity wave parameterization scheme. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 6, 4361–4381. doi:10.5194/acp-6-4361-2006.
Ern, M., Preusse, P., Gille, J. C., Hepplewhite, C. L., Mlynczak, M. G., Russell III, J. M., & Riese, M. (2011). Implications for atmospheric dynamics derived from global observations of gravity wave momentum flux in stratosphere and mesosphere. Journal of Geophysical Research, 116, D19107. doi:10.1029/2011JD015821.
Fleming, E. L., Chandra, S., Barnett, J. J., & Corney, M. (1990). Zonal mean temperature, pressure, zonal wind and geopotential height as functions of latitude. Advances in Space Research, 12, 1211–1259.
Fomichev, V. I., Ward, W. E., Beagley, S. R., McLandress, C., McConnell, J. C., McFarlane, N. A., & Shepherd, T. G. (2002). Extended Canadian Middle Atmosphere model: zonal-mean climatology and physical parameterizations. Journal of Geophysical Research, 107, 4087. doi:10.1029/2001JD000479.
Fritts, D. C., & Alexander, M. J. (2003). Gravity wave dynamics and effects in the middle atmosphere. Reviews of Geophysics, 41, 1003. doi:10.1029/2001RG000106.
Fröhlich, K., Ern, M., Jacobi, C., & Preusse, P. (2006). Implementation of the Warner-McIntyre scheme of gravity wave parametrization into COMMA-LIM, Part I: code transfer. Reports of the Institute of Meteorology, University of Leipzig, 37, 11–16.
Fröhlich, K., Schmidt, T., Ern, M., Preusse, P., de la Torre, A., Wickert, J., & Jacobi, C. (2007). The global distribution of gravity wave energy in the lower stratosphere derived from GPS data and gravity wave modelling: Attempt and challenges. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 69, 2238–2248. doi:10.1016/j.jastp.2007.07.005.
Garcia, R. R., & Randel, W. J. (2008). Acceleration of the Brewer Dobson circulation due to increases in greenhouse gases. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 65, 2731–2739.
Garcia, R. R., Marsh, D. E., Kinnison, D. E., Boville, B. A., & Sassi, F. (2007). Simulation of secular trends in the middle atmosphere, 1950–2003. Journal of Geophysical Research, 112, D09301. doi:10.1029/2006JD007485.
Gavrilov, N. M., Manson, A. H., & Meek, C. E. (1995). Climatological monthly characteristics of middle atmosphere gravity waves (10 min–10 h) during 1979–1993 at Saskatoon. Annales Geophysicae, 13, 285–295.
Gavrilov, N. M., Fukao, S., Nakamura, T., Jacobi, C., Kürschner, D., Manson, A. H., & Meek, C. E. (2002). Comparative study of interannual changes of the mean winds and gravity wave activity in the middle atmosphere over Japan, Central Europe and Canada. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 64, 1003–1010.
Gavrilov, N. M., Riggin, D. M., & Fritts, D. C. (2004). Interannual variations of the mean wind and gravity wave variances in the middle atmosphere over Hawaii. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 66, 637–645.
Hines, C. O. (1997a). Doppler-spread parameterization of gravity-wave momentum deposition in the middle atmosphere. Part 1: basic formulation. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 59, 371–386.
Hines, C. O. (1997b). Doppler-spread parameterization of gravity-wave momentum deposition in the middle atmosphere. Part 2: broad and quasi monochromatic spectra and implementation. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 59, 387–400.
Hocke, K., & Tsuda, T. (2001). Gravity waves and ionospheric irregularities over tropical convection zones observed by GPS/MET radio occultation. Geophysical Research Letters, 28, 2815–2818.
Hoffmann, P., Becker, E., Singer, W., & Placke, M. (2010). Seasonal variation of mesospheric waves at northern middle and high latitudes. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 72, 1068–1079. doi:10.1016/j.jastp.2010.07.002.
Holton, J. R. (1982). The role of gravity wave induced drag and diffusion in the momentum budget of the mesosphere. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 39, 791–799.
Holton, J. R. (1983). The influence of gravity wave breaking on the general circulation of the middle atmosphere. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 40, 2497–2507.
Holton, J. R., & Lindzen, R. S. (1972). An updated theory for the quasi-biennial cycle of the tropical stratosphere. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 29, 1076–1080.
Holton, J. R., & Tan, H.-C. (1980). The influence of the equatorial quasi-biennial oscillation on the global circulation at 50 mb. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 37, 2200–2208.
Jacobi, C., Gavrilov, N. M., Kürschner, D., & Fröhlich, K. (2006). Gravity wave climatology and trends in the mesosphere/lower thermosphere region deduced from low-frequency drift measurements 1984–2003 (52.1°N, 13.2°E). Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 68, 1913–1923. doi:10.1016/j.jastp.2005.12.007.
Jiang, J. H., Eckermann, S. D., Wu, D. L., & Ma, J. (2004a). A search for mountain waves in MLS stratospheric limb radiances from the winter northern hemisphere: Data analysis and global mountain wave modeling. Journal of Geophysical Research, 109, D03107. doi:10.1029/2003JD003974.
Jiang, J. H., Wang, B., Goya, K., Hocke, K., Eckermann, S. D., Ma, J., Wu, D. L., & Read, W. G. (2004b). Geographical distribution and interseasonal variability of tropical deep convection: UARS MLS observations and analyses. Journal of Geophysical Research, 109, D03111. doi:10.1029/2003JD003756.
Kodera, K., Matthes, K., Shibata, K., Langematz, U., & Kuroda, Y. (2003). Solar impact on the lower mesospheric subtropical jet: a comparative study with general circulation model simulations. Geophysical Research Letters, 30, 1315. doi:10.1029/2002GL016124.
Krebsbach, M., & Preusse, P. (2007). Spectral analysis of gravity wave activity in SABER temperature data. Geophysical Research Letters, 34, L03814. doi:10.1029/2006GL028040.
Li, F., Austin, J., & Wilson, J. (2008). The strength of the Brewer Dobson circulation in a changing climate: coupled chemistry climate model simulations. Journal of Climate, 21, 40–57. doi:10.1175/2007JCLI1663.1.
Lindzen, R. S. (1981). Turbulence and stress owing to gravity wave and tidal breakdown. Journal of Geophysical Research, 86, 9707–9714.
Lindzen, R. S., & Holton, J. R. (1968). A theory of the quasi-biennial oscillation. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 25, 1095–1107.
Lübken, F.-J. (1997). Seasonal variation of turbulent energy dissipation rates at high latitudes as determined by in situ measurements of neutral density fluctuations. Journal of Geophysical Research, 102, 13441–13456.
Marshall, A. G., & Scaife, A. A. (2009). Impact of the QBO on surface winter climate. Journal of Geophysical Research, 114, D18110. doi:10.1029/2009JD011737.
McLandress, C., & Scinocca, J. F. (2005). The GCM response to current parameterizations of nonorographic gravity wave drag. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 62, 2394–2413.
McLandress, C., & Shepherd, T. G. (2009). Simulated anthropogenic changes in the Brewer Dobson circulation, including its extension to high latitudes. Journal of Climate, 22, 1516–1540. doi:10.1175/2008JCLI2679.1.
Oberheide, J., Forbes, J. M., Häusler, K., Wu, Q., & Bruinsma, S. L. (2009). Tropospheric tides from 80 to 400 km: propagation, interannual variability, and solar cycle effects. Journal of Geophysical Research, 114, D00I05. doi:10.1029/2009JD012388.
Orr, A., Bechtold, P., Scinocca, J. F., Ern, M., & Janiskova, M. (2010). Improved middle atmosphere climate and forecasts in the ECMWF model through a non-orographic gravity wave drag parametrization. Journal of Climate, 23, 5905–5926. doi:10.1175/2010JCLI3490.1.
Placke, M., Stober, G., & Jacobi, C. (2011). Gravity wave momentum fluxes in the MLT—Part I: seasonal variation at Collm (51.3°N, 13.0°E). Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 73, 904–910. doi:10.1016/j.jastp.2010.07.012.
Pogoreltsev, A. I., Vlasov, A. A., Fröhlich, K., & Jacobi, C. (2007). Planetary waves in coupling the lower and upper atmosphere. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 69, 2083–2101. doi:10.1016/j.jastp.2007.05.014.
Powell, A. M., & Xu, J. (2011). Possible solar forcing of interannual and decadal stratospheric planetary wave variability in the northern hemisphere: an observational study. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 73, 825–838. doi:10.1016/j.jastp.2011.02.001.
Preusse, P., Ern, M., Eckermann, S. D., Warner, C. D., Picard, R. H., Knieling, P., Krebsbach, M., Russell III, J. M., Mlynczak, M. G., Mertens, C. J., & Riese, M. (2006). Tropopause to mesopause gravity waves in August: measurement and modeling. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 68, 1730–1751. doi:10.1016/j.jastp.2005.10.019.
Preusse, P., Schroeder, S., Hoffmann, L., Ern, M., Friedl-Vallon, F., Oelhaf, H., Fischer, H., & Riese, M. (2009a). New perspectives on gravity wave remote sensing by spaceborne infrared limb imaging. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2, 299–311.
Preusse, P., Eckermann, S. D., Ern, M., Oberheide, J., Picard, R. H., Roble, R. G., Riese, M., Russell III, J. M., & Mlynczak, M. G. (2009b). Global ray tracing simulations of the SABER gravity wave climatology. Journal of Geophysical Research, 114, D08126. doi:10.1029/2008JD011214.
Rauthe, M., Gerding, M., Höffner, J., & Lübken, F.-J. (2006). Lidar temperature measurements of gravity waves over Kühlungsborn (54°N) from 1 to 105 km: a winter-summer comparison. Journal of Geophysical Research, 111, D24108. doi:10.1029/2006JD007354.
Richter, J. H., Sassi, F., & Garcia, R. R. (2010). Toward a physically based gravity wave source parameterization in a general circulation model. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 67, 136–156.
Riese, M., Spang, R., Preusse, P., Ern, M., Jarisch, M., Offermann, D., & Grossmann, K. U. (1999). Cryogenic infrared spectrometers and telescopes for the atmosphere (CRISTA) data processing and atmospheric temperature and trace gas retrieval. Journal of Geophysical Research, 104, 16349–16367.
Schmidt, T., Beyerle, G., Heise, S., Wickert, J., & Rothacher, M. (2006). A climatology of multiple tropopauses derived from GPS radio occultations with CHAMP and SAC-C. Geophysical Research Letters, 33, L04808. doi:10.1029/2005GL024600.
Schmidt, T., de la Torre, A., & Wickert, J. (2008). Global gravity wave activity in the tropopause region from CHAMP radio occultation data. Geophysical Research Letters, 35, L16807. doi:10.1029/2008GL034986.
Song, I.-S., & Chun, H.-Y. (2008). A Lagrangian spectral parameterization of gravity wave drag induced by Cumulus convection. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 65, 1204–1224.
Stober, G., Jacobi, C., Fröhlich, K., & Oberheide, J. (2008). Meteor radar temperatures over Collm (51.3°N, 13°E). Advances in Space Research, 42, 1253–1258. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2007.10.018.
Warner, C. D., & McIntyre, M. E. (2001). An ultrasimple spectral parameterization for nonorographic gravity waves. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 58, 1837–1857.
Wickert, J., Schmidt, T., Beyerle, G., Heise, S., & Reigber, C. (2006). Global atmospheric sounding with GPS radio occultation aboard CHAMP. In J. Flury, R. Rummel, C. Reigber, M. Rothacher, G. Boedecker & U. Schreiber (Eds.), Observation of the Earth system from space (pp. 55–67). Berlin: Springer.
Wickert, J., Michalak, G., Schmidt, T., Beyerle, G., Cheng, C.-Z., Healy, S. B., Heise, S., Huang, C.-Y., Jakowski, N., Köhler, W., Mayer, C., Offiler, D., Ozawa, E., Pavelyev, A. G., Rothacher, M., Tapley, B., & Arras, C. (2009). GPS radio occultation: results from CHAMP, GRACE and FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC. Terrestrial Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, 20, 35–50. doi:10.3319/TAO.2007.12.26.01(F3C).
Wright, C. J., Osprey, S. M., Barnett, J. J., Gray, L. J., & Gille, J. C. (2010). High resolution dynamics limb sounder measurements of gravity wave activity in the 2006 Arctic stratosphere. Journal of Geophysical Research, 115, D02105. doi:10.1029/2009JD011858.
Acknowledgements
Very helpful comments of two anonymous reviewers are gratefully acknowledged. The projects GW-CODE/FZJ, GW-CODE/GFZ, GW-CODE/LIM, GRAPES, and GW-EXCITES were funded by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) grants no. ER474/1-1, WI2634/2-1, JA836/21-1, PR919/2-1, and ER474/2-1 within the DFG priority program CAWSES (SPP1176).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Ern, M. et al. (2013). Observations and Ray Tracing of Gravity Waves: Implications for Global Modeling. In: Lübken, FJ. (eds) Climate and Weather of the Sun-Earth System (CAWSES). Springer Atmospheric Sciences. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-4348-9_21
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-4348-9_21
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-007-4347-2
Online ISBN: 978-94-007-4348-9
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)