Abstract
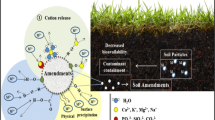
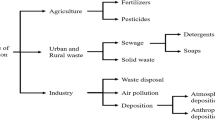
Heavy metals and metalloids are hazardous chemicals that very difficult undergo microbial or chemical degradation. Their presence in natural environment results mainly from anthropogenic sources, such as agriculture, oil and gas production, mining industry, and military activities. Soil pollution with heavy metals is recognized as “hot spots” posing a risk to the environment, agricultural production, food safety, and human health. Various technologies have been developed to reduce the potential for the release of metal ions into the environment and to scale down changes in the land use pattern. In situ remediation of contaminated soils by supplementing amendments is considered as a sound alternative both environmentally and economically. This method provides a long-term, relatively cheap remediation solution by reducing metal mobility and availability to plants. As steams from literature, amendments’ application can improve soil biological, chemical and physical properties and consequently enhance the plant growth. The present chapter presents the current trends (from the last decade) in the remediation of soil contaminated with heavy metal ions by their immobilization with various by-products and low-cost materials. The focus was put on the factors which determine the metal binding and transformation into more stable forms. An assessment of the effectiveness of these amendments on the soil properties and the phytoavailability to plants has been made as well.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adewuyi YG (2021) Recent advances in fly-ash-based geopolymers: potential on the utilization for sustainable environmental remediation. ACS Omega 6:15532–15542
Andrunik M, Wołowiec M, Wojnarski D, Zelek-Pogudz S, Bajda T (2020) Transformation of Pb, Cd, and Zn minerals using phosphates. Minerals 10:342
Ayaz M, Stulpinaite U, Feiziene D, Tilvikiene V, Akthar K, Baltenaite-Gedien E, Striugas N, Rehmani U, Alam S, Iqbal R, Toleikiene M, Doyeni M (2021) Pig manure digestate-derived biochar for soil management and crop cultivation in heavy metals contaminated soil. Soil Use Manage. https://doi.org/10.1111/sum.12773
Bian R, Chen D, Liu X, Cui L, Li L, Pan G, Xie D, Zheng J, Zhang X, Zheng J (2013) Biochar soil amendment as a solution to prevent Cd-tainted rice from China: results from a cross-site field experiment. Ecol Eng 58:378–383
Cakmak I, Marschner H (1992) Magnesium deficiency and high light intensity enhance activities of superoxide dismutase, ascorbate peroxidase, and glutathione reductase in bean leaves. Plant Physiol 98:1222–1227
Chatzistathis T, Papaioannou E, Giannakoula A, Papadakis IE (2021) Zeolite and vermiculite as inorganic soil amendments modify shoot-root allocation, mineral nutrition, photosystem II activity and gas exchange parameters of chestnut (Castanea sativa Mill) plants. Agronomy 11:109
Chen X, He HZ, Chen GK, Li HS (2020) Effects of biochar and crop straws on the bioavailability of cadmium in contaminated soil. Sci Rep 10:9528
Contin M, Miho L, Pellegrini E, Gjoka F, Shkurta E (2019) Effects of natural zeolites on ryegrass growth and bioavailability of Cd, Ni, Pb, and Zn in an Albanian contaminated soil. J Soils Sediments 19:4052–4062
Correia AAS, Matos MPSR, Gomes AR, Rasteiro MG (2020) Immobilization of heavy metals in contaminated soils—performance assessment in conditions similar to a real scenario. Appl Sci 10:7950
Dhaliwal SS, Singh J, Taneja PK, Mandal A (2020) Remediation techniques for removal of heavy metals from the soil contaminated through different sources: a review. Environ Sci Poll Res. 27:1319–1333
Dzionek A, Wojcieszyńska D, Guzik U (2016) Natural carriers in bioremediation: a review. Electr J Biotechnol 23:28–36
Eleswed BI (2020) Chemical evaluation of immobilization of wastes containing Pb, Cd, Cu and Zn in alkali-activated materials: a critical review. J Environ Chem Eng 8:104–194
European Biochar Certificate, Guidelines for a Sustainable Production of Biochar (EBC, 2012) (2012). http://www.europeanbiochar.org/en/download
Głąb T, Gondek K, Mierzwa-Hersztek M (2021) Biological effects of biochar and zeolite used for remediation of soil contaminated with toxic heavy metals. Sci Rep 11:6998
Guo M, Song W, Tian J (2020) Biochar-facilitated soil remediation. Mechanisms and efficacy variations. Front Environ Sci 8:1–23
Hamid Y, Tang L, Wang X, Hussain B, Yaseen M, Aziz MZ, Yang X (2018) Immobilization of cadmium and lead in contaminated paddy field using inorganic and organic additives. Sci Rep 8(1):17839
Hamid Y, Tang L, Hussain B, Usman M, Gurajal HK, Rashid MS, Yang X (2019) Efficiency of, biochar, Fe containing biochar and composite amendments for Cd and Pb immobilization in a co-contaminated alluvial soil. Environ Poll 196:113609
Hannan F, Huang Q, Farooq MA, Ayyaz A, Ma JY, Zhang N, Ali B, Deyett E, Zhou WJ, Islam F (2021a) Organic and inorganic amendments for the remediation of nickel contaminated soil and its improvement on Brassica napus growth and oxidative defense. J Hazard Mat 416:125921
Hannan F, Islam F, Huang Q, Farooq MA, Ayyaz A, Fang RY, Ali B, Xie XH, Zhou WJ (2021b) Interactive effects of biochar and mussel shell activated concoctions on immobilization of nickel and their amelioration on the growth of rapeseed in contaminated aged soil. Chemosphere 282:130897
Holland J, Bennet A, Newton A, White P, McKenzie B, Georg T, Pakeman R, Bailey J, Fornara D, Hayes R (2018) Liming impacts on soils, crops and biodiversity in the UK: a review. Sci Total Environ 610:316–332
Hu XM, Yuan XS, Dong L (2014) Coal fly ash and straw immobilize Cu, Cd and Zn from mining wasteland. Environ Chem Lett 12(2):289–295
Huang GY, Su XJ, Rizwan MS, Zhu YF, Hu HQ (2016) Chemical immobilization of Pb, Cu, and Cd by phosphatematerials and calciumcarbonate in contaminated soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:16845–16856
Irfan M, Mudassir M, Khan MJ, Dawar KM, Muhammad D, Mian IA, Ali W, Fahad S, Saud S, Hayat Z, Nawaz T, Khan SA, Alam S, Ali B, Banout J, Ahmed S, Mubeen S, Danish S, Datta R, Elgorban AM, Dewil R (2021) Heavy metals immobilization and improvement in maize (Zea mays L.) growth amended with biochar and compost. Sci Rep 11(1):18416
Jakkula V, Wani SP (2018) Zeolites: potential soil amendments for improving nutrient and water use efficiency and agriculture productivity. Sci Rev Chem Commun 8(1):119
Kabata-Pendias A (2011) Trace elements in soils and plants, 4th edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Kamari A, Putra W, Yusoff S, Ishak C, Hashim N, Mohamed A, Isa I, Bakar S (2015) Immobilisation of Cu, Pb and Zn in scrap metal yard soil using selected waste materials. Bull Environ Contamin Toxicol 95(6):790–795
Li YL, Yu H, Liu LN, Yu HB (2021) Application of co-pyrolysis biochar for the adsorption and immobilization of heavy metals in contaminated environmental substrates. J Hazard Mat 420:126655
Liang X, Han J, Xu Y, Sun Y, Wang L, Tan X (2014) In situ field-scale remediation of Cd polluted paddy soil using sepiolite and palygorskite. Geoderma 235:9–18
Liu L, Li JW, Wu GH, Shen HT, Fu GZ, Wang YF (2021) Combined effects of biochar and chicken manure on maize (Zea mays L.) growth, lead uptake and soil enzyme activities under lead stress. PEERJ 9:11754
Lwin CS, Seo BH, Kim HU, Owens G, Kim KR (2018) Application of soil amendments to contaminated soils for heavy metal immobilization and improved soil quality—a critical review. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 64(2):156–167
Mahmoud E, Abd E-K (2015) Heavy metal immobilization in contaminated soils using phosphogypsum and rice straw compost. Land Degrad Develop 26(8):819–824
Malik KM, Khan KS, Rukh S, Khan A, Akbar S, Billah M, Bashir S, Danish S, Alwahibi MS, Elshikh MS, Al-Ghamdi AA, Mustafa AMA (2021) Immobilization of Cd, Pb and Zn through organic amendments in wastewater irrigated soils. Sustainability 13(4):2392
Matłok M, Petrus R, Warchoł JK (2015) Equilibrium study of heavy metals adsorption on kaolin. Ind Eng Chem Res 54:6975–6984
Mondal SK, Welz A, Rezaei F, Kumar A, Okoronkwo MU (2020) Structure–property relationship of geopolymers for aqueous Pb removal. ACS Omega 5(34):21689–21699
Ogundiran MB, Lawal OO, Adejumo SA (2015) Stabilisation of Pb in Pb smelting slag-contaminated soil by compost-modified biochars and their effects on maize plant growth. J Environ Protect 6:771–780
Palansooriya KN, Shaheen SM, Chen SS, Tsang DCW, Hashimoto Y, Hou D, Bolan NS, Rinklebe J, Ok YS (2020) Soil amendments for immobilization of potentially toxic elements in contaminated soils: a critical review. Environ Int 134:105046
Parmar S, Singh V, Sharma VK, Yadav BK, Kharwar RN (2022) Effect of vermiculite soil amendment on immobilization of selected heavy metals of rhizospheric zone of maize. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 53(3):384–395
Pei PG, Xu YM, Zheng SN, Liang XF, Sun YB, Lin DS, Wang L (2021) The use of bentonite and organic amendments for remediation of Cd contaminated fields: an environmental perspective. Land Degrad Develop 32(13):3639–3652
Provis JL (2014) Geopolymers and other alkali activated materials: why, how, and what? Mater Struct 47:11–25
Qin C, Yuan X, Xiong T, Zen TY, Wang H (2020) Physicochemical properties, metal availability and bacterial community structure in heavy metal-polluted soil remediated by montmorillonite-based amendments. Chemosphere 261:128010
Quoc TN, Nejad ZD, Jung MC (2021) Effect of commercial amendments on immobilization of arsenic, copper, and zinc in contaminated soil: comprehensive assessing to plant uptake combined with a microbial community approach. Minerals 11(10):1143
Radziemska M, Gusiatin ZM, Mazur Z, Hammerschmiedt T, Bęś A, Kintl A, Vasinova GM, Holatko J, Blazejczyk A, Kumar V, Brtnicky M (2022) Biochar-assisted phytostabilization for potentially toxic element immobilization. Sustainability 14:445
Rodríguez-Eugenio N, McLaughlin M, Pennock D (2018) Soil pollution: a hidden reality. FAO, Rome, p 142
Rozek P, Florek P, Król M, Mozgawa W (2021) Immobilization of heavy metals in boroaluminosilicate geopolymers. Materials 14:214
Seshadri B, Bolan N, Choppala G, Kunhikrishnan A, Sanderson P, Wang H, Currie LD, Tsang D, Ok YS, Kim K (2017) Potential value of phosphate compounds in enhancing immobilization and reducing bioavailability of mixed heavy metal contaminants in shooting range soil. Chemosphere 184:197–206
Shah MP (2021a) Removal of emerging contaminants through microbial processes. Springer
Shah MP (2021b) Removal of refractory pollutants from wastewater treatment plants. CRC Press
Shaheen SM, Rinklebe J (2014) Impact of emerging and low cost alternative amendments on the (im)mobilization and phytoavailability of Cd and Pb in a contaminated floodplain soil. Ecolog Eng 74:319–326
Shaikh SMR, Nasser MS, Hussein I, Benamor A, Onaizi SA, Qiblawey H (2017) Influence of polyelectrolytes and other polymer complexes on the flocculation and rheological behaviors of clay minerals: a comprehensive review. Sep Pur Technol 187:137–161
Shan R, Li W, Chen Y, Sun X (2020) Effects of Mg-modified biochar on the bioavailability of cadmium in soil. BioResources 15(4):8008–8025
Shao HJ, Wei YF, Wei CJ, Zhang FP, Li FS (2021) Insight into cesium immobilization in contaminated soil amended with biochar, incinerated sewage sludge ash and zeolite. Environ Technol Innov 23:101587
Singh BP, Cowie AL, Smernik RJ (2012) Biochar carbon stability in a clayey soil as a function of feedstock and pyrolysis temperature. Environ Sci Technol 46:11770–11778
Siyal AA, Shamsuddin MR, Khan MI, Rabat NE, Zulfiqar M, Man Z, Siame J, Azizli KA (2018) A review on geopolymers as emerging materials for the adsorption of heavy metals and dyes. J Environ Manage 224:327–339
Tang B, Xu HP, Song FM, Ge HG, Chen L, Yue SY, Yang WS (2022) Effect of biochar on immobilization remediation of Cd center dot contaminated soil and environmental quality. Environ Res 204:111840
Tóth G, Hermann T, Da Silva MR, Montanarella L (2016) Heavy metals in agricultural soils of the European Union with implications for food safety. Environ Internat 88:299–309
Vitale E, Russo G, Dell’Agli G, Ferone C, Bartolomeo C (2017) Mechanical behaviour of soil improved by alkali activated binders. Environments 4:80
Vrinceanu NO, Motelică DM, Dumitru M, Calciu I, Tănase V, Preda M (2019) Assessment of using bentonite, dolomite, natural zeolite and manure for the immobilization of heavy metals in a contaminated soil: the Copșa Mică case study. CATENA 176:336–342
Wang FY, Zhang SQ, Cheng P, Zhang SW, Sun YH (2020) Effects of soil amendments on heavy metal immobilization and accumulation by maize grown in a multiple-metal-contaminated soil and their potential for safe crop production. Toxics 8(4):102
Wu D, Huang Y, Xiao G, Li X, Yao X, Deng Z, Tan R (2021) In situ synthesis of zeolites by geopolymerization with NaOH/KOH mixed solution and their potential application for Cd(II) immobilization in paddy soil. Clay Miner 56:156–167
Xia Y, Li Y, Sun YT, Miao W, Liu ZG (2021) Co-pyrolysis of corn stover with industrial coal ash for in situ efficient remediation of heavy metals in multi-polluted soil. Environ Pollut 289:117840
Xu P, Sun CX, Ye XZ, Xiao WD, Zhang Q, Wang Q (2016). The effect of biochar and crop straws on heavy metal bioavailability and plant accumulation in a Cd and Pb polluted soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 132:94–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.05.031
Xu C, Zhao J, Yang W, He L, Wei W, Tan X, Wang J, Lin A (2020) Evaluation of biochar pyrolyzed from kitchen waste, corn straw, and peanut hulls on immobilization of Pb and Cd in contaminated soil. Environ Pollut 261:114133
Zhou C, Yuan H, Ning C, Li S, Xia Z, Zhu M, Ma Q, Yu W (2020) Evaluation of different types and amounts of amendments on soil Cd immobilization and its uptake to wheat. Environ Manag 65:818–828
Acknowledgements
This chapter was prepared in the framework of the project entitled “Biomass valorization to enhance efficiency of toxic metals bioremediation from military and industry areas” financed by OPCW (No: L/ICA/ICB-105/21, The Hague, The Netherlands, 31.12.2021–31.12.2023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Michalak, I., Warchoł, J. (2023). Remediation of Soil Contaminated with Heavy Metals by Immobilization with Organic and Inorganic Amendments. In: Shah, M.P. (eds) Modern Approaches in Waste Bioremediation. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-24086-7_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-24086-7_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-24085-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-24086-7
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)