Abstract
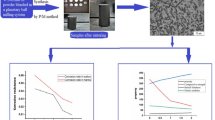
Titanium (Ti) and Ti alloys are widely used for the manufacture of dental implants and orthopedic prostheses due to suitable properties such as zero toxicity, good mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. The addition of niobium (Nb) to commercially pure Ti (cp-Ti) can results in elastic moduli lower than Ti. So in this work the elastic modulus of Ti-Nb alloys with 10% and 20%, in weight submitted to anodic oxidation (AO) has been investigated to verify how to obtain elastic modulus closer to bone. The AO has been realized using phosphoric acid as electrolyte applying a voltage of 250V/60s. Elastic modulus values were obtained using instrumented indentation technique. The results indicated that it was possible to obtain Ti-Nb alloys with lower elastic modulus values compared with cp-Ti.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
IVANOVA, E. P.; BAZAKA K.; CRAWFORD, R. J. Metallic Biomaterials: Types and Advanced Applications. New Functional Biomaterials for Medicine and Healthcare(Woodhead Publishing, 2014) 121–147.
VITALI G et al. “Bone and Metal: An Orthopaedic Perspective on Osseointegration of Metals” Acta Biomaterialia, 10 (2014), 4043–4057.
OKAZAKI. Y. et al., “Cytocompatibility of Various Metal and Development of New Titanium Alloys For Medical Implants.”, Materials Science and Engineering , (1998), 250–256.
YU. S. et al., “Biocompatibility and Osteoconduction of Active Porous Calcium–Phosphate Films on a Novel Ti–3Zr–2Sn–3Mo–25Nb Biomedical Alloy”, Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 85 (2011), 103–115.
NIINOMI. M, “Mechanical Biocompatibilities of Titanium Alloys for Biomedical Applications”, J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater., 1 (2008), 30–42.
METIKOS-HUKOVI. M, KWOKAL. A, Pilj. J. “The Influence of Niobium and Vanadium on Passivity of Titanium-Based Implants in Physiological Solution”, Biomaterials, 24 (2003), 3765–3775.
SILVA, L.M. et al., “Influence of the Substitutional Solute on the Mechanical Properties of Ti-Nb Binary Alloys for Biomadical Use”, Materials Research, 15 (2012), 355–358, http://dx.doi10.1590/S1516–14392012005000040.
ALEIXO, G. T., “Estabilidade e Metaestabilidade de Fases em Ligas Ti-Nb”, Dissertação de Mestrado, Universidade Estadual de Campinas, Faculdade de Engenharia Mecânica, Departamento de Engenharia de Materiais, 2006.
SOUZA. G. B. et al., “Tribo-mechanical characterization of rough, porous and bioactive Ti anodic layers” , Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 4 (2011), 796–806.
MOHAMMED. M. T, et al., “Surface Modifications of Titanium Materials for developing Corrosion Behavior in Human Body Environment: A Review”, Procedia Materials Science, 6 (2014), 1610–1618.
SIMKA. W, “Preliminary investigations on the anodic oxidation of Ti-13Nb-13Zr alloy in a solution containing calcium and phosphorus”, Electrochimica Acta, 56 (2011), 9831–9837.
SIMKA. W. et al., “Anodic oxidation of Ti-13Nb-13Zr alloy in silicate solutions”, Applied Surface Science, 279 (2013), 317–323
CALDERON-MORENO. J. et al., “Microstructural and Mechanical Properties, Surface and Electrochemical Characterization of a New Ti-Zr-Nb Alloy for Implant Applications”, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 612 (2014), 398–410.
OLIVER, W. C; PHARR, G. M., “Measurement of Hardness and Elastic Modulus by Instrumented Indentation: Advances in Understanding and Refinements to Methodology”, J. Mater. Res., 19 (2004), 3–20.
GEETHA, M. et al, “Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants — A review” Progress in Materials Science 54 (2009), 397–425.
LIU, X.; CHU, P.; Ding, C. Surface modification of titanium, titanium alloys, and related materials for biomedical applications, Materials Science and Engineering: R: Reports, 47 (2004), 49–121.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 TMS (The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society)
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kuromoto, N.K. et al. (2015). Elastic Modulus of Oxidized Ti-Nb Alloys. In: TMS 2015 144th Annual Meeting & Exhibition. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48127-2_68
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48127-2_68
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-48608-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-48127-2
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)