Abstract
The energy needs for seawater desalinization by reverse osmosis are such that they constitute the largest share of operating costs. Seventy percent of this energy is absorbed by the only device used to bring pressure membranes, and hence its importance in the price structure of the cubic meter desalinated water. Thus, research in the field of energy recovery from the concentrate was an important factor in lowering desalination cost.
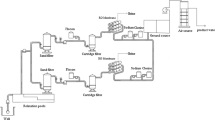
The pressure exchanger (PX) is a device used for transferring pressure energy from a relatively high-pressure fluid flow to a relatively low-pressure fluid flow.
The PX transfers the high-pressure concentrate (reject) of reverse osmosis system to seawater from the filter cartridges, reducing by nearly 50–60% the pump size and pumping cost, with the efficiency exceeding sometimes 97%.
The application of the pressure exchanger technique in BOUSMAIL desalinization station located 30 km west of Algiers gives an energy gain of 18% compared to the Pelton turbine, which is being used now. It recovers energy directly by reducing the size of the high-pressure pump of 231.5–108 m3/h and works as a pump independent of the main pump, which gives a stable system.
It is also noted that the compact size and reduced PX modules allow its location in smaller premises, minimizing the visual impact with its optimum integration on its environment.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agashicheva, S.P., Lootahb, K.N.: Influence of temperature and permeate recovery on energy consumption of a reverse osmosis system. Desalination. 154(3), 253–266 (2003)
Audinos, R..: SÕparations électrochimiques: Électrodialyse, Technique de l'IngÕnieur (1997)
Ballif, J.L.P.: L’eau, ressource vitale. Editions JOHANET, Paris (2002)
Barlow, M., Clarke, T.: L’or bleu : l’eau, le grand enjeu du XXIème siècle, Hachette Litteratures, Paris (2002)
Cerci, Y.: Exergy analysis of a reverse osmosis desalination plant in California. Desalination. 142, 257–266 (2002)
Danis, P.: Techniques de l’Ingénieur, et dessalement d’eau de mer. Paris (2007)
Maurel, A.: Techniques séparatives à membranes – considérations théoriques. In: Techniques de l’Ingénieur. Paris (2003)
Sharif, A.O., Merdaw, A.A., Al Bahadili, H., Al Taee, A., Al Aibi, A., Rahal, Z., Derwish, G.A.W.: A new theoretical approach to estimate the specific energy consumption of reverse osmosis and other pressure driven liquid phase membrane processes. Desalination Water Treat. 3, 111–119 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Bouzid-Lagha, S., Matrouh, Y. (2018). Optimization of Energy Cost Seawater Desalinization by Reverse Osmosis: Case of Bousmail Station in Algeria. In: Aloui, F., Dincer, I. (eds) Exergy for A Better Environment and Improved Sustainability 2. Green Energy and Technology. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-62575-1_52
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-62575-1_52
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-62574-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-62575-1
eBook Packages: EnergyEnergy (R0)