Abstract
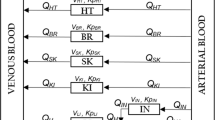
Two-compartment model has common usage in modeling stage of dynamical systems. It is possible to consider the two-compartment model as a regression model which is intrinsically nonlinear in parameters. Evaluation of the nonlinear model parameters in statistical perspective will help to improve the compartmental system. In this study, statistical inference of two-compartment model parameters is achieved in respect to point estimation and interval estimation. The point estimates of compartment model parameters are obtained according to the nonlinear least squares (NLS) approach. Genetic algorithm (GA), a well-known population-based evolutionary algorithm, is preferred as an optimization tool. The main contribution of the study is obtaining bias-corrected point estimates and bias-corrected accelerated confidence interval (CI) estimates of compartment parameters. In order to obtain the CIs, sampling distribution of parameter estimates is defined with the application of fixed-X nonlinear bootstrap method which preserves the fixed nature of predictor variable. Two bootstrap methods are used for CI calculations: (i) Percentile and (ii) bias-corrected accelerated (BCa). A simulated data set and a real data set from the pharmacokinetic (PK) literature are chosen for application purpose. It is seen from the results that bias-reduced point estimates and sampling distribution of parameter estimates can be obtained by preserving the time-dependent nature of the dynamical system by using fixed-X bootstrapping. Besides, BCa method gives more realistic interval estimates than percentile method.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ağabeyoğlu, İ.: Basic Pharmacokinetic. Chapter 11, Ankara, Turkey, pp. 183–226 (1999)
Beyaztaş, U., Alın, A., Martin, M.A.: Robust BCa-Jab method as a diagnostic tool for linear regression models. J. Appl. Stat. 41(7), 1593–1610 (2014)
Bonate, P.L.: Pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic Modeling and Simulation. Springer, New York (2011)
Burns, R.N., Chaturvedula, A., Turner, D.C., Zhang, H., van der Berg, C.M.: Population pharmacokinetic pharmacodynamic modeling of caffeine using visual analogue scales. Pharmacol. Pharm. 5, 444–454 (2014)
Contreras, M., Walter, G.G.: Numerical Methods for Point and Interval Parameter Estimation in Compartmental Models Used in Small Sample Pharmacokinetic and Epidemiological Studies. Report, numbered BU-1542–M, pp. 1–25 (2000)
Efron, B.: Bootstrap methods: another look at the jackknife. Ann. Stat. 7(1), 1–26 (1979)
Efron, B.: Better bootstrap confidence intervals. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 82(397), 171–185 (1987)
Efron, B.: More accurate confidence intervals in exponential families. Biometrika 79, 231–245 (1992)
Efron, B., Tibshirani, R.J.: An Introduction to Bootstrap. Chapman and Hall, CRC Press (1994)
Haukoos, J.S., Lewis, R.J.: Advanced statistics: bootstrapping confidence intervals for statistics with “Difficult” distributions. Acad. Emerg. Med. 12(4), 360–365 (2005)
Holland, J.: Adaptation in natural and artificial systems. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, USA (1975)
Honda, N., Nakade, S., Kasai, H., Hashimoto, Y., Ohno, T., Kitagawa, J., Yamauchi, A., Hasegava, C., Kikawa, S., Kunisawa, T., Tanigawara, Y., Miyata, Y.: Population pharmacokinetics of landiolol hydrochloride in healthy subjects. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 23(6), 447–455 (2008)
Hunt, C.A., Givens, G.H., Guzy, S.: Bootstrapping for pharmacokinetic models: visualization of predictive and parameter uncertainty. Pharm. Res. 15(5), 690–697 (1998)
Kundu, D., Mitra, A.: Estimating the parameters of the linear compartment model. J. Stat. Plan. Infer. 70, 317–334 (1998)
Lai, T.L.: Regression analysis of compartmental models. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stan. 90(6), 525–530 (1985)
Midi, H.: Bootstrap methods in a class of non-linear regression models. Pertanika J. Sci. Technol. 8(2), 175–189 (2000)
Ogden, R.T., Jiang, H.: Nonparametric evaluation of heterogeneity of brain regions in neuroreceptor mapping applications. Stat. Its Interface 3, 59–67 (2010)
Seber, G.A.F., Wild, J.: Nonlinear Regression. Wiley (1989)
Thai, H.T., Mentre, F., Holford, N., Follet, C.V., Comets, E.: Evaluation of bootstrap methods for estimating uncertainty of parameters in nonlinear mixed-effects models: a simulation study in population pharmacokinetics. J. Pharmacokinet. Pharmacodyn., Springer Verlag 41(1), 15–33 (2014). (HAL archives-ouvertes)
Thompson, Z.J.: Statistical Estimation of Physiologically-based Pharmacokinetic Models: Identifiability, Variation, and Uncertainty with an Illustration of Chronic Exposure to Dioxin and Dioxin-like-compounds. Graduate Theses and Dissertations. University of South Florida (2012)
Türkşen, Ö., Tez, M.: An application of nelder-mead heuristic-based hybrid algorithms: estimation of compartment model parameters. Int. J. Artif. Intell. 14(1), 525–530 (2016)
Wagner, J.G.: Application of the Loo-Riegelman absorption method. J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm. 3(1), 51–67 (1975)
Wu, C.F.J.: Jackknife, bootstrap and other resampling methods in regression analysis. Ann. Stat. 14(4), 1261–1295 (1986)
Yang, X.-S.: Nature-Inspired Optimization Algorithms. Elsevier, USA (2014)
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TÜBİTAK-2218). The authors thank the two reviewers for their very helpful comments, useful insights, and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Türkşen, Ö., Tez, M. (2018). Statistical Inference for Two-Compartment Model Parameters with Bootstrap Method and Genetic Algorithm. In: Tez, M., von Rosen, D. (eds) Trends and Perspectives in Linear Statistical Inference . Contributions to Statistics. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-73241-1_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-73241-1_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-73240-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-73241-1
eBook Packages: Mathematics and StatisticsMathematics and Statistics (R0)