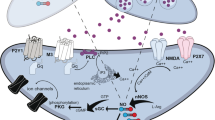
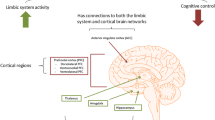
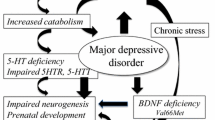
Abstract
The pathogenesis of mood disorders remains elusive, but it is evident that multiple factors, genetic and environmental, play a crucial role in adult psychopathology and neurobiology. Concerning therapy, a significant proportion of affective disorder patients are partial or non-responders. There has been no breakthrough in finding novel, valuable drug targets since introducing the current marketed antidepressant drugs in the 1950s to the 1980s, which all are based on monoaminergic pharmacological effects. Consequently, there is a pressing need to develop novel treatment strategies—and ultimately understand the aetiology and pathophysiology of affective disorders. Nitric Oxide serves an essential role in the nervous system. It acts as a messenger molecule in several physiological processes, including processes linked to major psychiatric diseases. The present chapter will review the general aspects of the NO system in Major depressive disorder (MDD) and focus on reducing NO production as putative therapeutic agents towards depression.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Olesen J, Leonardi M (2003) The burden of brain diseases in Europe. Eur J Neurol 10(5):471–477
Olesen J, Sobscki P, Truelsen T, Sestoft D, Jonsson B (2008) Cost of disorders of the brain in Denmark. NordJ Psychiatry. 62(2):114–120
Wittchen HU, Jacobi F, Rehm J, Gustavsson A, Svensson M, Jonsson B et al (2011) The size and burden of mental disorders and other disorders of the brain in Europe 2010. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 21(9):655–679
Olesen J, Gustavsson A, Svensson M, Wittchen HU, Jonsson B, group Cs, et al. The economic cost of brain disorders in Europe. Eur J Neurol. 2012;19(1):155–62.
Gustavsson A, Svensson M, Jacobi F, Allgulander C, Alonso J, Beghi E et al (2011) Cost of disorders of the brain in Europe 2010. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 21(10):718–779
Caspi A, Sugden K, Moffitt TE, Taylor A, Craig IW, Harrington H et al (2003) Influence of life stress on depression: moderation by a polymorphism in the 5-HTT gene. Science 301(5631):386–389
Palmer RM, Ferrige AG, Moncada S (1987) Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature 327(6122):524–526
Hibbs JB Jr, Taintor RR, Vavrin Z (1987) Macrophage cytotoxicity: role for L-arginine deiminase and imino nitrogen oxidation to nitrite. Science 235(4787):473–476
Bredt DS, Snyder SH (1989) Nitric oxide mediates glutamate-linked enhancement of cGMP levels in the cerebellum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86(22):9030–9033
Garthwaite J, Garthwaite G, Palmer RM, Moncada S (1989) NMDA receptor activation induces nitric oxide synthesis from arginine in rat brain slices. Eur J Pharmacol 172(4–5):413–416
Knott AB, Bossy-Wetzel E (2009) Nitric oxide in health and disease of the nervous system. Antioxid Redox Signal 11(2). https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2008.234
Oosthuizen F, Wegener G, Harvey BH (2005) Nitric oxide as inflammatory mediator in post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD): evidence from an animal model. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 1(2):109–123
Reif A, Herterich S, Strobel A, Ehlis AC, Saur D, Jacob CP et al (2006) A neuronal nitric oxide synthase (NOS-I) haplotype associated with schizophrenia modifies prefrontal cortex function. Mol Psychiatry 11(3):286–300
Reif A, Jacob CP, Rujescu D, Herterich S, Lang S, Gutknecht L et al (2009) Influence of functional variant of neuronal nitric oxide synthase on impulsive behaviors in humans. Arch Gen Psychiatry 66(1):41–50
Garthwaite J, Charles SL, Chess-Williams R (1988) Endothelium-derived relaxing factor release on activation of NMDA receptors suggests role as intercellular messenger in the brain. Nature 336(6197):385–388
Garthwaite J (2008) Concepts of neural nitric oxide-mediated transmission. Eur J Neurosci 27(11):2783–2802
Guix FX, Uribesalgo I, Coma M, Munoz FJ (2005) The physiology and pathophysiology of nitric oxide in the brain. Prog Neurobiol 76(2):126–152
Blum-Degen D, Heinemann T, Lan J, Pedersen V, Leblhuber F, Paulus W et al (1999) Characterization and regional distribution of nitric oxide synthase in the human brain during normal ageing. Brain Res 834(1–2):128–135
Amitai Y (2010) Physiologic role for “inducible” nitric oxide synthase: a new form of astrocytic-neuronal interface. Glia 58(15):1775–1781
Feil R, Kleppisch T (2008) NO/cGMP-dependent modulation of synaptic transmission. Handb Exp Pharmacol 184:529–560
Kleppisch T, Feil R (2009) cGMP signalling in the mammalian brain: role in synaptic plasticity and behaviour. Handb Exp Pharmacol 191:549–579
Ding JD, Burette A, Nedvetsky PI, Schmidt HH, Weinberg RJ (2004) Distribution of soluble guanylyl cyclase in the rat brain. J Comp Neurol 472(4):437–448
Jaffrey SR, Erdjument-Bromage H, Ferris CD, Tempst P, Snyder SH (2001) Protein S-nitrosylation: a physiological signal for neuronal nitric oxide. Nat Cell Biol 3(2):193–197
Brenman JE, Chao DS, Gee SH, McGee AW, Craven SE, Santillano DR et al (1996) Interaction of nitric oxide synthase with the postsynaptic density protein PSD-95 and α1-syntrophin mediated by PDZ domains. Cell 84(5):757–767
Nedvetsky PI, Sessa WC, Schmidt HHHW (2002) There’s NO binding like NOS binding: Protein-protein interactions in NO/cGMP signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99(26):16510–16512
Doucet MV, Harkin A, Dev KK (2012) The PSD-95/nNOS complex: New drugs for depression? Pharmacol Ther 133(2):218–229
Osuka K, Watanabe Y, Usuda N, Nakazawa A, Fukunaga K, Miyamoto E et al (2002) Phosphorylation of Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase at Ser847 by CaM-KII in the Hippocampus of Rat Brain after Transient Forebrain Ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 22(9):1098–1106
Zhou Q-G, Zhu X-H, Nemes AD, Zhu D-Y (2018) Neuronal nitric oxide synthase and affective disorders. IBRO Reports. 5:116–132
Jaffrey SR, Snowman AM, Eliasson MJL, Cohen NA, Snyder SH (1998) CAPON: A protein associated with neuronal nitric oxide synthase that regulates its interactions with PSD95. Neuron 20(1):115–124
Fang M, Jaffrey SR, Sawa A, Ye K, Luo X, Snyder SH (2000) Dexras1: A G protein specifically coupled to neuronal nitric oxide synthase via CAPON. Neuron 28(1):183–193
Jaffrey SR, Benfenati F, Snowman AM, Czernik AJ, Snyder SH (2002) Neuronal nitric-oxide synthase localization mediated by a ternary complex with synapsin and CAPON. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99(5):3199–3204
Riccio A, Alvania RS, Lonze BE, Ramanan N, Kim T, Huang Y et al (2006) A Nitric Oxide Signaling Pathway Controls CREB-Mediated Gene Expression in Neurons. Mol Cell 21(2):283–294
Hara MR, Agrawal N, Kim SF, Cascio MB, Fujimuro M, Ozeki Y et al (2005) S-nitrosylated GAPDH initiates apoptotic cell death by nuclear translocation following Siah1 binding. Nat Cell Biol 7(7):665–674
Ghasemi M, Claunch J, Niu K (2019) Pathologic role of nitrergic neurotransmission in mood disorders. Prog Neurobiol 173:54–87
Hara MR, Snyder SH (2007) Cell Signaling and Neuronal Death. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 47(1):117–141
Spiers JG, Chen H-JC, Bourgognon J-M, Steinert JR. Dysregulation of stress systems and nitric oxide signaling underlies neuronal dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 2019;134:468–83.
Yuste JE, Tarragon E, Campuzano CM, Ros-Bernal F. Implications of glial nitric oxide in neurodegenerative diseases. Frontiers in cellular neuroscience. 2015;9(322).
Bernstein HG, Stanarius A, Baumann B, Henning H, Krell D, Danos P et al (1998) Nitric oxide synthase-containing neurons in the human hypothalamus: reduced number of immunoreactive cells in the paraventricular nucleus of depressive patients and schizophrenics. Neurosci 83(3):867–875
Bernstein HG, Heinemann A, Krell D, Mawrin C, Bielau H, Danos P et al (2002) Further immunohistochemical evidence for impaired NO signaling in the hypothalamus of depressed patients. Ann N Y Acad Sci 973:91–93
Xing G, Chavko M, Zhang LX, Yang S, Post RM (2002) Decreased calcium-dependent constitutive nitric oxide synthase (cNOS) activity in prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia and depression. Schizophr Res 58(1):21–30
Karolewicz B, Szebeni K, Stockmeier CA, Konick L, Overholser JC, Jurjus G et al (2004) Low nNOS protein in the locus coeruleus in major depression. J Neurochem 91(5):1057–1066
Oliveira RM, Guimaraes FS, Deakin JF (2008) Expression of neuronal nitric oxide synthase in the hippocampal formation in affective disorders. Braz J Med Biol Res 41(4):333–341
Gao S, Zhang T, Jin L, Liang D, Fan G, Song Y et al (2019) CAPON Is a Critical Protein in Synaptic Molecular Networks in the Prefrontal Cortex of Mood Disorder Patients and Contributes to Depression-Like Behavior in a Mouse Model. Cereb Cortex 29(9):3752–3765
Kim YK, Paik JW, Lee SW, Yoon D, Han C, Lee BH (2006) Increased plasma nitric oxide level associated with suicide attempt in depressive patients. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 30(6):1091–1096
Lee BH, Lee SW, Yoon D, Lee HJ, Yang JC, Shim SH et al (2006) Increased plasma nitric oxide metabolites in suicide attempters. Neuropsychobiology 53(3):127–132
Suzuki E, Yagi G, Nakaki T, Kanba S, Asai M (2001) Elevated plasma nitrate levels in depressive states. J Affect Disord 63(1–3):221–224
Herken H, Gurel A, Selek S, Armutcu F, Ozen ME, Bulut M et al (2007) Adenosine deaminase, nitric oxide, superoxide dismutase, and xanthine oxidase in patients with major depression: impact of antidepressant treatment. Arch Med Res 38(2):247–252
Suzuki E, Yoshida Y, Shibuya A, Miyaoka H (2003) Nitric oxide involvement in depression during interferon-alpha therapy. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 6(4):415–419
Srivastava N, Barthwal MK, Dalal PK, Agarwal AK, Nag D, Seth PK et al (2002) A study on nitric oxide, beta-adrenergic receptors and antioxidant status in the polymorphonuclear leukocytes from the patients of depression. J Affect Disord 72(1):45–52
Wallerath T, Gath I, Aulitzky WE, Pollock JS, Kleinert H, Förstermann U (1997) Identification of the NO synthase isoforms expressed in human neutrophil granulocytes, megakaryocytes and platelets. Thromb Haemost 77(1):163–167
Chrapko WE, Jurasz P, Radomski MW, Lara N, Archer SL, Le Melledo JM (2004) Decreased platelet nitric oxide synthase activity and plasma nitric oxide metabolites in major depressive disorder. Biol Psychiatry 56(2):129–134
Chrapko W, Jurasz P, Radomski MW, Archer SL, Newman SC, Baker G et al (2006) Alteration of decreased plasma NO metabolites and platelet NO synthase activity by paroxetine in depressed patients. Neuropsychopharmacol 31(6):1286–1293
Loeb E, El Asmar K, Trabado S, Gressier F, Colle R, Rigal A, et al. Nitric Oxide Synthase activity in major depressive episodes before and after antidepressant treatment: Results of a large case-control treatment study. Psychological Medicine. 2020:1–10.
Ali-Sisto T, Tolmunen T, Viinamäki H, Mäntyselkä P, Valkonen-Korhonen M, Koivumaa-Honkanen H et al (2018) Global arginine bioavailability ratio is decreased in patients with major depressive disorder. J Affect Disord 229:145–151
Boger RH, Diemert A, Schwedhelm E, Luneburg N, Maas R, Hecher K (2009) The Role of Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibition by Asymmetric Dimethylarginine in the Pathophysiology of Preeclampsia. Gynecol Obstet Invest 69(1):1–13
Boger RH, Maas R, Schulze F, Schwedhelm E (2009) Asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) as a prospective marker of cardiovascular disease and mortality-An update on patient populations with a wide range of cardiovascular risk. Pharmacol Res 60(6):7
Boger RH, Sullivan LM, Schwedhelm E, Wang TJ, Maas R, Benjamin EJ et al (2009) Plasma asymmetric dimethylarginine and incidence of cardiovascular disease and death in the community. Circulation 119(12):1592–1600
McEvoy MA, Schofield P, Smith W, Agho K, Mangoni AA, Soiza RL et al (2013) Serum methylarginines and incident depression in a cohort of older adults. J Affect Disord 151(2):493–499
Ozden A, Angelos H, Feyza A, Elizabeth W, John P (2020) Altered plasma levels of arginine metabolites in depression. J Psychiatr Res 120:21–28
Selley ML (2004) Increased (E)-4-hydroxy-2-nonenal and asymmetric dimethylarginine concentrations and decreased nitric oxide concentrations in the plasma of patients with major depression. J Affect Disord 80(2–3):249–256
Das I, Khan NS, Puri BK, Hirsch SR (1996) Elevated endogenous nitric oxide synthase inhibitor in schizophrenic plasma may reflect abnormalities in brain nitric oxide production. Neurosci Lett 215(3):209–211
Arlt S, Schulze F, Eichenlaub M, Maas R, Lehmbeck JT, Schwedhelm E et al (2008) Asymmetrical dimethylarginine is increased in plasma and decreased in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 26(1):58–64
Nasyrova RF, Moskaleva PV, Vaiman EE, Shnayder NA, Blatt NL, Rizvanov AA (2020) Genetic Factors of Nitric Oxide’s System in Psychoneurologic Disorders. Int J Mol Sci 21(5):1604
Yu YW, Chen TJ, Wang YC, Liou YJ, Hong CJ, Tsai SJ (2003) Association analysis for neuronal nitric oxide synthase gene polymorphism with major depression and fluoxetine response. Neuropsychobiology 47(3):137–140
Buttenschon HN, Mors O, Ewald H, McQuillin A, Kalsi G, Lawrence J et al (2004) No association between a neuronal nitric oxide synthase (NOS1) gene polymorphism on chromosome 12q24 and bipolar disorder. AmJMedGenetB NeuropsychiatrGenet. 124(1):73–75
Okumura T, Kishi T, Okochi T, Ikeda M, Kitajima T, Yamanouchi Y et al (2010) Genetic association analysis of functional polymorphisms in neuronal nitric oxide synthase 1 gene (NOS1) and mood disorders and fluvoxamine response in major depressive disorder in the Japanese population. Neuropsychobiology 61(2):57–63
Wigner P, Czarny P, Synowiec E, Bijak M, Białek K, Talarowska M et al (2018) Variation of genes involved in oxidative and nitrosative stresses in depression. Eur Psychiat 48(1):38–48
Sullivan PF, de Geus EJ, Willemsen G, James MR, Smit JH, Zandbelt T et al (2009) Genome-wide association for major depressive disorder: a possible role for the presynaptic protein piccolo. Mol Psychiatry 14(4):359–375
Galecki P, Maes M, Florkowski A, Lewinski A, Galecka E, Bienkiewicz M et al (2011) Association between inducible and neuronal nitric oxide synthase polymorphisms and recurrent depressive disorder. J Affect Disord 129(1–3):175–182
Montesanto A, Crocco P, Tallaro F, Pisani F, Mazzei B, Mari V et al (2013) Common polymorphisms in nitric oxide synthase (NOS) genes influence quality of aging and longevity in humans. Biogerontology 14(2):177–186
Sarginson JE, Deakin JFW, Anderson IM, Downey D, Thomas E, Elliott R et al (2014) Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase (NOS1) Polymorphisms Interact with Financial Hardship to Affect Depression Risk. Neuropsychopharmacol 39(12):2857–2866
Gałecki P, Gałecka E, Maes M, Chamielec M, Orzechowska A, Bobińska K et al (2012) The expression of genes encoding for COX-2, MPO, iNOS, and sPLA2-IIA in patients with recurrent depressive disorder. J Affect Disord 138(3):360–366
Gałecki P, Maes M, Florkowski A, Lewiński A, Gałecka E, Bieńkiewicz M et al (2010) An inducible nitric oxide synthase polymorphism is associated with the risk of recurrent depressive disorder. Neurosci Lett 486(3):184–187
Lawford BR, Morris CP, Swagell CD, Hughes IP, Young RM, Voisey J (2013) NOS1AP is associated with increased severity of PTSD and depression in untreated combat veterans. J Affect Disord 147(1–3):87–93
Cheah SY, Lawford BR, Young RM, Morris CP, Voisey J (2015) Association of NOS1AP variants and depression phenotypes in schizophrenia. J Affect Disord 188:263–269
Ikenouchi-Sugita A, Yoshimura R, Kishi T, Umene-Nakano W, Hori H, Hayashi K et al (2011) Three polymorphisms of the eNOS gene and plasma levels of metabolites of nitric oxide in depressed Japanese patients: a preliminary report. Hum Psychopharmacol Clin Exp 26(7):531–534
Moraes-Neto TB, Scopinho AA, Biojone C, Corrêa FMA, Resstel LBM (2014) Involvement of dorsal hippocampus glutamatergic and nitrergic neurotransmission in autonomic responses evoked by acute restraint stress in rats. Neurosci 258:364–373
Echeverry MB, Guimaraes FS, Del Bel EA (2004) Acute and delayed restraint stress-induced changes in nitric oxide producing neurons in limbic regions. Neurosci 125(4):981–993
Zhou QG, Zhu LJ, Chen C, Wu HY, Luo CX, Chang L et al (2011) Hippocampal neuronal nitric oxide synthase mediates the stress-related depressive behaviors of glucocorticoids by downregulating glucocorticoid receptor. J Neurosci 31(21):7579–7590
Wegener G, Harvey BH, Bonefeld B, Muller HK, Volke V, Overstreet DH et al (2010) Increased stress-evoked nitric oxide signalling in the Flinders sensitive line (FSL) rat: a genetic animal model of depression. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 13(4):461–473
Filipović D, Todorović N, Bernardi RE, Gass P (2017) Oxidative and nitrosative stress pathways in the brain of socially isolated adult male rats demonstrating depressive- and anxiety-like symptoms. Brain Struct Funct 222(1):1–20
Brown GC, Neher JJ (2010) Inflammatory Neurodegeneration and Mechanisms of Microglial Killing of Neurons. Mol Neurobiol 41(2):242–247
Brown GC, Vilalta A (2015) How microglia kill neurons. Brain Res 1628:288–297
Munhoz CD, García-Bueno B, Madrigal JLM, Lepsch LB, Scavone C, Leza JC (2008) Stress-induced neuroinflammation: mechanisms and new pharmacological targets. Braz J Med Biol Res 41:1037–1046
Wang Y, Ni J, Zhai L, Gao C, Xie L, Zhao L et al (2019) Inhibition of activated astrocyte ameliorates lipopolysaccharide- induced depressive-like behaviors. J Affect Disord 242:52–59
Gądek-Michalska A, Tadeusz J, Rachwalska P, Bugajski J (2013) Cytokines, prostaglandins and nitric oxide in the regulation of stress-response systems. Pharmacological reports : PR. 65(6):1655–1662
Gądek-Michalska A, Tadeusz J, Bugajski A, Bugajski J (2019) Chronic Isolation Stress Affects Subsequent Crowding Stress-Induced Brain Nitric Oxide Synthase (NOS) Isoforms and Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) Axis Responses. Neurotox Res 36(3):523–539
Rivier C (1998) Role of Nitric Oxide and Carbon Monoxide in Modulating the ACTH Response to Immune and Nonimmune Signals. NeuroImmunoModulation 5(3–4):203–213
Gądek-Michalska A, Tadeusz J, Rachwalska P, Spyrka J, Bugajski J (2012) Effect of repeated restraint on homotypic stress-induced nitric oxide synthases expression in brain structures regulating HPA axis. Pharmacological reports : PR. 64(6):1381–1390
Vernet D, Bonavera JJ, Swerdloff RS, Gonzalez-Cadavid NF, Wang C (1998) Spontaneous Expression of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase in the Hypothalamus and Other Brain Regions of Aging Rats*. Endocrinology 139(7):3254–3261
Dinerman JL, Dawson TM, Schell MJ, Snowman A, Snyder SH (1994) Endothelial nitric oxide synthase localized to hippocampal pyramidal cells: implications for synaptic plasticity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91(10):4214–4218
Sparrow JR (1994) Inducible nitric oxide synthase in the central nervous system. J Mol Neurosci 5(4):219–229
Tanda K, Nishi A, Matsuo N, Nakanishi K, Yamasaki N, Sugimoto T et al (2009) Abnormal social behavior, hyperactivity, impaired remote spatial memory, and increased D1-mediated dopaminergic signaling in neuronal nitric oxide synthase knockout mice. Mol Brain 2(1):19
Weitzdoerfer R, Hoeger H, Engidawork E, Engelmann M, Singewald N, Lubec G et al (2004) Neuronal nitric oxide synthase knock-out mice show impaired cognitive performance. Nitric Oxide 10(3):130–140
Nelson RJ, Demas GE, Huang PL, Fishman MC, Dawson VL, Dawson TM et al (1995) Behavioural abnormalities in male mice lacking neuronal nitric oxide synthase. Nature 378(6555):383–386
Bilbo SD, Hotchkiss AK, Chiavegatto S, Nelson RJ (2003) Blunted stress responses in delayed type hypersensitivity in mice lacking the neuronal isoform of nitric oxide synthase. J Neuroimmunol 140(1–2):41–48
Juch M, Smalla KH, Kahne T, Lubec G, Tischmeyer W, Gundelfinger ED et al (2009) Congenital lack of nNOS impairs long-term social recognition memory and alters the olfactory bulb proteome. Neurobiol Learn Mem 92(4):469–484
Zhou QG, Hu Y, Hua Y, Hu M, Luo CX, Han X et al (2007) Neuronal nitric oxide synthase contributes to chronic stress-induced depression by suppressing hippocampal neurogenesis. J Neurochem 103(5):1843–1854
Sugimoto K, Iadecola C (2002) Effects of aminoguanidine on cerebral ischemia in mice: comparison between mice with and without inducible nitric oxide synthase gene. Neurosci Lett 331(1):25–28
Akasaka S, Nomura M, Nishii H, Fujimoto N, Ueta Y, Tsutsui M et al (2006) The hypothalamo-pituitary axis responses to lipopolysaccharide-induced endotoxemia in mice lacking inducible nitric oxide synthase. Brain Res 1089(1):1–9
De Luca G, Di Giorgio RM, Macaione S, Calpona PR, Di Paola ED, Costa N et al (2006) Amino acid levels in some brain areas of inducible nitric oxide synthase knock out mouse (iNOS−/−) before and after pentylenetetrazole kindling. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 85(4):804–812
Kawano T, Kunz A, Abe T, Girouard H, Anrather J, Zhou P et al (2007) iNOS-Derived NO and Nox2-Derived Superoxide Confer Tolerance to Excitotoxic Brain Injury through Peroxynitrite. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27(8):1453–1462
Montezuma K, Biojone C, Lisboa SF, Cunha FQ, Guimaraes FS, Joca SR (2012) Inhibition of iNOS induces antidepressant-like effects in mice: pharmacological and genetic evidence. Neuropharmacol 62(1):485–491
Lisboa SF, Gomes FV, Silva AL, Uliana DL, Camargo LHA, Guimarães FS, et al. Increased Contextual Fear Conditioning in iNOS Knockout Mice: Additional Evidence for the Involvement of Nitric Oxide in Stress-Related Disorders and Contribution of the Endocannabinoid System. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015;18(8).
Dere E, De Souza Silva MA, Topic B, Fiorillo C, Li J-S, Sadile AG et al (2002) Aged endothelial nitric oxide synthase knockout mice exhibit higher mortality concomitant with impaired open-field habituation and alterations in forebrain neurotransmitter levels. Genes, Brain and Behav 1(4):204–213
Frisch C, Dere E, Silva MADS, Gödecke A, Schrader J, Huston JP (2000) Superior Water Maze Performance and Increase in Fear-Related Behavior in the Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase-Deficient Mouse Together with Monoamine Changes in Cerebellum and Ventral Striatum. J Neurosci 20(17):6694–6700
Hopper RA, Garthwaite J (2006) Tonic and Phasic Nitric Oxide Signals in Hippocampal Long-Term Potentiation. J Neurosci 26(45):11513–11521
Jefferys D, Funder J (1996) Nitric oxide modulates retention of immobility in the forced swimming test in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 295(2–3):131–135
Harkin AJ, Bruce KH, Craft B, Paul IA. Nitric oxide synthase inhibitors have antidepressant-like properties in mice. 1. Acute treatments are active in the forced swim test. European Journal of Pharmacology. 1999;372(3):207–13.
Harkin A, Connor TJ, Burns MP, Kelly JP (2004) Nitric oxide synthase inhibitors augment the effects of serotonin re-uptake inhibitors in the forced swimming test. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 14(4):274–281
Gigliucci V, Buckley KN, Nunan J, O’Shea K, Harkin A (2010) A role for serotonin in the antidepressant activity of NG-Nitro-L-arginine, in the rat forced swimming test. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 94(4):524–533
Karolewicz B, Bruce KH, Lee B, Paul IA. Nitric oxide synthase inhibitors have antidepressant-like properties in mice. 2. Chronic treatment results in downregulation of cortical beta-adrenoceptors. European Journal of Pharmacology. 1999;372(3):215–20.
Volke V, Wegener G, Bourin M, Vasar E (2003) Antidepressant- and anxiolytic-like effects of selective neuronal NOS inhibitor 1-(2-trifluoromethylphenyl)-imidazole in mice. Behav Brain Res 140(1–2):141–147
Joca SR, Guimaraes FS (2006) Inhibition of neuronal nitric oxide synthase in the rat hippocampus induces antidepressant-like effects. Psychopharmacology 185(3):298–305
Silva M, Aguiar DC, Diniz CR, Guimaraes FS, Joca SR (2012) Neuronal NOS inhibitor and conventional antidepressant drugs attenuate stress-induced fos expression in overlapping brain regions. Cell Mol Neurobiol 32(3):443–453
Sales AJ, Hiroaki-Sato VA, Joca SR (2017) Participation of hippocampal nitric oxide synthase and soluble guanylate cyclase in the modulation of behavioral responses elicited by the rat forced swimming test. Behav Pharmacol 28(1):19–29
Stanquini LA, Biojone C, Guimaraes FS, Joca SR (2018) Repeated treatment with nitric oxide synthase inhibitor attenuates learned helplessness development in rats and increases hippocampal BDNF expression. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 30(3):127–136
Yazir Y, Utkan T, Aricioglu F (2012) Inhibition of Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase and Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Prevents Depression-Like Behaviour in Rats Exposed to Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 111(3):154–160
Palumbo ML, Fosser NS, Rios H, Zubilete MAZ, Guelman LR, Cremaschi GA et al (2007) Loss of hippocampal neuronal nitric oxide synthase contributes to the stress-related deficit in learning and memory. J Neurochem 102(1):261–274
Heiberg IL, Wegener G, Rosenberg R (2002) Reduction of cGMP and nitric oxide has antidepressant-like effects in the forced swimming test in rats. Behav Brain Res 134(1–2):479–484
Pereira VS, Romano A, Wegener G, Joca SR (2015) Antidepressant-like effects induced by NMDA receptor blockade and NO synthesis inhibition in the ventral medial prefrontal cortex of rats exposed to the forced swim test. Psychopharmacology 232(13):2263–2273
Pereira VS, Suavinha A, Wegener G, Joca SRL (2019) Prelimbic neuronal nitric oxide synthase inhibition exerts antidepressant-like effects independently of BDNF signalling cascades. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 31(3):143–150
Frey C, Narayanan K, McMillan K, Spack L, Gross SS, Masters BS, et al. L-thiocitrulline. A stereospecific, heme-binding inhibitor of nitric-oxide synthases. J Biol Chem. 1994;269(42):26083–91.
Wiesinger H (2001) Arginine metabolism and the synthesis of nitric oxide in the nervous system. Prog Neurobiol 64(4):365–391
Zomkowski AD, Hammes L, Lin J, Calixto JB, Santos AR, Rodrigues AL (2002) Agmatine produces antidepressant-like effects in two models of depression in mice. NeuroReport 13(4):387–391
Aricioglu F, Altunbas H (2003) Is agmatine an endogenous anxiolytic/antidepressant agent? Ann N Y Acad Sci 1009:136–140
Li YF, Gong ZH, Cao JB, Wang HL, Luo ZP, Li J (2003) Antidepressant-like effect of agmatine and its possible mechanism. Eur J Pharmacol 469(1–3):81–88
Krass M, Wegener G, Vasar E, Volke V (2008) Antidepressant-like effect of agmatine is not mediated by serotonin. Behav Brain Res 188(2):324–328
Halaris A, Zhu H, Feng Y, Piletz JE (1999) Plasma agmatine and platelet imidazoline receptors in depression. Ann N Y Acad Sci 881:445–451
Halaris A, Piletz JE (2001) Imidazoline receptors: possible involvement in the pathophysiology and treatment of depression. Hum Psychopharmacol Clin Exp 16(1):65–69
Halaris A, Piletz JE (2003) Relevance of imidazoline receptors and agmatine to psychiatry: a decade of progress. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1009:1–20
Taksande BG, Kotagale NR, Tripathi SJ, Ugale RR, Chopde CT (2009) Antidepressant like effect of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors involve modulation of imidazoline receptors by agmatine. Neuropharmacol 57(4):415–424
Ogawa T, Kimoto M, Watanabe H, Sasaoka K (1987) Metabolism of NG, NG-and NG, N’G-dimethylarginine in rats. Arch Biochem Biophys 252(2):526–537
Liebenberg N, Joca S, Wegener G (2015) Nitric oxide involvement in the antidepressant-like effect of ketamine in the Flinders sensitive line rat model of depression. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 27(2):90–96
Doucet MV, Levine H, Dev KK, Harkin A (2013) Small-molecule inhibitors at the PSD-95/nNOS interface have antidepressant-like properties in mice. Neuropsychopharmacol 38(8):1575–1584
Tillmann S, Pereira VS, Liebenberg N, Christensen AK, Wegener G (2017) ZL006, a small molecule inhibitor of PSD-95/nNOS interaction, does not induce antidepressant-like effects in two genetically predisposed rat models of depression and control animals. PLoS ONE 12(8):e0182698
Doucet MV, O’Toole E, Connor T, Harkin A (2015) Small-molecule inhibitors at the PSD-95/nNOS interface protect against glutamate-induced neuronal atrophy in primary cortical neurons. Neurosci 301:421–438
Finkel MS, Laghrissi-Thode F, Pollock BG, Rong J (1996) Paroxetine is a novel nitric oxide synthase inhibitor. Psychopharmacol Bull 32(4):653–658
Wegener G, Volke V, Harvey BH, Rosenberg R (2003) Local, but not systemic, administration of serotonergic antidepressants decreases hippocampal nitric oxide synthase activity. Brain Res 959(1):128–134
Musazzi L, Treccani G, Mallei A, Popoli M (2013) The action of antidepressants on the glutamate system: regulation of glutamate release and glutamate receptors. Biol Psychiatry 73(12):1180–1188
Chanrion B, Mannoury la Cour C, Bertaso F, Lerner-Natoli M, Freissmuth M, Millan MJ, et al. Physical interaction between the serotonin transporter and neuronal nitric oxide synthase underlies reciprocal modulation of their activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(19):8119–24.
Harkin A, Connor TJ, Walsh M, St John N, Kelly JP (2003) Serotonergic mediation of the antidepressant-like effects of nitric oxide synthase inhibitors. Neuropharmacol 44(5):616–623
Hiroaki-Sato VA, Sales AJ, Biojone C, Joca SR (2014) Hippocampal nNOS inhibition induces an antidepressant-like effect: involvement of 5HT1A receptors. Behav Pharmacol 25(3):187–196
Jesse CR, Bortolatto CF, Savegnago L, Rocha JB, Nogueira CW (2008) Involvement of L-arginine-nitric oxide-cyclic guanosine monophosphate pathway in the antidepressant-like effect of tramadol in the rat forced swimming test. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 32(8):1838–1843
Dhir A, Kulkarni SK (2007) Involvement of nitric oxide (NO) signaling pathway in the antidepressant action of bupropion, a dopamine reuptake inhibitor. Eur J Pharmacol 568(1–3):177–185
Ghasemi M, Sadeghipour H, Mosleh A, Sadeghipour HR, Mani AR, Dehpour AR (2008) Nitric oxide involvement in the antidepressant-like effects of acute lithium administration in the mouse forced swimming test. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 18(5):323–332
Ferreira FR, Oliveira AM, Dinarte AR, Pinheiro DG, Greene LJ, Silva WA Jr et al (2012) Changes in hippocampal gene expression by 7-nitroindazole in rats submitted to forced swimming stress. Genes Brain Behav 11(3):303–313
Chiavegatto S, Dawson VL, Mamounas LA, Koliatsos VE, Dawson TM, Nelson RJ (2001) Brain serotonin dysfunction accounts for aggression in male mice lacking neuronal nitric oxide synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(3):1277–1281
Kuhn DM, Aretha CW, Geddes TJ (1999) Peroxynitrite inactivation of tyrosine hydroxylase: Mediation by sulfhydryl oxidation, not tyrosine nitration. J Neurosci 19(23):10289–10294
Smith JC, Whitton PS (2000) Nitric oxide modulates N-methyl-D-aspartate-evoked serotonin release in the raphe nuclei and frontal cortex of the freely moving rat. Neurosci Lett 291(1):5–8
Trabace L, Kendrick KM (2000) Nitric oxide can differentially modulate striatal neurotransmitter concentrations via soluble guanylate cyclase and peroxynitrite formation. J Neurochem 75(4):1664–1674
Wegener G, Volke V, Rosenberg R (2000) Endogenous nitric oxide decreases hippocampal levels of serotonin and dopamine in vivo. Br J Pharmacol 130(3):575–580
Segieth J, Pearce B, Fowler L, Whitton PS (2001) Regulatory role of nitric oxide over hippocampal 5-HT release in vivo. Naunyn Schmiedebergs ArchPharmacol. 363(3):302–306
Wegener G, Volke V, Rosenberg R. Endogenous nitric oxide decreases the release of serotonin in the hippocampus: An in vivo microdialysis study. Nord J Psychiat. 2000;54(2):87-.
Strasser A, McCarron RM, Ishii H, Stanimirovic D, Spatz M (1994) L-arginine induces dopamine release from the striatum in vivo. NeuroReport 5(17):2298–2300
Asano S, Matsuda T, Nakasu Y, Maeda S, Nogi H, Baba A (1997) Inhibition by nitric oxide of the uptake of [3H]serotonin into rat brain synaptosomes. JpnJ Pharmacol. 75(2):123–128
Bryan-Lluka LJ, Papacostas MH, Paczkowski FA, Wanstall JC (2004) Nitric oxide donors inhibit 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) uptake by the human 5-HT transporter (SERT). Br J Pharmacol 143(1):63–70
Lu Y, Simpson KL, Weaver KJ, Lin RC (2010) Coexpression of serotonin and nitric oxide in the raphe complex: cortical versus subcortical circuit. Anat Rec (Hoboken) 293(11):1954–1965
Manji HK, Moore GJ, Rajkowska G, Chen G (2000) Neuroplasticity and cellular resilience in mood disorders. Mol Psychiatry 5(6):578–593
Manji HK, Drevets WC, Charney DS (2001) The cellular neurobiology of depression. NatMed. 7(5):541–547
Levy MJF, Boulle F, Steinbusch HW, van den Hove DLA, Kenis G, Lanfumey LJP (2018) Neurotrophic factors and neuroplasticity pathways in the pathophysiology and treatment of depression. 235(8):2195–2220
Leal G, Bramham CR, Duarte CB. Chapter Eight - BDNF and Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity. In: Litwack G, editor. Vitam Horm. 104: Academic Press; 2017. p. 153–95.
Canossa M, Giordano E, Cappello S, Guarnieri C, Ferri S (2002) Nitric oxide down-regulates brain-derived neurotrophic factor secretion in cultured hippocampal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(5):3282–3287
Pinnock SB, Herbert J (2008) Brain-derived neurotropic factor and neurogenesis in the adult rat dentate gyrus: interactions with corticosterone. Eur J Neurosci 27(10):2493–2500
Salehpour M, Khodagholi F, Zeinaddini Meymand A, Nourshahi M, Ashabi G (2017) Exercise training with concomitant nitric oxide synthase inhibition improved anxiogenic behavior, spatial cognition, and BDNF/P70S6 kinase activation in 20-month-old rats. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 43(1):45–53
Xiong H, Yamada K, Han D, Nabeshima T, Enikolopov G, Carnahan J et al (1999) Mutual regulation between the intercellular messengers nitric oxide and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in rodent neocortical neurons. 11(5):1567–1576
Silva Pereira V, Elfving B, Joca SRL, Wegener G (2017) Ketamine and aminoguanidine differentially affect Bdnf and Mtor gene expression in the prefrontal cortex of adult male rats. Eur J Pharmacol 815:304–311
Joca S, Biojone C, Casarotto P, Montezuma K, Cunha F, Guimaraes F (2012) BDNF-TrkB signaling is involved in the antidepressant-like effect induced by genetic deletion of iNOS. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 15:44–45
Yuen EC, Gunther EC, Bothwell M (2000) Nitric oxide activation of TrkB through peroxynitrite. 11(16):3593–3597
Kolarow R, Kuhlmann CR, Munsch T, Zehendner C, Brigadski T, Luhmann HJ et al (2014) BDNF-induced nitric oxide signals in cultured rat hippocampal neurons: time course, mechanism of generation, and effect on neurotrophin secretion. Front Cell Neurosci 8(323):323
Biojone C, Casarotto PC, Joca SR, Castren E (2015) Interplay Between Nitric Oxide and Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Neuronal Plasticity. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 14(8):979–987
Cheng A, Wang S, Cai J, Rao MS, Mattson MP (2003) Nitric oxide acts in a positive feedback loop with BDNF to regulate neural progenitor cell proliferation and differentiation in the mammalian brain. DevBiol. 258(2):319–333
Mizoguchi Y, Kato TA, Seki Y, Ohgidani M, Sagata N, Horikawa H et al (2014) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) induces sustained intracellular Ca2+ elevation through the up-regulation of surface transient receptor potential 3 (TRPC3) channels in rodent microglia. J Biol Chem 289(26):18549–18555
Cai C-Y, Chen C, Zhou Y, Han Z, Qin C, Cao B et al (2018) PSD-95-nNOS Coupling Regulates Contextual Fear Extinction in the Dorsal CA3. Sci Rep 8(1):12775
Manucha W (2017) Mitochondrial dysfunction associated with nitric oxide pathways in glutamate neurotoxicity. Clínica e Investigación en Arteriosclerosis. 29(2):92–97
Sunico CR, Portillo F, Gonzalez-Forero D, Moreno-Lopez B (2005) Nitric-oxide-directed synaptic remodeling in the adult mammal CNS. J Neurosci 25(6):1448–1458
Joca SR, Guimaraes FS, Del-Bel E (2007) Inhibition of nitric oxide synthase increases synaptophysin mRNA expression in the hippocampal formation of rats. Neurosci Lett 421(1):72–76
Nikonenko I, Boda B, Steen S, Knott G, Welker E, Muller D. PSD-95 promotes synaptogenesis and multiinnervated spine formation through nitric oxide signaling. 2008;183(6):1115–27.
Gray WP, Cheung A. Chapter Four - Nitric Oxide Regulation of Adult Neurogenesis. In: Litwack G, editor. Vitam Horm. 96: Academic Press; 2014. p. 59–77.
Chong CM, Ai N, Ke M, Tan Y, Huang Z, Li Y et al (2018) Roles of Nitric Oxide Synthase Isoforms in Neurogenesis. Mol Neurobiol 55(3):2645–2652
Duman RS, Malberg J, Nakagawa S (2001) Regulation of Adult Neurogenesis by Psychotropic Drugs and Stress. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 299(2):401–407
Duman RS, Nakagawa S, Malberg J (2001) Regulation of Adult Neurogenesis by Antidepressant Treatment. Neuropsychopharmacol 25(6):836–844
Spalding KL, Bergmann O, Alkass K, Bernard S, Salehpour M, Huttner HB et al (2013) XDynamics of hippocampal neurogenesis in adult humans. Cell 153(6):X1219–X1227
Santarelli L, Saxe M, Gross C, Surget A, Battaglia F, Dulawa S et al (2003) Requirement of Hippocampal Neurogenesis for the Behavioral Effects of Antidepressants. Science 301(5634):805–809
Ehninger D, Kempermann G (2008) Neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus. Cell Tissue Res 331(1):243–250
Romero-Grimaldi C, Moreno-López B, Estrada C (2008) Age-dependent effect of nitric oxide on subventricular zone and olfactory bulb neural precursor proliferation. J Comp Neurol 506(2):339–346
Shariful Islam ATM, Kuraoka A, Kawabuchi M (2003) Morphological basis of nitric oxide production and its correlation with the polysialylated precursor cells in the dentate gyrus of the adult guinea pig hippocampus. Anat Sci Int 78(2):98–103
Luo C-X, Jin X, Cao C-C, Zhu M-M, Wang B, Chang L et al (2010) BIdirectional Regulation of Neurogenesis by Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase Derived from Neurons and Neural Stem Cells. 28(11):2041–2052
Matarredona ER, Murillo-Carretero M, Moreno-López B, Estrada C (2004) Nitric oxide synthesis inhibition increases proliferation of neural precursors isolated from the postnatal mouse subventricular zone. Brain Res 995(2):274–284
Zhu XJ, Hua Y, Jiang J, Zhou QG, Luo CX, Han X et al (2006) Neuronal nitric oxide synthase-derived nitric oxide inhibits neurogenesis in the adult dentate gyrus by down-regulating cyclic AMP response element binding protein phosphorylation. Neurosci 141(2):827–836
Packer MA, Stasiv Y, Benraiss A, Chmielnicki E, Grinberg A, Westphal H et al (2003) Nitric oxide negatively regulates mammalian adult neurogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100(16):9566–9571
Park S-Y, Kang M-J, Han J-SJMN. Neuronal NOS Induces Neuronal Differentiation Through a PKCα-Dependent GSK3β Inactivation Pathway in Hippocampal Neural Progenitor Cells. 2017;54(7):5646–56.
Islam ATMS, Kuraoka A, Kawabuchi MJASI (2003) Morphological basis of nitric oxide production and its correlation with the polysialylated precursor cells in the dentate gyrus of the adult guinea pig hippocampus. 78(2):98–103
Izumi Y, Zorumski CF (1993) Nitric oxide and long-term synaptic depression in the rat hippocampus. NeuroReport 4(9):1131–1134
Zorumski CF, Izumi Y (1993) Nitric oxide and hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Biochem Pharmacol 46(5):777–785
Hölscher C (1997) Nitric oxide, the enigmatic neuronal messenger: its role in synaptic plasticity. Trends Neurosci 20(7):298–303
Hardingham N, Dachtler J, Fox K (2013) The role of nitric oxide in pre-synaptic plasticity and homeostasis. Front Cell Neurosci 7(190):190
Nikonenko I, Nikonenko A, Mendez P, Michurina TV, Enikolopov G, Muller D (2013) Nitric oxide mediates local activity-dependent excitatory synapse development. 110(44):E4142–E4151
Rabinovich D, Yaniv Shiri P, Alyagor I, Schuldiner O (2016) Nitric Oxide as a Switching Mechanism between Axon Degeneration and Regrowth during Developmental Remodeling. Cell 164(1):170–182
Ribeiro DE, Roncalho AL, Glaser T, Ulrich H, Wegener G, Joca S (2019) P2X7 Receptor Signaling in Stress and Depression. Int J Mol Sci 20(11):2778
Miller AH, Maletic V, Raison CL (2009) Inflammation and Its Discontents: The Role of Cytokines in the Pathophysiology of Major Depression. Biol Psychiatry 65(9):732–741
Suneson K, Lindahl J, Chamli Hårsmar S, Söderberg G, Lindqvist D (2021) Inflammatory Depression—Mechanisms and Non-Pharmacological Interventions. Int J Mol Sci 22(4):1640
Dantzer R, Kelley KW (2007) Twenty years of research on cytokine-induced sickness behavior. Brain Behav Immun 21:153–160
Liu JJ, Wei YB, Strawbridge R, Bao Y, Chang S, Shi L et al (2020) Peripheral cytokine levels and response to antidepressant treatment in depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol Psychiatry 25(2):339–350
Yuan Z, Chen Z, Xue M, Zhang J, Leng L (2020) Application of antidepressants in depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of clinical neuroscience : official journal of the Neurosurgical Society of Australasia. 80:169–181
Inserra A, Mastronardi CA, Rogers G, Licinio J, Wong M-L (2019) Neuroimmunomodulation in Major Depressive Disorder: Focus on Caspase 1, Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase, and Interferon-Gamma. Mol Neurobiol 56(6):4288–4305
Acknowledgements
This study was financed by Aarhus University Research Foundation (AUFF starting grant to SJ), and Independent Research Fund Denmark (grant 8020-00310B to GW).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
GW reports having received lecture/consultancy fees/research support from H. Lundbeck A/S, Servier SA, Astra Zeneca AB, Eli Lilly A/S, Sun Pharma Pty Ltd, Pfizer Inc, Shire A/S, HB Pharma A/S, Alkermes Inc, Mundipharma International Ltd., J&J Inc., and Jannsen Pharma A/S. SJ reports no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Wegener, G., Joca, S.R.L. (2023). Nitric Oxide in Major Depressive Disorder. In: Ray, A., Gulati, K. (eds) Nitric Oxide: From Research to Therapeutics. Advances in Biochemistry in Health and Disease, vol 22. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-24778-1_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-24778-1_15
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-24777-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-24778-1
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)