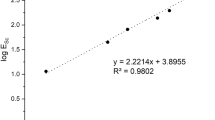
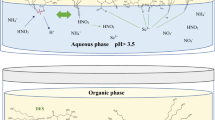
Abstract
The extraction of scandium from its oxide with a task specific ionic liquid [Hbet][Tf2N] offers potential advantages of lower energy consumption, recycling of the extractant and reduced environmental impact compared to conventional methods. In this paper, the influence of reaction temperature , solid to liquid ratio and water to the ionic liquid ratio on the extraction of scandium from a synthetic scandium oxide (Sc2O3) system was studied. The influence of investigated parameters on leaching was very significant as approximately 98% scandium was extracted from its oxide after 72 h. Furthermore, the ionic liquid also selectively extracted 47% scandium after 48 h from a mixture of pure metal oxides containing oxides of tantalum , niobium , and scandium . The research demonstrated the potential of [Hbet][Tf2N] to selectively extract scandium from columbite processing tailings and other scandium bearing ores like Ixiolite, Heftetjernite and Tantalite which predominately contain tantalum and niobium .
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gambogi J (2016) U.S. geological survey. Mineral commodity summaries, pp 146–147
Duyvesteyn WPC, Putnam GF (2014) White paper scandium: a review of the element, its characteristics, and current and emerging commercial applications. EMC Metals Corporation, Nevada
Wang W, Pranolo Y, Cheng CY (2011) Metallurgical processes for scandium recovery from various resources: a review. Hydrometallurgy 108:100–108
Onghena B, Borra CR, Van Gerven T, Binnemans K (2017) Recovery of scandium from sulfation-roasted leachates of bauxite residue by solvent extraction with the ionic liquid betainium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imid. Sep Purif Technol 176:208–219
Davris P et al (2015) Leaching of bauxite residue using task specific ionic liquid HbetTf2N. Paper presented at the 7th European metallurgical conference June 14–17 2015
Black WD, Tierney RD, Notzl-Loiselle H (1998) Process for recovering tantalum and or niobium compounds from composite contanining a variety of metal compounds. US Patent 5,787,332, 26 Sep 1998
Odekirk MD (1996) Separation of scandium from tantalum residue using fractional liquid-liquid extraction. US Patent 5,492,680. 20 Jan 1996
Tian G, Jian L, Hua YX (2010) Application of ionic liquids in hydrometallurgy of nonferrous metals. T Nonferr Metal Soc 20:13–520
Abbott AP, Capper G, Davies DL, McKenzie KJ, Obi SU (2006) Solubility of metal oxides in deep eutectic solvents based on choline chloride. J Chem Eng Data 1280–1282
Johnson KE (2007) What’s an ionic liquid? Electrochem Soc Interface 16:38–41
Wasserscheid P, Welton T (2008) Ionic liquids in synthesis, 2nd edn. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co, Weinheim
Tian G (2012) Application of Ionic liquids in extraction and separation of metals. In: Mohammad, A, Inamuddin, E (eds) Green solvents II 2012. Springer, Berlin, pp 119–153
Hoogerstraete TV, Onghena B, Binnemans K (2013) Homogeneous liquid-liquid extraction of rare earths with the betaine-betainium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide ionic liquid system. Int J Mol Sci 14:21354–21377
Onghena B, Binnemans K (2015) Recovery of scandium(iii) from aqueous solutions by solvent extraction with the functionalized ionic liquid betainium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide. Ind Eng Chem Res 54:1887–1898
Dupont D, Binnemans K (2015) Rare-earth recycling using a functionalized ionic liquid for the selective dissolution and revalorization of Y2O3:Eu3 + from lamp phosphor waste. Green Chem 17:856–868
Wise MA, Cerny P, Falster AU (1998) Scandium substitution in columbite group minerals and ixiolite. Can Mineral 36:673–680
Nockemann P, Thijs B, Pittois S, Thoen J, Glorieux C, Hecke KV, Meervelt LV, Kirchner B, Binnemans K (2008) Task-specific ionic liquid for solubilizing metal oxides. Inorg Chem 47:9987–9999
Cardarelli F (2008) Materials handbook. Springer, London
Crabtree RH (2005) The organometallic chemistry of the transition metals, 4th edn. Wiley, New Jersey
Deveau S, Young S (2003) Metal recovery process. US Patent US20030152503 A1, 14 Aug 2003
Wellens S, Hoogerstraete TV, Möller C, Thijs B, Luyten J, Binnemans K (2014) Dissolution of metal oxides in an acid-saturated ionic liquid solution and investigation of the back-extraction behaviour to the aqueous phase. Hydrometallurgy 144:27–33
Welty JR, Wicks CE, Wilson RE, Rorrer GL (2007) Fundamentals of momentum, heat, and mass transfer, 5th edn. Wiley, Hoboken
Nockemann P, Thijs B, Pittois S, Thoen J, Glorieux C, Hecke KV, Meervelt LV, Kirchner B, Binnemans K (2006) Task-specific ionic liquid for solubilizing metal oxides. J Phys Chem B. 110:20978–20992
Dupont D, Raiguel S, Binnemans K (2015) Sulfonic acid functionalized ionic liquids for dissolution of metal oxides and solvent extraction of metal ions. Chem Commun 51:9006–9009
Knorring OV, Sahama TH, Lehtinen M (1969) Scandium ixiolite from mozambique and madagascar. B Geol Soc Finland 41:75–77
Kolitsch U, Kristiansen R, Raade G, Tillmanns E (2010) Heftetjernite, a new scandium mineral from the Heftetjern pegmatite, Tørdal, Norway. Eur J Mineral 22:309–316
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Michelle Kange, Michael Gustavo and Jenilee Ferreira for their assistance with some of the experimental work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society
About this paper
Cite this paper
Mawire, G., van Dyk, L. (2018). Extraction of Scandium (Sc) Using a Task-Specific Ionic Liquid Protonated Betaine Bis(Trifluoromethylsulfonyl)Imide [Hbet][Tf2N]. In: Davis, B., et al. Extraction 2018. The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-95022-8_230
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-95022-8_230
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-95021-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-95022-8
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)