Abstract
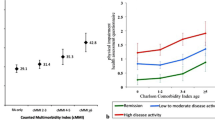
The impact of comorbidity on the outcomes of interest in rheumatic diseases is noteworthy: comorbidity has proven to be a more significant predictor of premature death than shared epitope, rheumatoid factor, or erosions in inflammatory arthritis. Therefore, controlling for coexisting clinical conditions, or comorbidities, booked its place as a main confounder, both in standard healthcare practice and in research. Comorbidity indices are tools used to quantify the total burden of comorbidity contributing to the patient’s overall illness. The simplest method to measure comorbidity is to use the summation of each comorbid illness to generate a total value of comorbidity, often termed a “comorbidity count.” However, not all comorbid diseases have the same impact on the outcome of interest. Thus, more complex comorbidity indices were created to select and weight specific comorbid illnesses to measure more accurately the burden and impact of overall comorbidity. Comorbidities can also be categorized based on the way they have been recorded, whether by administrative data, e.g., the International Classification of Diseases, or by self-administered questionnaires. With the substantial impact that comorbidity exerts on health outcomes in patients with rheumatic diseases, and given the lack of a standardized comorbidity index for clinical or research use, there is an obvious need for an accurate tool to measure the burden of comorbidity in patients with rheumatic disease. This chapter discusses the most commonly used instruments, as well as the recently developed comorbidity indices, their implication onto standard rheumatology clinical practice as well as on patients’ management.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wolfe F, Mitchell DM, Sibley JT, et al. The mortality of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1994;37:481–94.
Gabriel SE, Michaud K. Epidemiological studies in incidence, prevalence, mortality, and comorbidity of the rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11:229.
Gabriel SE. Why do people with rheumatoid arthritis still die prematurely? Ann Rheum Dis. 2008;67:30–4.
Feinstein AR. The pre-therapeutic classification of co-morbidity in chronic disease. J Chronic Dis. 1970;23(7):455–68.
Avina-Zubieta JA, Choi HK, Sadatsafavi M, et al. Risk of cardiovascular mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;59:1690–7.
Lindhardsen J, Ahlehoff O, Gislason GH, et al. The risk of myocardial infarction in rheumatoid arthritis and diabetes mellitus: a Danish nationwide cohort study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70:929–34.
Listing J, Gerhold K, Zink A. The risk of infections associated with rheumatoid arthritis, with its comorbidity and treatment. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2013;52:53–61.
Wotton CJ, Goldacre MJ. Risk of invasive pneumococcal disease in people admitted to hospital with selected immune-mediated diseases: record linkage cohort analyses. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2012;66:1177–81.
Uresson C, Matteson EL. Malignancy as a comorbidity in rheumatic diseases. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2013;52:5–14.
England B, Sayles H, Mikuls TED, Johnson D, Michaud A. Validation of the rheumatic disease comorbidity index. Arthritis Care Res. 2015;67(6):865–72.
Charlson ME, Pompei P, Ales KL, MacKenzie CR. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis. 1987;40:373–83.
Groll DL, To T, Bombardier C, Wright JG. The development of a comorbidity index with physical function as the outcome. J Clin Epidemiol. 2005;58:595–602.
Kaplan MH, Feinstein AR. The importance of classifying initial co-morbidity in evaluating the outcome of diabetes mellitus. J Chronic Dis. 1974;27:387–404.
Miller MD, Paradis CF, Houck PR, Mazumdar S, Stack JA, Rifai AH, et al. Rating chronic medical illness burden in geropsychiatric practice and research: application of the cumulative illness rating scale. Psychiatry Res. 1992;41:237–48.
Von Korff M, Wagner EH, Saunders K. A chronic disease score from automated pharmacy data. J Clin Epidemiol. 1992;45:197–203.
Elixhauser A, Steiner C, Harris DR, Coffey RM. Comorbidity measures for use with administrative data. Med Care. 1998;36:8–27.
Hall SF. A user’s guide to selecting a comorbidity index for clinical research. J Clin Epidemiol. 2006;59:849–55.
Kiefe CI, Funkhouser E, Fouad MN, May DS. Chronic disease as a barrier to breast and cervical cancer screening. J Gen Intern Med. 1998;13:357–65.
Streiner DL, Norman GR. Health measurement scales. A practical guide to their development and use, vol. 2. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1995. p. 1–230.
Rochon PA, Katz JN, Morrow LA, et al. Comorbid illness is associated with survival and length of hospital stay in patients with chronic disability. A prospective comparison of three comorbidity indices. Med Care. 1996;34:1093–101.
Gabriel SE, Crowson CS, O’Fallon WM. A comparison of two comorbidity instruments in arthritis. J Clin Epidemiol. 1999;52:1137–42.
Kieszak SM, Flanders WD, Kosinski AS, Shipp CC, Karp H. A comparison of the Charlson comorbidity index derived from medical record data and administrative billing data. J Clin Epidemiol. 1999;52:137–42.
Poses RM, McClish DK, Smith WR, Bekes C, Scott WE. Prediction of survival of critically ill patients by admission comorbidity. J Clin Epidemiol. 1996;49:743–7.
Fletcher RH, Fletcher SW, WAGNER EH. Clinical epidemiology: the essentials. 3rd ed. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins; 1996.
de Groot V, Beckerman H, Lankhorst GJ, Bouter LM. How to measure comorbidity. A critical review of available methods. J Clin Epidemiol. 2003;56:221–9.
Katz JN, Chang LC, Sangha O, Fossel AH, Bates DW. Can comorbidity be assessed by questionnaire rather than medical record review ? Med Care. 1996;34:73–84.
Deyo RA, Cherkin DC, Ciol MA. Adapting a clinical comorbidity index for use with ICD-9-CM administrative databases. J Clin Epidemiol. 1992;45(6):613–9.
Romano PS, Roos LL, Jollis JG. Adapting a clinical comorbidity index for use with ICD-9-CM administrative data: differing perspectives. J Clin Epidemiol. 1993;46(10):1075–9.
Halfon P, Eggli Y, van Melle G, Chevalier J, Wasserfallen JB, Burnand B. Measuring potentially avoidable hospital readmissions. J Clin Epidemiol. 2002;55(6):573–87.
Quan H, Sundararajan V, Halfon P, Fong A, Burnand B, Luthi JC, Saunders LD, Beck CA, Feasby TE, Ghali WA. Coding algorithms for defining comorbidities in ICD-9-CM and ICD-10 administrative data. Med Care. 2005;43(11):1130–9.
Schneeweiss S, Wang PS, Avorn J, Glynn RJ. Improved comorbidity adjustment for predicting mortality in Medicare populations. Health Serv Res. 2003;38(4):1103–20.
Sarfati D, Tan L, Blakely T, et al. Comorbidity among patients with colon cancer in New Zealand. N Z Med J. 2011;124(1338):76–88.
Mnatzaganian G, Ryan P, Norman PE, et al. Accuracy of hospital morbidity data and the performance of comorbidity scores as predictors of mortality. J Clin Epidemiol. 2012;65(1):107–15.
Needham DM, Scales DC, Laupacis A, Pronovost PJ. A systematic review of the Charlson comorbidity index using Canadian administrative databases: a perspective on risk adjustment in critical care research. J Crit Care. 2005;20(1):12–9.
Moltó A, Dougados M. Comorbidity indices. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2014;32(Suppl. 85):S131–4.
Condon JR, You J, McDonnell J. Performance of comorbidity indices in measuring outcomes after acute myocardial infarction in Australian indigenous and non-indigenous patients. Intern Med J. 2012;42:e165–73.
Southern DA, Quan H, Ghali WA. Comparison of the Elixhauser and Charlson/Deyo methods of comorbidity measurement in administrative data. Med Care. 2004;42:355–60.
Menendez ME, Neuhaus V, van Dijk CN, Ring D. The Elixhauser comorbidity method outperforms the Charlson index in predicting inpatient death after orthopaedic surgery. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472:2878–86.
Dominick KL, Dudley TK, Coffman CJ, Bosworth HB. Comparison of three comorbidity measures for predicting health service use in patients with osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;53:666–72.
Antoniou T, Ng R, Glazier RH, Kopp A, Austin PC. Comparison of comorbidity classification methods for predicting outcomes in a population-based cohort of adults with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Ann Epidemiol. 2014;24:532–7.
Gandjour A, Ku-Goto MH, Ho V. Comparing the validity of different measures of illness severity: a hospital-level analysis for acute myocardial infarction. Health Serv Manag Res. 2012;25:138–43.
Sharabiani M, Aylin P, Bottle A. Systematic review of comorbidity indices for administrative data. Med Care. 2012;50(12):1109–18.
Garland A, Fransoo R, Olafson K, Ramsey C, Yogendran M, Chateau D, McGowan K. The epidemiology and outcomes of critical illness in Manitoba. Winnipeg: Manitoba Centre for Health Policy; 2012.
Van Walraven C, Austin PC, Jenings A, Quan H, Forster AJ. A modification of the Elixhauser comorbidity measures into a point system for hospital death using administrative data. Med Care. 2009;47(6):626–33.
Linn BS, Linn MW, Gurel L. Cumulative illness rating scale. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1968;16:622–6.
Extermann M, Overcash J, Lyman G, Parr J, Balducci L. Comorbidity and functional status are independent in older cancer patients. J Clin Oncol. 1998;16(4):1582–7.
Repetto L, Fratino L, Audisio RA, Venturino A, Gianni W, Vercelli M, Parodi S, Dal Lago D, Gioia F, Monfardini S, Aapro MS, Serraino D, Zagonel V. Comprehensive geriatric assessment adds information to Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status in elderly cancer patients: an Italian Group for Geriatric Oncology Study. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20(2):494–502.
Grolla D, Tob T, Bombardierc C, Wrightd J. The development of a comorbidity index with physical function as the outcome. J Clin Epidemiol. 2005;58:595–602.
Michaud K, Wolfe F. Comorbidities in rheumatoid arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2007;21:885–906.
Chang TI, Paik J, Greene T, Miskulin DC, Chertow GM. Updated comorbidity assessments and outcomes in prevalent hemodialysis patients. Hemodial Int. 2010;14:478–85.
Rander H, Yoshida K, Mjaavatten M, Aletaha D, et al. Development of a multimorbidity index: impact on quality of life using a rheumatoid arthritis cohort. Semin Arth Rheumatsim. 2015;45(2):167–73.
Radner H, Smolen JS, Aletaha D. Comorbidity affects all domains of physical function and quality of life in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010;50:381–8.
Frenkel WJ, Jongerius EJ, Mandjes-van Uitert MJ, van Munster BC, de Rooij SE. Validation of the Charlson comorbidity index in acutely hospitalized elderly adults: a prospective cohort study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014;62:342–6.
Sangha O, Stucki G, Liang M, Fossel AH, Katz JN. The self-administered comorbidity questionnaire: a new method to assess comorbidity for clinical and health services research. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;49:156–63.
Stolwijk C, van Tubergen A, Ramiro S, et al. Aspects of validity of the self-administered comorbidity questionnaire in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014;53:1054–64.
El Miedany Y. Co-morbidity index in rheumatoid arthritis: time to think. Clin Rheumatol. 2015;34(12):1995–2000.
El Miedany Y, El Gaafary M, Youssef S, Bahlas S, Ahmed I, Hegazi M. Rheumatoid arthritis comorbidity index: development and validation of a new specific tool for classifying prognostic comorbidity in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75(Suppl2):154.
El Miedany Y, El Gaafary M, Youssef S, Bahlas S, Hegazi M. Psoriatic arthritis comorbidity index: development and validation of a new specific tool for classifying prognostic comorbidity in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis patients. Rheumatol Orthop Med. 2017;2 doi: 10.15761/ROM.1000117.
NICEguidelines [CG79]. Rheumatoidarthritis:the management of rheumatoid arthritis in adults. http://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg79. 2009.
Smolen J, Landewé R, Breedveld F, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2013 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(3):492–509. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2013204573.
Dougados M, Soubrier M, Antunez A, et al. Prevalence of comorbidities in rheumatoid arthritis and evaluation of their monitoring: results of an international, cross-sectional study (COMORA). Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;1:1–7. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis2013-204223.
Jacobsson LT, Knowler WC, Pillemer S, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis and mortality. A longitudinal study in pima Indians. Arthritis Rheum. 1993;36:1045–53.
Turesson C, McClelland RL, Christianson TJ, et al. Severe extra-articular disease manifestations are associated with an increased risk of first ever cardiovascular events in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007;66:70–5.
Nicola PJ, Maradit-Kremers H, Roger VL, et al. The risk of congestive heart failure in rheumatoid arthritis: a population-based study over 46 years. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52:412–20.
Gabriel SE, Crowson CS, Kremers HM, et al. Survival in rheumatoid arthritis: a population-based analysis of trends over 40 years. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48:54–8.
Weinblatt ME, Coblyn JS, Fox DA, et al. Efficacy of lowdose methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 1985;312:818–22.
Radner H, Yoshida K, Smolen J, Solomon D. Multimorbidity and rheumatic conditions—enhancing the concept of comorbidity. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014;10:252–6.
Miskulin DC, Athienites NV, Yan G, Martin AA, Ornt DB, et al. Comorbidity assessment using the index of coexistent diseases in a multicenter clinical trial. Kidney Int. 2001;60(4):1498–510.
Lieffers JR, Baracos VE, Winget M, Fassbender K. A comparison of Charlson and Elixhauser comorbidity measures to predict colorectal cancer survival using administrative health data. Cancer. 2011;117:1957–65.
Baillet A, Gossec L, Carmona L, de Wit M, et al. Points to consider for reporting, screening for and preventing selected comorbidities in chronic inflammatory rheumatic diseases in daily practice: a EULAR initiative. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(3):492–509. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209233.
Acknowledgment
Special thanks to Dr. Loreto Carmona, MD, PhD, Research Director, Instituto de Salud Musculoesquelética, Madrid, Spain, for peer reviewing this chapter.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
El Miedany, Y. (2017). Comorbidity Index. In: El Miedany, Y. (eds) Comorbidity in Rheumatic Diseases. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59963-2_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59963-2_16
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-59962-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-59963-2
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)