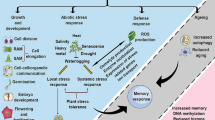
Abstract
Polyamines (PAs) are low molecular weight aliphatic cations that are ubiquitous in all organisms, including plants. PA accumulation occurs under stress in plants, and modulation of the PA biosynthetic pathway confers tolerance to stresses. Over the past two decades, many reports have unraveled significant functions of PAs in the regulation of abiotic stress tolerance in plants. Here, we focused on the involvement of PA pathways in plants, including those of horticultural crops, in ameliorating abiotic stresses such as salt, drought, heat, chilling, and heavy metals. The possible mechanisms of PA functions on stress tolerance have also been summarized. In addition, the current research trends and future perspectives, especially in horticultural crops, are discussed.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcázar R, Marco F, Cuevas JC, Patrón M, Ferrando A, Carrasco P, Tiburcio AF, Altabella T (2006) Involvement of polyamines in plant response to abiotic stress. Biotechnol Lett 28:1867–1876
Alcázar R, Cuevas JC, Planas J, Zarza X, Bortolotti C, Carrasco P, Salinas J, Tiburcio AF, Altabella T (2011) Integration of polyamines in the cold acclimation response. Plant Sci 180:31–38
Bitrián M, Zarza X, Altabella T, Tiburcio AF, Alcázar R (2012) Polyamines under abiotic stress: metabolic crossroads and hormonal crosstalks in plants. Metabolites 2:516–528
Cheng L, Zou YJ, Ding SL, Zhang JJ, Yu XL, Cao JS, Lu G (2009) Polyamine accumulation in transgenic tomato enhances the tolerance to high temperature stress. J Int Plant Biol 51:489–499
Choudhary SP, Oral HV, Bhardwaj R, Yu JQ, Tran LSP (2012) Interaction of brassinosteroids and polyamines enhances copper stress tolerance in Raphanus sativus. J Exp Bot 63:5659–5675
Cona A, Rea G, Angelini R, Fererico R, Tavladoraki P (2006) Functions of amine oxidases in plant development and defence. Trends Plant Sci 11:80–88
Cuevas JC, Lopez-Cobollo R, Alcazar R, Zarza X, Koncz C, Altabella T, Salinas J, Tiburcio AF, Ferrando A (2009) Putrescine as a signal to modulate the indispensable ABA increase under cold stress. Plant Signal Behav 4:219–220
Fujita Y, Fujita M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2011) ABA-mediated transcriptional regulation in response to osmotic stress in plants. J Plant Res 124:509–525
Groppa MD, Tomaro ML, Benavides MP (2001) Polyamines as protectors against cadmium or copper-induced oxidative damage in sunflower leaf discs. Plant Sci 161:481–488
Groppa MD, Benavides MP, Tomaro ML (2003) Polyamine metabolism in sunflower and wheat leaf discs under cadmium or copper stress. Plant Sci 164:293–299
Ha HC, Sirosoma NS, Kuppusamy P, Zweiler JL, Woster PM, Casero RA (1998) The natural polyamine spermine functions directly as a free radical scavenger. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:11140–11145
Hanzawa Y, Takahashi T, Michael AJ, Burtin D, Long D, Pineiro M, Coupland G, Komeda Y (2000) ACAULIS5, an Arabidopsis gene required for stem elongation, encodes a spermine synthase. EMBO J 19:4248–4256
Hazarika P, Rajam MV (2011) Biotic and abiotic stress tolerance in transgenic tomatoes by constitutive expression of S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase gene. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 17:115–128
He LX, Nada K, Tachibana S (2002) Effects of spermidine pretreatment through the roots on growth and photosynthesis of chilled cucumber plants (Cucumis sativus L.). J Jpn Soc Hortic Sci 71:490–498
He L, Ban Y, Inoue H, Matsuda N, Liu J, Moriguchi T (2008) Enhancement of spermidine content and antioxidant capacity in transgenic pear shoots overexpressing apple spermidine synthase in response to salinity and hyperosmosis. Phytochemistry 69:2133–2141
Hussain SS, Ali M, Ahmad M, Siddique KH (2011) Polyamines: natural and engineered abiotic and biotic stress tolerance in plants. Biotechnol Adv 29:300–311
Kasukabe Y, He LX, Nada K, Misawa S, Ihara I, Tachibana S (2004) Overexpression of spermidine synthase enhances tolerance to multiple environmental stresses and up-regulates the expression of various stress-regulated genes in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol 45:712–722
Knott JM, Römer P, Sumper M (2007) Putative spermine synthases from Thalassinosira pseudonana and Arabidopsis thaliana synthesize thermospermine rather than spermine. FEBS Lett 581:3081–3086
Königshofer H, Lechner S (2002) Are polyamines involved in the synthesis of heat-shock proteins in cell suspension cultures of tobacco and alfalfa in response to high-temperature stress? Plant Physiol Biochem 40:51–59
Lee S-H, Ahsan N, Lee K-W, Kim D-H, Lee D-G, Kwak S-S, Kwon S-Y, Kim T-H, Lee B-H (2007) Simultaneous overexpression of both CuZn superoxide dismutase and ascorbate peroxidase in transgenic tall fescue plants confers increased tolerance to a wide range of abiotic stresses. J Plant Physiol 164:1626–1638
Liu K, Fu H, Bei Q, Luan S (2000) Inward potassium channel in guard cells as a target for polyamine regulation of stomatal movements. Plant Physiol 124:1315–1326
Neily HM, Baldet P, Arfaoui I, Saito T, Li Q, Asamizu E, Matsukura C, Moriguchi T, Hirsohi E (2011) Overexpression of apple spermidine synthase 1 (MdSPDS1) leads to significant salt tolerance in tomato plants. Plant Biotechnol 28:33–42
Palavan-Unsal N, Arisan D (2009) Nitric oxide signalling in plants. Bot Rev 75:203–229
Papadakis AK, Roubelakis-Angelakis KA (2005) Polyamines inhibit NADPH oxidase-mediated superoxides generation and putrescine prevents programmed cell death syndrome induced by the polyamine oxidase generated hydrogen peroxide. Planta (Berl) 220:826–837
Paschalidis KA, Toumi I, Moschou PN, Roubelakis-Angelakis KA (2010) ABA-dependent amine oxidases-derived H2O2 affects stomata conductance. Plant Signal Behav 5:1153–1156
Rhee SG (2006) H2O2, a necessary evil for cell signaling. Science 312:1882–1883
Sagor GHM, Berberich T, Takahashi Y, Niitsu M, Kusano T (2013) The polyamine spermine protects Arabidopsis from heat stress-induced damage by increasing expression of heat shock-related genes. Transgenic Res 22:595–605
Sharma SS, Dietz K-J (2008) The relationship between metal toxicity and cellular redox imbalance. Trends Plant Sci 14:43–50
Shen WY, Nada K, Tachibana S (2000) Involvement of polyamines in the chilling tolerance of cucumber cultivars. Plant Physiol 124:431–439
Shevyakova NI, Cheremisina AI, Kuznetsov VV (2011) Phytoremediation potential of Amaranthus hybrids: antagonism between nickel and iron and chelating role of polyamines. Russ J Plant Physiol 58:634–642
Shi H, Zhu J-K (2002) Regulation of expression of the vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene AtNHX1 by salt stress and abscisic acid. Plant Mol Biol 50:543–550
Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2000) Molecular responses to dehydration and low temperature: differences and cross-talk between two stress signaling pathways. Curr Opin Plant Biol 3:217–223
Takahashi Y, Cong R, Sagor GHM, Niitsu M, Berberich T, Kusano T (2010) Characterization of five polyamine oxidase isoforms in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Rep 29:955–965
Theocharis A, Clément EA, Barka EA (2012) Physiological and molecular changes in plants grown at low temperatures. Planta (Berl) 235:1091–1105
Toumi I, Moschou PN, Paschalidis KA, Bouamama B, Salem-fnayou AB, Ghorbel AW, Mliki A, Roubelakis-Angelakis KA (2010) Abscisic acid signals reorientation of polyamine metabolism to orchestrate stress responses via the polyamine exodus pathway in grapevine. J Plant Physiol 167:519–525
Tun NN, Santa-Catarina C, Begum T, Silveira V, Handro W, Floh EIS, Scherer GFE (2006) Polyamines induce rapid biosynthesis of nitric oxide (NO) in Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings. Plant Cell Physiol 47:346–354
Urano K, Yoshiba Y, Nanjo T, Ito T, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2004) Arabidopsis stress-inducible gene for arginine decarboxylase AtADC2 is required for accumulation of putrescine in salt tolerance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 313:369–375
Wang H, Huang J, Liang W, Liang X, Bi Y (2012) Involvement of putrescine and nitric oxide in aluminum tolerance by modulating citrate secretion from roots of red kidney bean. Plant Soil 366:479–490
Wen XP, Pang XM, Matsuda N, Kita M, Hao YJ, Kitashiba H, Honda C, Moriguchi T (2008) Overexpression of the apple spermidine synthase gene in pear confers multiple abiotic stress tolerance by altering polyamine titers. Transgenic Res 17:251–263
Wen XP, Ban Y, Inoue H, Matsuda N, Moriguchi T (2009) Aluminum tolerance in a spermidine synthase-overexpressing transgenic European pear is correlated with the enhanced level of spermidine via alleviating oxidative status. Environ Exp Bot 66:471–478
Wen XP, Ban Y, Inoue H, Matsuda N, Moriguchi T (2010) Spermidine levels are implicated in heavy metal tolerance in a spermidine synthase overexpressing transgenic European pear by exerting antioxidant activities. Transgenic Res 19:91–103
Wen XP, Ban Y, Inoue H, Matsuda N, Kita M, Moriguchi T (2011) Antisense inhibition of a spermidine synthase gene highlights the role of polyamines for stress alleviation in pear shoots subjected to salinity and cadmium. Environ Exp Bot 72:157–166
Yamaguchi K, Takahashi Y, Berberich T, Imai A, Miyazaki A, Takahashi T, Michael A, Kusano T (2006) The polyamine spermine protects against high salt stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. FEBS Lett 580:6783–6788
Yamasaki H, Cohen MF (2006) NO signal at the crossroads: polyamine induced nitric oxide synthesis in plants. Trends Plant Sci 11:522–524
Zhang J, Shu W-S (2006) Mechanisms of heavy metal cadmium tolerance in plants. J Plant Physiol Mol Biol 32:1–8
Zhang CM, Zou ZR, Huang Z, Zhang ZX (2010) Effects of exogenous spermidine on photosynthesis of tomato seedlings under drought stress. Agric Res Arid Areas 3:182–187
Zhu J-K (2003) Regulation of ion homeostasis under salt stress. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:441–445
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer Japan
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Wen, X., Moriguchi, T. (2015). Role of Polyamines in Stress Response in Horticultural Crops. In: Kanayama, Y., Kochetov, A. (eds) Abiotic Stress Biology in Horticultural Plants. Springer, Tokyo. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-55251-2_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-55251-2_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Tokyo
Print ISBN: 978-4-431-55250-5
Online ISBN: 978-4-431-55251-2
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)