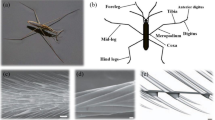
Abstract
When water strider robots row on water, the periodically stroking water surface of the actuating legs will unavoidably bring vibrations and instabilities that might cause the robots to sink into water. In this work, a stability analysis model for water strider robots rowing on water was proposed and a mass-spring-damper-like model was defined to describe the robot-water interactions. We applied this model to evaluate the water-surface stability of a miniature surface tension-driven water strider robot by detaily discussing the effects of the actuating legs’ rowing with different rowing frequencies on the vibration, pitching and swinging motions. The theoretical results indicates the robot possesses a good water-surface stability. The stability analysis model presented in this study can help with the design of water strider robots in future.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hu, D.L., Chan, B., Bush, J.W.: The hydrodynamics of water strider locomotion. Nature 424, 663–666 (2003)
Gao, X., Jiang, L.: Biophysics: water-repellent legs of water striders. Nature 432, 36–36 (2004)
Hu, D.L., Bush, J.W.: The hydrodynamics of water-walking arthropods. J. Fluid Mech. 644, 5–33 (2010)
Suhr, S., Song, Y., Lee, S., Sitti, M.: Biologically inspired miniature water strider robot. Proc. Robot. Sci. Syst. I 319-326 (2005)
Takonobu, H., Kodaira, K., Takeda, H.: Water strider’s muscle arrangement-based robot. In: Proceedings of IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 1754–1759. IEEE Press, Edmonton (2005)
Suzuki, K., Takanobu, H., Noya, K., Koike, H., Miura, H.: Water strider robots with microfabricated hydrophobic legs. In: Proceedings of IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 590–595. IEEE Press, San Diego (2007)
Zhang, X., Zhao, J., Zhu, Q., Chen, N., Zhang, M., Pan, Q.: Bioinspired aquatic microrobot capable of walking on water surface like a water strider. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 3, 2630–2636 (2011)
Shin, B., Kim, H. Cho, K.: Towards a biologically inspired small-scale water jumping robot. In: Proceedings of IEEE/RAS-EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics, pp. 590–595. IEEE Press, Scottsdale (2008)
Koh, J.S., Yang, E., Jung, G.P., Jung, S.P., Son, J.H., Lee, S.I., Cho, K.J.: Jumping on water: Surface tension–dominated jumping of water striders and robotic insects. Science 349, 517–521 (2015)
Zhao, J., Zhang, X., Chen, N., Pan, Q.: Why Superhydrophobicity is crucial for a water-jumping microrobot? Experimental and theoretical investigations. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 4, 3706–3711 (2012)
Yan, J., Zhang, X., Zhao, J., Liu, G., Cai, H., Pan, Q.: A miniature surface tension-driven robot using spatially elliptical moving legs to mimic a water strider’s locomotion. Bioinspiration Biomimetics 10, 046016 (2015)
Zhang, X., Yan, J., Zhao, J., Wang, Y., Pan, Q.: Vertical force acting on partly submerged spindly cylinders. AIP Adv. 4, 047118 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, Grant 51305098).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Yan, J., Zhang, X., Zhao, J., Cai, H. (2017). Water-Surface Stability Analysis of a Miniature Surface Tension-Driven Water Strider Robot. In: Chen, W., Hosoda, K., Menegatti, E., Shimizu, M., Wang, H. (eds) Intelligent Autonomous Systems 14. IAS 2016. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 531. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48036-7_57
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48036-7_57
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-48035-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-48036-7
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)