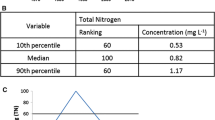
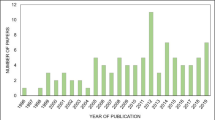
Abstract
Freshwater Ecological Integrity (EI) incorporates the concepts of ecosystem “health”, unimpaired structure, composition and function and a capacity for self-renewal and, as such, it is a holistic advance over standard water quality metrics for assessing lake condition. In the New Zealand freshwater context, EI has been defined as a composite of nativeness, pristineness, diversity and resilience to perturbations. Measurable lake attributes have been proposed and calibrated against pre-impaired “reference” conditions for different lake types. Related to EI, LakeSPI (Submerged Plant Indicator) also assesses lake ecological condition and has been calibrated for a wide range of New Zealand lakes. These EI approaches are thus able to measure departures from reference conditions (or other defined endpoints) and for all these reasons, EI approaches are beneficial for setting lake restoration goals or targets and for tracking the success and progress of restoration activities. Recently, EI approaches have been making inroads with regard to environmental policy and monitoring. This chapter discusses the current development and future possibilities for using EI to help restore degraded lakes.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Augustinas P, Reid M, Andersson S, Deng Y, Horrocks M (2006) Biological and geochemical record of anthropogenic impacts in recent sediments from Lake Pupuke, Auckland City, New Zealand. J Paleolimnol 35:789–805
Ayres KR, Sayer CD, Skeate ER, Perrow MR (2008) Palaeolimnology as a tool to inform shallow lake management: an example from Upton Great Broad, Norfolk, UK. Biodivers Conserv 17:2153–2168
Barbour MT, Swietlik WF, Jackson SK, Courtemanch DL, Davies SP, Yoder CO (2000) Measuring the attainment of biological integrity in the USA: a critical element of ecological integrity. Hydrobiologia 422/423:453–464
Blindow I, Hargeby A, Hilt S (2014) Facilitation of clear-water conditions in shallow lakes by macrophytes: differences between charophyte and angiosperm dominance. Hydrobiologia 737:99–110
Boon PJ, Pringle CM (2009) Background, philosophy and context. In: Boon PJ, Pringle CM (eds) Assessing the conservation value of fresh waters: an international perspective. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 6–38
Brucet S, Poikane S, Lyche-Solheim A, Birk S (2013) Biological assessment of European lakes: ecological rationale and human impacts. Freshw Biol 58:1106–1115
Bunn SE, Davies PM (2000) Biological processes in running waters and their implications for the assessment of ecological integrity. Hydrobiologia 422:61–70
Canada National Parks Act (2000) Government of Canada, Ottawa. http://laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/PDF/N-14.01.pdf. Accessed 5 Sep 2017
Cardoso AC, Solimini A, Premazzi G, Carvalho L, Lyche A, Rekolainen S (2007) Phosphorus reference concentrations in European lakes. Hydrobiologia 584:3–12
Carvalho L, Poikane S, Lyche-Solheim A, Phillips G, Borics G, Catalan J, de Hoyos C, Drakare S, Dudley B, Järvinen M et al (2013) Strength and uncertainty of lake phytoplankton metrics for assessing eutrophication impacts in lakes. Hydrobiologia 704:127–140
Champion PD (2002) Egeria densa – an alien invasive plant responsible for the devegetation of New Zealand shallow lakes. Proceedings of the Thirteenth Australian Weeds Conference, Council of Australasian weed societies. http://www.caws.org.au/awc/2002/awc200211261.pdf. Accessed 5 Sep 2017
Champion P, de Winton M (2012) Northland lakes strategy. NIWA Report HAM2012–121 prepared for Northland Regional Council, Whangarei. National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research, Hamilton, New Zealand
Champion PD, Wells RDS (2014) Proactive management of aquatic weeds to protect the nationally important Northland dune lakes, New Zealand. Proceedings of the Nineteenth Australasian Weeds Conference, pp 139–142. http://caws.org.au/awc/2014/awc201411391.pdf. Accessed 9 Sep 2018
Clapcott J, Young R, Goodwin EO, Leathwick JR, Kelly DJ (2011) Relationships between multiple land-use pressures and individual and combined indicators of stream ecological integrity. Research and Development Series 326, Department of Conservation, Wellington. https://www.doc.govt.nz/documents/science-and-technical/drds326lowres.pdf. Accessed 5 Sep 2018
Clayton J, Edwards T (2006a) Aquatic plants as environmental indicators of ecological condition in New Zealand lakes. Hydrobiologia 570:147–151
Clayton J, Edwards T (2006b) LakeSPI: a method for monitoring ecological condition in New Zealand lakes. NIWA Report HAM2002–012. National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research, Hamilton, New Zealand
Closs GP, Dean T, Champion P, Hofstra D (2004) Aquatic invaders and pest species in lakes. In: Harding JS, Mosley MP, Pearson CP, Sorrell BK (eds) Freshwaters of New Zealand. New Zealand Hydrological Society Inc. and New Zealand Limnological Society Inc., Christchurch, New Zealand, pp 27.1–27.14
Cosgrove S (2011) Anthropogenic impacts on Waituna Lagoon: reconstructing the environmental history. Unpublished M.Sc. thesis, University of Otago, New Zealand
Cunningham BT, Moar NT, Torrie AW, Parr PJ (1953) A survey of the western coastal dune lakes of the North Island. Aust J Mar Freshwat Res 4:343–386
de Winton MD, Clayton JS (1996) The impact of invasive submerged weed species on seed banks in lake sediments. Aquat Bot 53:31–45
de Winton MD, Clayton JS, Edwards T (2012) Incorporating invasive weeds into a plant indicator method (LakeSPI) to assess lake ecological condition. Hydrobiologia 691:47–58
Drake DC, Kelly D, Schallenberg M (2011) Shallow coastal lakes in New Zealand: current conditions, catchment-scale human disturbance, and determination of ecological integrity. Hydrobiologia 658:87–101
Duarte CM, Conley DJ, Carstensen J, Sánchez-Camacho M (2009) Return to Neverland: shifting baselines affect eutrophication restoration targets. Estuar Coast 32:29–36
Ecke F, Hellsten S, Mjelde M, Kuoppala M, Schlacke S (2010) Potential conflicts between environmental legislation and conservation exemplified by aquatic macrophytes. Hydrobiologia 656:107–115
European Environment Agency (2012) European waters: assessment of status and pressures. European Environment Agency, Copenhagen, Denmark
Flöder S, Sommer U (1999) Diversity in planktonic communities: an experimental test of the intermediate disturbance hypothesis. Limnol Oceanogr 44:1114–1119
Gluckman P (2017) New Zealand’s freshwaters: values, state, trends and human impacts. Office of the Prime Minister’s Chief Science Advisor, Wellington. http://www.pmcsa.org.nz/wp-content/uploads/PMCSA-Freshwater-Report.pdf. Accessed 5 Sep 2017
Goodman JM, Dunn NR, Ravenscroft PJ, Allibone RM, Boubée JAT, David BO, Griffiths M, Ling N, Hitchmough RA, Rolfe JP (2014) Conservation status of New Zealand’s freshwater fish, 2013. New Zealand Threat Classification Series 7. Department of Conservation, Wellington.https://www.doc.govt.nz/Documents/science-and-technical/nztcs7entire.pdf. Accessed 5 Sep 2018
Harmsworth GR, Awatere S, Pauling C (2013) Using mātauranga Māori to inform freshwater management. Landcare Research Policy Brief. Integrated Valuation and Monitoring Framework for Improved Freshwater Outcomes. https://www.landcareresearch.co.nz/__data/assets/pdf_file/0003/74433/Policy-Brief-7-Using-Maori-to-inform-freshwater.pdf. Accessed 5 Sep 2018
Hawkins CP, Olson JR, Hill RA (2010) The reference condition: predicting benchmarks for ecological and water-quality assessments. J N Am Benthol Soc 29:312–343
Herlihy AT, Sobota JB, McDonnell TC, Sullivan TJ, Lehmann S, Tarquinio E (2013a) An a priori process for selecting candidate reference lakes for a national survey. Freshw Sci 32:385–396
Herlihy AT, Kamman NC, Sifneos JC, Charles D, Enache MD, Stevenson RS (2013b) Using multiple approaches to develop nutrient criteria for lakes in the conterminous USA. Freshw Sci 32:367–384
Howard-Williams C, Clayton J, Coffey B, Johnstone I (1987) Macrophyte invasions. In: Viner AB (ed) Inland waters of New Zealand. DSIR, Wellington, New Zealand, pp 307–332
Karr JR (1996) Ecological integrity and ecological health are not the same. In: Schulze P (ed) Engineering within ecological constraints. National Academy, Washington, DC, pp 97–109
Karr JR, Dudley DR (1981) Ecological perspective on water quality goals. Environ Manag 5:55–68
Kelly DJ, Hawes I (2005) Effects of invasive macrophytes on littoral-zone productivity and foodweb dynamics in a New Zealand high-country lake. J N Am Benthol Soc 24:300–320
Kelly FL, Harrison AJ, Allen M, Connor L, Rosell R (2012) Development and application of an ecological classification tool for fish in lakes in Ireland. Ecol Indic 18:608–619
Kelly D, West D, Robertson H, Doehring KAM, Gansell O (2013) Development of a freshwater tier 1 biodiversity monitoring programme: scoping report 2013. Cawthron Institute Report 2362. Prepared for the Department of Conservation, Wellington. Cawthron Institute, Nelson, New Zealand
Kelly M, Urbanic G, Acs E, Bertrin V, Burgess A, Denys L, Gottschalk S, Kahlert M, Karjalainen SM, Kennedy B et al (2014) Comparing aspirations: intercalibration of ecological status concepts across European lakes using littoral diatoms. Hydrobiologia 734:125–141
Kirk T (1871) Notes on the botany of certain places in the Waikato District, April and May, 1870. Trans N Z Inst 3:142–147
Kitto SG (2010) The environmental history of Te Waihora – Lake Ellesmere. Unpublished Ph.D. thesis, University of Canterbury, New Zealand
Kowalewski GA (2013) Changes in Lake Rotcze catchment over the last 200 years: implications for lake development reconstruction. Limnol Rev 13:197–207
Lee W, McGlone M, Wright S (2005) Biodiversity inventory and monitoring: a review of national and international systems and a proposed framework for future biodiversity monitoring by the Department of Conservation. Landcare Research Contract Report LC0405/122. Prepared by Landcare Research for the Department of Conservation. Landcare Research, Lincoln
Luoto TP, Nevalainen L, Sarmaja-Korjonen K (2013) Zooplankton (Cladocera) in assessments of biologic integrity and reference conditions: application of sedimentary assemblages from shallow boreal lakes. Hydrobiologia 707:173–185
Manuel-Navarrete D, Kay JJ, Dolderman D (2004) Ecological integrity discourses: linking ecology with cultural transformation. Hum Ecol Rev 11:215–229
McDowall RM (2006) Crying wolf, crying foul, or crying shame: alien salmonids and a biodiversity crisis in the southern cool-temperate galaxioid fishes? Rev Fish Biol Fish 16:233–422
McFarland B, Carse F, Sandin L (2010) Littoral macroinvertebrates as indicators of lake acidification within the UK. Aquat Conserv 20:105–116
Miller JA (1991) Biosciences and ecological integrity—do the advances of modern biology threaten the ecosystem, or do they provide the tools to conserve it? Bioscience 41:206–210
Ministry for the Environment (2014) National policy statement for freshwater management 2014. Ministry for the Environment, Wellington. http://www.mfe.govt.nz/publications/fresh-water/nationalpolicy-statement-freshwater-management-2014. Accessed 5 Sep 2018
Olin M, Rask M, Ruuhijärvi J, Tammi J (2013) Development and evaluation of the Finnish fish-based lake classification method. Hydrobiologia 713:49–166
Özkundakci D, Hamilton DP, Kelly D, Schallenberg M, de Winton M, Verburg P, Trolle D (2014) Ecological integrity of deep lakes in New Zealand across anthropogenic pressure gradients. Ecol Indic 37:45–57
Pall K, Moser V (2009) Austrian Index Macrophytes (AIM-Module 1) for lakes: a water framework directive compliant assessment system. Hydrobiologia 633:83–104
Park G (2000) New Zealand as ecosystems: the ecosystem concept as a tool for environmental management and conservation. Department of Conservation, Wellington, New Zealand
Penning WE, Dudley B, Mjelde M, Hellsten S, Hanganu J, Kolada A, van den Berg M, Poikane S, Phillips G, Willby N, Ecke F (2008) Using aquatic macrophyte community indices to define the ecological status of European lakes. Aquat Ecol 42:253–264
Peters RH (1991) A critique for ecology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Poikane S, Alves M, Argillier C, van den Berg M, Buzzi F, Hoehn E, de Hoyos C, Karottki I, Laplace-Treyture C, Solheim A et al (2010) Defining chlorophyll-a reference conditions in European lakes. Environ Manag 45:1286–1298
Poikane S, Zampoukas N, Borja A, Davies SP, van de Bund W, Birk S (2014) Intercalibration of aquatic ecological assessment methods in the European Union: lessons learned and way forward. Environ Sci Pollut 44:237–246
Rapport DJ, Costanza R, Epstein PR, Gaudet C, Levins R (eds) (1998) Ecosystem health. Blackwell, Oxford
Reeves P, Dean-Speirs T, Shaw W (2009) Methodologies for ranking of lake ecosystems for biodiversity management in the Waikato region. Wildlands Consulting report number 2029 prepared for Environment Waikato, Hamilton, New Zealand
Reid M (2005) Diatom-based models for reconstructing past water quality and productivity in New Zealand lakes. J Paleolimnol 33:13–38
Ribaudo C, Bertrin V, Dutartre A (2014) Dissolved gas and nutrient dynamics within an Egeria densa Planch. bed. Acta Bot Gall: Bot Lett 161:233–241
Sagoff M (2000) Ecosystem design in historical and philosophical context. In: Pimentel D, Westra L, Noss RF (eds) Ecological integrity. Island Press, Washington, pp 61–78
Schallenberg M (2011) Ecological values and condition of the Kaihoka Lakes and Lake Otuhie, Northwest Nelson. Report prepared for the Tasman District Council, Tasman District Council, Nelson. http://envirolink.govt.nz/assets/Envirolink/942-TSDC75-Ecological-values-and-condition-of-the-Kaihoka-Lakes-and-Lake-Otuhie-northwest-Nelson.pdf. Accessed 5 Sep 2017
Schallenberg M, Kelly D (2013) Estimates of reference conditions for Southland’s shallow, lowland lakes. Report prepared for Environment Southland, Environment Southland, Invercargill. http://www.es.govt.nz/Document%20Library/Research%20and%20reports/Surface%20water%20quality%20reports/estimates_of_reference_conditions_for_southland_s_shallow__lowland_lakes.pdf. Accessed 5 Sep 2017
Schallenberg M, Saulnier-Talbot É (2015) Trajectory of an anthropogenically-induced ecological regime shift in a New Zealand shallow coastal lake. Mar Freshw Res 67(10):1522–1533
Schallenberg M, Schallenberg L (2014) Lake Forsyth/Wairewa: a literature review. Report prepared by Hydrosphere Research Ltd for Environment Canterbury, Environment Canterbury, Christchurch. https://api.ecan.govt.nz/TrimPublicAPI/documents/download/1972863. Accessed 5 Sep 2017
Schallenberg M, Sorrell B (2009) Regime shifts between clear and turbid water in New Zealand lakes: environmental correlates and implications for management and restoration. N Z J Mar Freshw Res 43:701–712
Schallenberg M, Kelly D, Clapcott J, Death R, MacNiel C, Young R, Sorrell B, Scarsbrook M (2011) Approaches to assessing ecological integrity of New Zealand freshwaters. Science for Conservation 307. Department of Conservation, Wellington, New Zealand
Schallenberg M, Goff J, Harper MA (2012) Gradual, catastrophic and human induced environmental changes from a coastal lake, southern New Zealand. Sediment Geol 273–274:48–57
Schaumburg J, Schranz C, Hofmann G, Stelzer D, Schneider S, Schmedtje U (2004) Macrophytes and phytobenthos as indicators of ecological status in German lakes – a contribution to the implementation of the water framework directive. Limnologica 34:302–314
Scheffer M (2004) The ecology of shallow lakes. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht
Schindler DW (1987) Detecting ecosystem responses to anthropogenic stress. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 44(Suppl 1):6–25
Schwarz A-M, Howard-Williams C, Clayton J (2000) Analysis of relationships between maximum depth limits of aquatic plants and underwater light in 63 New Zealand lakes. N Z J Mar Freshw Res 34:157–174
Scrimgeour GJ, Wicklum D (1996) Aquatic ecosystem health and integrity: problems and potential solutions. J N Am Benthol Soc 15:254–261
Sidagyte E, Visinskiene G, Arbaciauskas K (2013) Macroinvertebrate metrics and their integration for assessing the ecological status and biocontamination of Lithuanian lakes. Limnologica 43:308–318
Steedman RJ (1994) Ecosystem health as a management goal. J N Am Benthol Soc 13:605–610
Stoddard JI, Larsen DP, Hawkins CP, Johnson RK, Norris RH (2006) Setting expectations for the ecological condition of streams: the concept of reference condition. Ecol Appl 16:1267–1276
Strayer DL, Dudgeon D (2010) Freshwater biodiversity conservation: recent progress and future challenges. J N Am Benthol Soc 29:344–358
Tipa G, Nelson K (2008) Introducing cultural opportunities: a framework for incorporating cultural perspectives in contemporary resource management. J Environ Policy Plan 10:313–337
Tipa G, Teirney LD (2006) Using the cultural health index: how to assess the health of streams and waterways. Ministry for the Environment, Wellington. http://www.mfe.govt.nz/publications/cultural-health-index-streams-and-waterways-feb06. Accessed 5 Sep 2017
Weeks ES, Anderson-Lederer R, Death RG, Joy MK (2015) The plight of New Zealand’s freshwater biodiversity. Conservation Science Statement No. 1. Society for Conservation Biology (Oceania), Sydney, Australia
Woodward CA, Shulmeister J (2006) New Zealand chironomids as proxies for human-induced and natural environmental change: transfer functions for temperature and lake production (chlorophyll a). J Paleolimnol 36:407–429
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Schallenberg, M., de Winton, M.D., Kelly, D.J. (2018). Indicators of Ecological Integrity. In: Hamilton, D., Collier, K., Quinn, J., Howard-Williams, C. (eds) Lake Restoration Handbook. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-93043-5_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-93043-5_11
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-93042-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-93043-5
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)