Abstract
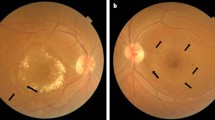
Idiopathic macular telangiectasia is a spectrum of rare disorders with the common feature of abnormalities of the perifoveal capillaries. In macular telangiectasia type 1, aneurysmal changes, lipid exudation, and cystoid macular edema predominate. The clinical presentation resembles a mild variant of Coats’ disease. Macular telangiectasia type 2 is a slowly progressive, neurodegenerative disorder that is typically diagnosed in the fifth and sixth decades of life. Commonly referred to as MacTel, this form is characterized by typical blue reflectance changes and cavitary spaces on optical coherence tomography that can proceed capillary changes. Characteristic features include perifoveal capillary telangiectasia temporal to the fovea and corresponding leakage on fluorescein angiography. Right-angle vessels, perifoveal retinal crystalline deposits, and retinal pigment epithelium migration are also typical. Subretinal neovascular proliferation can occur in late stages. Macular telangiectasia type 3 is a poorly understood condition with a familial component and systemic associations. MacTel is the most frequently occurring form and has been the most extensively characterized. Historical strategies for treating MacTel involved laser destruction of abnormal vasculature using various modalities, resulting in limited success. With the advent of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapies, intravitreal agents and steroids have been trialed with variable results. As understanding of the underlying pathophysiologic mechanisms driving these disease processes has evolved, there has been a shift toward development of neuroprotective treatment strategies. International collaboration through the MacTel Project has accelerated the pace of discovery of this disease, and promising research in this area is currently underway.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reese AB. Telangiectasis of the retina and Coats' disease. Am J Ophthalmol. 1956;42(1):1–8. Epub 1956/07/01
Gass JD. A fluorescein angiographic study of macular dysfunction secondary to retinal vascular disease. VI. X-ray irradiation, carotid artery occlusion, collagen vascular disease, and vitritis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1968;80(5):606–17. Epub 1968/11/01
Gass JD. Stereoscopic atlas of macular diseases. 2nd ed. St. Louis: Mosby; 1977.
Hutton WL, Snyder WB, Fuller D, Vaiser A. Focal parafoveal retinal telangiectasis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1978;96(8):1362–7. Epub 1978/08/01
Gass JD, Oyakawa RT. Idiopathic juxtafoveolar retinal telangiectasis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1982;100(5):769–80. Epub 1982/05/01
Gass JD, Blodi BA. Idiopathic juxtafoveolar retinal telangiectasis. Update of classification and follow-up study. Ophthalmology. 1993;100(10):1536–46. Epub 1993/10/01
Yannuzzi LA, Bardal AM, Freund KB, Chen KJ, Eandi CM, Blodi B. Idiopathic macular telangiectasia. Arch Ophthalmol. 2006;124(4):450–60. Epub 2006/04/12
Cahill M, O'Keefe M, Acheson R, Mulvihill A, Wallace D, Mooney D. Classification of the spectrum of Coats' disease as subtypes of idiopathic retinal telangiectasis with exudation. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2001;79(6):596–602.. Epub 2002/01/10
Chopdar A. Retinal telangiectasis in adults: fluorescein angiographic findings and treatment by argon laser. Br J Ophthalmol. 1978;62(4):243–50. Epub 1978/04/01
Lowe MA, Akduman L, Olk RJ. Laser photocoagulation and glucose metabolism in idiopathic juxtafoveolar retinal telangiectasis. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers. 1998;29(2):126–39. Epub 1998/03/21
Millay RH, Klein ML, Handelman IL, Watzke RC. Abnormal glucose metabolism and parafoveal telangiectasia. Am J Ophthalmol. 1986;102(3):363–70. Epub 1986/09/15
Charbel Issa P, Gillies MC, Chew EY, Bird AC, Heeren TF, Peto T, et al. Macular telangiectasia type 2. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2013;34:49–77.. Epub 2012/12/12
Gamulescu MA, Walter A, Sachs H, Helbig H.Bevacizumab in the treatment of idiopathic macular telangiectasia. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol = Albrecht von Graefes Archiv fur klinische und experimentelle Ophthalmologie. 2008;246(8):1189–93. Epub 2008/04/04
Matsumoto Y, Yuzawa M. Intravitreal bevacizumab therapy for idiopathic macular telangiectasia. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2010;54(4):320–4. Epub 2010/08/12
Takayama K, Ooto S, Tamura H, Yamashiro K, Otani A, Tsujikawa A, et al. Intravitreal bevacizumab for type 1 idiopathic macular telangiectasia. Eye. 2010;24(9):1492–7. Epub 2010/05/01
Gurwin EB, Fitzsimons RB, Sehmi KS, Bird AC. Retinal telangiectasis in facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy with deafness. Arch Ophthalmol. 1985;103(11):1695–700. Epub 1985/11/01
Fitzsimons RB, Gurwin EB, Bird AC. Retinal vascular abnormalities in facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy. A general association with genetic and therapeutic implications. Brain J Neurol. 1987;110(Pt 3):631–48.. Epub 1987/06/01
Klein R, Blodi BA, Meuer SM, Myers CE, Chew EY, Klein BE. The prevalence of macular telangiectasia type 2 in the Beaver Dam eye study. Am J Ophthalmol. 2010;150(1):55–62 e2. Epub 2010/07/09
Aung KZ, Wickremasinghe SS, Makeyeva G, Robman L, Guymer RH. The prevalence estimates of macular telangiectasia type 2: the Melbourne Collaborative Cohort Study. Retina. 2010;30(3):473–8. Epub 2009/12/03
Sallo FB, Leung I, Mathenge W, Kyari F, Kuper H, Gilbert CE, et al. The prevalence of type 2 idiopathic macular telangiectasia in two African populations. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2012;19(4):185–9. Epub 2012/03/01
Clemons TE, Gillies MC, Chew EY, Bird AC, Peto T, Figueroa MJ, et al. Baseline characteristics of participants in the natural history study of macular telangiectasia (MacTel) MacTel Project Report No. 2. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2010;17(1):66–73. Epub 2010/01/27
Parmalee NL, Schubert C, Merriam JE, Allikmets K, Bird AC, Gillies MC, et al. Analysis of candidate genes for macular telangiectasia type 2. Mol Vis. 2010;16:2718–26. Epub 2010/12/24
Menchini U, Virgili G, Bandello F, Malara C, Rapizzi E, Lanzetta P. Bilateral juxtafoveolar telangiectasis in monozygotic twins. Am J Ophthalmol. 2000;129(3):401–3. Epub 2000/03/08
Siddiqui N, Fekrat S. Group 2A idiopathic juxtafoveolar retinal telangiectasia in monozygotic twins. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005;139(3):568–70. Epub 2005/03/16
Isaacs TW, McAllister IL. Familial idiopathic juxtafoveolar retinal telangiectasis. Eye. 1996;10(Pt 5):639–42.. Epub 1996/01/01
Oh KT, Park DW. Bilateral juxtafoveal telangiectasis in a family. Retina. 1999;19(3):246–7. Epub 1999/06/24
Heeren TF, Holz FG, Charbel Issa P. First symptoms and their age of onset in macular telangiectasia type 2. Retina. 2014;34(5):916–9. Epub 2013/12/20
Peto T, Heeren TFC, Clemons TE, Sallo FB, Leung I, Chew EY, et al. Correlation of clinical and structural progression with visual acuity loss in macular telangiectasia type 2: MacTel Project Report No. 6-The MacTel Research Group. Retina. 2018;38(Suppl 1):S8–S13. Epub 2017/05/16
Wong WT, Forooghian F, Majumdar Z, Bonner RF, Cunningham D, Chew EY. Fundus autofluorescence in type 2 idiopathic macular telangiectasia: correlation with optical coherence tomography and microperimetry. Am J Ophthalmol. 2009;148(4):573–83. Epub 2009/07/04
Spaide RF, Suzuki M, Yannuzzi LA, Matet A, Behar-Cohen F. Volume-rendered angiographic and structural optical coherence tomography angiography of macular telangiectasia type 2. Retina. 2017;37(3):424–35. Epub 2016/10/18
Okada M, Egan CA, Heeren TFC, Tufail A, Fruttiger M, Maloca PM. Macular telangiectasis type 2: quantitative analysis of a novel phenotype and implications for the pathobiology of the disease. Retina. 2018;38(Suppl 1):S97–S104. Epub 2017/08/24
Chew EY, Friedlander M. Global connections to study idiopathic macular telangiectasia type 2. Retina. 2018;38(Suppl 1):S3–7. Epub 2017/12/01
Wang JC, Lains I, Oellers P, Kim IK, Miller JW, Miller JB. Choroidal thickness and vascular density in macular telangiectasia type 2 using en face swept-source optical coherence tomography. Br J Ophthalmol. 2019;103(11):1584–1589. Epub 2019/01/04.
Nalci H, Sermet F, Demirel S, Ozmert E. Optical coherence tomography angiography findings in type-2 macular telangiectasia. Turkish J Ophthalmol. 2017;47(5):279–84. Epub 2017/11/08
Spaide RF, Klancnik JM Jr, Cooney MJ. Retinal vascular layers in macular telangiectasia type 2 imaged by optical coherence tomographic angiography. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2015;133(1):66–73. Epub 2014/10/16
Thorell MR, Zhang Q, Huang Y, An L, Durbin MK, Laron M, et al. Swept-source OCT angiography of macular telangiectasia type 2. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging Retina. 2014;45(5):369–80. Epub 2014/10/08
Theelen T, Berendschot TT, Boon CJ, Hoyng CB, Klevering BJ. Analysis of visual pigment by fundus autofluorescence. Exp Eye Res. 2008;86(2):296–304.. Epub 2007/12/22
Okada M, Robson AG, Egan CA, Sallo FB, Esposti SD, Heeren TFC, et al. Electrophysiological characterization of macular telangiectasia type 2 and structure-function correlation. Retina. 2018;38(Suppl 1):S33–42. Epub 2017/06/28
Vujosevic S, Heeren TFC, Florea D, Leung I, Pauleikhoff D, Sallo F, et al. Scotoma characteristics in macular telangiectasia type 2: MacTel project report No. 7-The MacTel Research Group. Retina. 2018;38(Suppl 1):S14–S9. Epub 2017/06/14
Park DW, Schatz H, McDonald HR, Johnson RN. Grid laser photocoagulation for macular edema in bilateral juxtafoveal telangiectasis. Ophthalmology. 1997;104(11):1838–46. Epub 1997/12/31
De Lahitte GD, Cohen SY, Gaudric A. Lack of apparent short-term benefit of photodynamic therapy in bilateral, acquired, parafoveal telangiectasis without subretinal neovascularization. Am J Ophthalmol. 2004;138(5):892–4. Epub 2004/11/09
Charbel Issa P, Finger RP, Kruse K, Baumuller S, Scholl HP, Holz FG. Monthly ranibizumab for nonproliferative macular telangiectasia type 2: a 12-month prospective study. Am J Ophthalmol. 2011;151(5):876–86 e1. Epub 2011/02/22
Toy BC, Koo E, Cukras C, Meyerle CB, Chew EY, Wong WT. Treatment of nonneovascular idiopathic macular telangiectasia type 2 with intravitreal ranibizumab: results of a phase II clinical trial. Retina. 2012;32(5):996–1006.. Epub 2012/01/24
Do DV, Bressler SB, Cassard SD, Gower EW, Tabandeh H, Jefferys JL, et al. Ranibizumab for macular telangiectasia type 2 in the absence of subretinal neovascularization. Retina. 2014;34(10):2063–71. Epub 2014/07/01
Kupitz EH, Heeren TF, Holz FG, Charbel Issa P. Poor long-term outcome of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy in nonproliferative macular telangiectasia type 2. Retina. 2015;35(12):2619–26. Epub 2015/09/05
Park D, Schatz H, McDonald HR, Johnson RN. Fibrovascular tissue in bilateral juxtafoveal telangiectasis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1996;114(9):1092–6. Epub 1996/09/01
Friedman SM, Mames RN, Stewart MW. Subretinal hemorrhage after grid laser photocoagulation for idiopathic juxtafoveolar retinal telangiectasis. Ophthalmic Surg. 1993;24(8):551–3. Epub 1993/08/01
Engelbrecht NE, Aaberg TM Jr, Sung J, Lewis ML. Neovascular membranes associated with idiopathic juxtafoveolar telangiectasis. Arch Ophthalmol. 2002;120(3):320–4. Epub 2002/03/07
Watzke RC, Klein ML, Folk JC, Farmer SG, Munsen RS, Champfer RJ, et al. Long-term juxtafoveal retinal telangiectasia. Retina. 2005;25(6):727–35. Epub 2005/09/06
Shukla D, Singh J, Kolluru CM, Kim R, Namperumalsamy P. Transpupillary thermotherapy for subfoveal neovascularization secondary to group 2A idiopathic juxtafoveolar telangiectasis. Am J Ophthalmol. 2004;138(1):147–9. Epub 2004/07/06
Potter MJ, Szabo SM, Chan EY, Morris AH. Photodynamic therapy of a subretinal neovascular membrane in type 2A idiopathic juxtafoveolar retinal telangiectasis. Am J Ophthalmol. 2002;133(1):149–51. Epub 2002/01/05
TAP-Study-Group. Photodynamic therapy of subfoveal choroidal neovascularization in age-related macular degeneration with verteporfin: one-year results of 2 randomized clinical trials--TAP report. Treatment of age-related macular degeneration with photodynamic therapy (TAP) Study Group. Arch Ophthalmol. 1999;117(10):1329–45. Epub 1999/10/26
Potter MJ, Szabo SM, Sarraf D, Michels R, Schmidt-Erfurth U. Photodynamic therapy for subretinal neovascularization in type 2A idiopathic juxtafoveolar telangiectasis. Can J Ophthalmol J Canadien d'ophtalmologie. 2006;41(1):34–7. Epub 2006/02/08
Hussain N, Das T, Sumasri K, Ram LS. Bilateral sequential photodynamic therapy for sub-retinal neovascularization with type 2A parafoveal telangiectasis. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005;140(2):333–5. Epub 2005/08/10
Shanmugam MP, Agarwal M. RPE atrophy following photodynamic therapy in type 2A idiopathic parafoveal telangiectasis. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2005;53(1):61–3. Epub 2005/04/15
Narayanan R, Chhablani J, Sinha M, Dave V, Tyagi M, Pappuru RR, et al. Efficacy of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy in subretinal neovascularization secondary to macular telangiectasia type 2. Retina. 2012;32(10):2001–5. Epub 2012/09/20
Jorge R, Costa RA, Calucci D, Scott IU. Intravitreal bevacizumab (Avastin) associated with the regression of subretinal neovascularization in idiopathic juxtafoveolar retinal telangiectasis. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol = Albrecht von Graefes Archiv fur klinische und experimentelle Ophthalmologie. 2007;245(7):1045–8. Epub 2006/12/01
Mandal S, Venkatesh P, Abbas Z, Vohra R, Garg S. Intravitreal bevacizumab (Avastin) for subretinal neovascularization secondary to type 2A idiopathic juxtafoveal telangiectasia. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol = Albrecht von Graefes Archiv fur klinische und experimentelle Ophthalmologie. 2007;245(12):1825–9. Epub 2007/03/09
Roller AB, Folk JC, Patel NM, Boldt HC, Russell SR, Abramoff MD, et al. Intravitreal bevacizumab for treatment of proliferative and nonproliferative type 2 idiopathic macular telangiectasia. Retina. 2011;31(9):1848–55. Epub 2011/05/26
Smithen LM, Spaide RF. Photodynamic therapy and intravitreal triamcinolone for a subretinal neovascularization in bilateral idiopathic juxtafoveal telangiectasis. Am J Ophthalmol. 2004;138(5):884–5. Epub 2004/11/09
Rishi P, Shroff D, Rishi E. Combined photodynamic therapy and intravitreal ranibizumab as primary treatment for subretinal neovascular membrane (SRNVM) associated with type 2 idiopathic macular telangiectasia. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol = Albrecht von Graefes Archiv fur klinische und experimentelle Ophthalmologie. 2008;246(4):619–21. Epub 2008/01/15
Ruys J, De Laey JJ, Vanderhaeghen Y, Van Aken EH. Intravitreal bevacizumab (Avastin) for the treatment of bilateral acquired juxtafoveal retinal telangiectasis associated with choroidal neovascular membrane. Eye. 2007;21(11):1433–4. Epub 2007/08/19
Berger AS, McCuen BW, 2nd, Brown GC, Brownlow RL, Jr. Surgical removal of subfoveal neovascularization in idiopathic juxtafoveolar retinal telangiectasis. Retina 1997;17(2):94–8. Epub 1997/01/01.
Davidorf FH, Pressman MD, Chambers RB. Juxtafoveal telangiectasis-a name change? Retina. 2004;24(3):474–8. Epub 2004/06/10
Karth PA, Raja SC, Brown DM, Kim JE. Outcomes of macular hole surgeries for macular telangiectasia type 2. Retina. 2014;34(5):907–15. Epub 2013/11/26
Pauleikhoff D, Bonelli R, Dubis AM, Gunnemann F, Rothaus K, Charbel Issa P, et al. Progression characteristics of ellipsoid zone loss in macular telangiectasia type 2. Acta Ophthalmol. 2019;97(7):e998–e1005. Epub 2019/04/11.
Christakis PG, Fine HF, Wiley HE. The diagnosis and management of macular telangiectasia. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging Retina. 2019;50(3):139–44. Epub 2019/03/21
Powner MB, Gillies MC, Tretiach M, Scott A, Guymer RH, Hageman GS, et al. Perifoveal muller cell depletion in a case of macular telangiectasia type 2. Ophthalmology. 2010;117(12):2407–16. Epub 2010/08/04
Powner MB, Gillies MC, Zhu M, Vevis K, Hunyor AP, Fruttiger M. Loss of Muller's cells and photoreceptors in macular telangiectasia type 2. Ophthalmology. 2013;120(11):2344–52. Epub 2013/06/19
Chew EY, Clemons TE, Jaffe GJ, Johnson CA, Farsiu S, Lad EM, et al. Effect of ciliary neurotrophic factor on retinal neurodegeneration in patients with macular telangiectasia type 2: a randomized clinical trial. Ophthalmology. 2019;126(4):540–9. Epub 2018/10/08
Parmalee NL, Schubert C, Figueroa M, Bird AC, Peto T, Gillies MC, et al. Identification of a potential susceptibility locus for macular telangiectasia type 2. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e24268. Epub 2012/09/07
Scerri TS, Quaglieri A, Cai C, Zernant J, Matsunami N, Baird L, et al. Genome-wide analyses identify common variants associated with macular telangiectasia type 2. Nat Genet. 2017;49(4):559–67. Epub 2017/03/03
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Section Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry
Aronow, M.E., Miller, J.W. (2020). Idiopathic Macular Telangiectasia. In: Albert, D., Miller, J., Azar, D., Young, L.H. (eds) Albert and Jakobiec's Principles and Practice of Ophthalmology. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-90495-5_123-1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-90495-5_123-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-90495-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-90495-5
eBook Packages: Springer Reference MedicineReference Module Medicine