Abstract
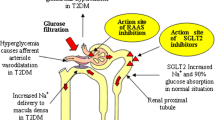
Diabetic nephropathy is a leading cause of end-stage renal disease worldwide [1]. When it was discovered that blocking the renin angiotensin system can have a renoprotective effect, research was initiated to study these effects using medications such as angiotensin-II-receptor antagonists (ARBs) and angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors in patients with type 1 diabetic nephropathy. Although type 2 is the most common form of diabetes, it was not until later that there was research on the renoprotective effects of medications for this population [1]. This study advanced the field by studying the effect of ARBs on type 2 diabetic nephropathy.
Brenner, B. M., Cooper, M. E., de Zeeuw, D., Keane, W. F., Mitch, W. E., Parving, H. H., Remuzzi, G., Snapinn, S. M., Zhang, Z., Shahinfar, S., & RENAAL Study Investigators (2001). Effects of Losartan on Renal and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Nephropathy. The New England journal of medicine, 345(12), 861–869.
Hyperlink to PDF: https://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJMoa011161?url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori:rid:crossref.org&rfr_dat=cr_pub%20%200www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mallik R, Chowdhury TA. Pharmacotherapy to delay the progression of diabetic kidney disease in people with type 2 diabetes: past, present and future. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 2022;13:20420188221081601.
Rayner B. Advances in the treatment of diabetic renal disease: focus on losartan. Curr Med Res Opin. 2004;20(3):333–40.
American Diabetes Association. Microvascular complications and foot care. Sec. 9. In standards of medical Care in Diabetes 2016. Diabetes Care. 2016;39(Suppl. 1):S72–80.
Lewis EJ, Hunsicker LG, Clarke WR, Berl T, Pohl MA, Lewis JB, Ritz E, Atkins RC, Rohde R, Raz I, Collaborative Study Group. Renoprotective effect of the angiotensin-receptor antagonist irbesartan in patients with nephropathy due to type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2001;345(12):851–60.
Sica DA, Weber M. The losartan intervention for endpoint reduction (LIFE) trial-have angiotensin-receptor blockers come of age? J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2002;4(4):301–5.
Viberti G, Wheeldon NM, MicroAlbuminuria Reduction With VALsartan (MARVAL) Study Investigators. Microalbuminuria reduction with valsartan in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a blood pressure-independent effect. Circulation. 2002;106(6):672–8.
Makino H, Haneda M, Babazono T, Moriya T, Ito S, Iwamoto Y, Kawamori R, Takeuchi M, Katayama S, INNOVATION Study Group. Prevention of transition from incipient to overt nephropathy with telmisartan in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2007;30(6):1577–8.
Haller H, Viberti GC, Mimran A, Remuzzi G, Rabelink AJ, Ritz E, Rump LC, Ruilope LM, Katayama S, Ito S, Izzo JL Jr, Januszewicz A. Preventing microalbuminuria in patients with diabetes: rationale and design of the randomised Olmesartan and diabetes microalbuminuria prevention (ROADMAP) study. J Hypertens. 2006;24(2):403–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Buchbinder, S. (2023). ARB and the Slowing of Progression of Diabetic Nephropathy 2001. In: Russell, J., Skolnik, N.S. (eds) Top Articles in Primary Care. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25620-2_40
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25620-2_40
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-25619-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-25620-2
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)