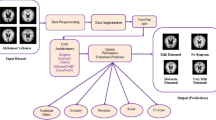
Abstract
Alzheimer is a neurological disorder that causes cell damage and memory loss. The late symptoms of Alzheimer disease necessitate early identification to minimise the progression of disease and mortality rate. Machine learning and deep learning techniques are required to thoroughly read the MRI images and extract the most relevant information about disease progression. Transfer learning approaches assist in the reduction of computational requirements and minimise the overfitting issues. This study identifies the most appropriate technique for the classification of Alzheimer's disease using machine learning, deep learning, and transfer learning techniques. The classification is performed on the ADNI MRI dataset with the minimal pre-processing of data to compare the results on the same scale. Results suggested that transfer learning approaches outperformed the other algorithms and can be used with other feature extraction techniques to further improve model performance.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Association, A.: 2018 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 14(3), 367–429 (2018)
Geerlings, M.I., den Heijer, T., Koudstaal, P.J., Hofman, A., Breteler, M.M.B.: History of depression, depressive symptoms, and medial temporal lobe atrophy and the risk of Alzheimer disease. Neurology 70(15), 1258–1264 (2008)
Guillozet, A.L., Weintraub, S., Mash, D.C., Mesulam, M.M.: Neurofibrillary tangles, amyloid, and memory in aging and mild cognitive impairment. Arch. Neurol. 60(5), 729–736 (2003)
Reitz, C., Mayeux, R.: Alzheimer disease: epidemiology, diagnostic criteria, risk factors and biomarkers. Biochem. Pharmacol. 88(4), 640–651 (2014)
Dickerson, B.C., Sperling, R.A.: Large-scale functional brain network abnormalities in Alzheimer’s disease: insights from functional neuroimaging. Behav. Neurol. 21(12), 63–75 (2009)
Simpson, S.L., Bowman, F.D., Laurienti, P.J.: Analyzing complex functional brain networks: fusing statistics and network science to understand the brain. Statist. Surv. 7, 1 (2013)
Braun, U., et al.: Dynamic reconfiguration of frontal brain networks during executive cognition in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 112(37), 11678–11683 (2015)
Marsh, H.W., Morin, A.J., Parker, P.D., Kaur, G.: Exploratory structural equation modeling: an integration of the best features of exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 10, 85–110 (2014)
Vieira, S., Pinaya, W.H., Mechelli, A.: Using deep learning to investigate the neuroimaging correlates of psychiatric and neurological disorders: Methods and applications. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 74, 58–75 (2017)
Razzak, M.I., Naz, S., Zaib, A.: Deep learning for medical image processing: overview, challenges and the future. In: Dey, N., Ashour, A.S., Borra, S. (eds.) Classification in BioApps. LNCVB, vol. 26, pp. 323–350. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-65981-7_12
Rauschert, S., Raubenheimer, K., Melton, P.E., Huang, R.C.: Machine learning and clinical epigenetics: a review of challenges for diagnosis and classification. Clin. Epigenetics 12(1), 1–11 (2020)
Abuhmed, T., El-Sappagh, S., Alonso, J.M.: Robust hybrid deep learning models for Alzheimer’s progression detection. Knowl.-Based Syst. 213, 106688 (2021)
Battineni, G., Chintalapudi, N., Amenta, F.: Machine learning in medicine: Performance calculation of dementia prediction by support vector machines (SVM). Inf. Med. Unlocked 16, 100200 (2019)
Jha, D., Kwon, G.R.: Alzheimer disease detection in MRI using curvelet transform with KNN. J. Korean Inst. Inf. Technol. 14(8), 121 (2016)
Alickovic, E., Subasi, A.: Automatic detection of alzheimer disease based on histogram and random forest. In: Badnjevic, A., Škrbić, R., Pokvić, L.G. (eds.) CMBEBIH 2019. IP, vol. 73, pp. 91–96. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-17971-7_14
Dana, A.D., Alashqur, A.: Using decision tree classification to assist in the prediction of Alzheimer's disease. In: 2014 6th international conference on computer science and information technology (CSIT), pp. 122–126. IEEE (2014)
Mehmood, A., Maqsood, M., Bashir, M., Shuyuan, Y.: A deep siamese convolution neural network for multi-class classification of alzheimer disease. Brain Sci. 10(2), 84 (2020)
Álvarez, I., et al.: Automatic classification system for the diagnosis of alzheimer disease using Component-Based SVM aggregations. In: Köppen, M., Kasabov, N., Coghill, G. (eds.) Advances in Neuro-Information Processing, pp. 402–409. Springer, Heidelberg (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-03040-6_49
Khedher, L., Ramírez, J., Górriz, J.M., Brahim, A., Illán, I.A.: Independent component analysis-based classification of Alzheimer’s disease from segmented MRI data. In: Vicente, J.M.F., Álvarez-Sánchez, J.R., de la Paz, F., López, F.J.T.-M., Adeli, H. (eds.) IWINAC 2015. LNCS, vol. 9107, pp. 78–87. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-18914-7_9
Sheng, J., et al.: A novel joint HCPMMP method for automatically classifying Alzheimer’s and different stage MCI patients. Behav. Brain Res. 365, 210–221 (2019)
Mishra, S., Beheshti, I., Khanna, P., Initiative, A.D.N.: A statistical region selection and randomized volumetric features selection framework for early detection of Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 28(4), 302–314 (2018)
Islam, J., Zhang, Y.: A novel deep learning based multi-class classification method for Alzheimer’s disease detection using brain MRI data. In: Zeng, Y., et al. (eds.) BI 2017. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 10654, pp. 213–222. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-70772-3_20
Jain, R., Jain, N., Aggarwal, A., Hemanth, D.J.: Convolutional neural network based Alzheimer’s disease classification from magnetic resonance brain images. Cogn. Syst. Res. 57, 147–159 (2019)
Dimiduk, D.M., Holm, E.A., Niezgoda, S.R.: Perspectives on the impact of machine learning, deep learning, and artificial intelligence on materials, processes, and structures engineering. Integr. Mater. Manuf. Innov. 7(3), 157–172 (2018)
Tanveer, M., et al.: Machine learning techniques for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: a review. ACM Trans. Multimedia Comput. Commun. Appl. (TOMM) 16(1s), 1–35 (2020)
Khvostikov, A., Aderghal, K., Benois-Pineau, J., Krylov, A., Catheline, G.: 3D CNN-based classification using sMRI and MD-DTI images for Alzheimer disease studies (2018). arXiv preprint arXiv:1801.05968
Liu, W., Wang, Z., Liu, X., Zeng, N., Liu, Y., Alsaadi, F.E.: A survey of deep neural network architectures and their applications. Neurocomputing 234, 11–26 (2017)
Glozman, T., Liba, O.: Hidden cues: Deep learning for Alzheimer’s disease classification CS331B project final report (2016)
Korolev, S., Safiullin, A., Belyaev, M., Dodonova, Y.: Residual and plain convolutional neural networks for 3D brain MRI classification. In: 2017 IEEE 14th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2017), pp. 835–838. IEEE (2017)
Park, T., Liu, M.Y., Wang, T.C., Zhu, J.Y.: Semantic image synthesis with spatially-adaptive normalization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2337–2346 (2019))
Isensee, F., Petersen, J., Kohl, S.A., Jäger, P.F., Maier-Hein, K.H.: nnu-net: Breaking the spell on successful medical image segmentation, vol. 1, pp. 1–8. arXiv preprint arXiv:1904.08128 (2019)
Suthaharan, S.: Support vector machine. In: Machine learning models and algorithms for big data classification. ISIS, vol. 36, pp. 207–235. Springer, Boston, MA (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4899-7641-3_9
Biau, G., Scornet, E.: A random forest guided tour. TEST 25(2), 197–227 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11749-016-0481-7
Webb, G.I., Keogh, E., Miikkulainen, R.: Naïve bayes. Encycl. Mach. Learn. 15, 713–714 (2010)
Guo, G., Wang, H., Bell, D., Bi, Y., Greer, K.: KNN model-based approach in classification. In: Meersman, R., Tari, Z., Schmidt, D.C. (eds.) OTM 2003. LNCS, vol. 2888, pp. 986–996. Springer, Heidelberg (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-39964-3_62
Buhrmester, V., Münch, D., Arens, M.: Analysis of explainers of black box deep neural networks for computer vision: a survey (2019). arXiv preprint arXiv:1911.12116
Hon, M., Khan, N.M.: Towards Alzheimer's disease classification through transfer learning. In: 2017 IEEE International conference on bioinformatics and biomedicine (BIBM), pp. 1166–1169. IEEE (2017)
Maqsood, M., et al.: Transfer learning assisted classification and detection of Alzheimer’s disease stages using 3D MRI scans. Sensors 19(11), 2645 (2019)
Oh, K., Chung, Y.C., Kim, K.W., Kim, W.S., Oh, I.S.: Classification and visualization of Alzheimer’s disease using volumetric convolutional neural network and transfer learning. Sci. Rep. 9(1), 1–16 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Bhade, A.W., Bamnote, G.R. (2023). Performance Evaluation of Machine and Deep Transfer Learning Techniques for the Classification of Alzheimer Disease Using MRI Images. In: Sharma, H., Saha, A.K., Prasad, M. (eds) Proceedings of International Conference on Intelligent Vision and Computing (ICIVC 2022). ICIVC 2022. Proceedings in Adaptation, Learning and Optimization, vol 17. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-31164-2_26
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-31164-2_26
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-31163-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-31164-2
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)