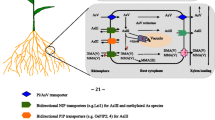
Abstract
Rice is the staple diet for more than 3.5 billion people around the world. Elevation of arsenic (As) in paddy rice ecosystems has become an environmental, economic, and public concern due to its adverse consequences on global rice production, food safety, and human health. Mining exploitation, weathering of As-bearing minerals, dissolution of aquifer sediments, and As-contaminated groundwater irrigation have extensively contributed to the contamination of paddy soil by As in high levels. Speciation, mobility and sequestration of As in paddy soil–water interfaces are controlled by iron (Fe) plaque formation, redox sensitive mineral surfaces (Fe and Mn), organic matter and competing substances (PO\(_{4}^{3-}\) and Si(OH)4). During flooding season, paddy soil porewater is contaminated with high concentrations of inorganic As species, particularly by more toxic arsenite (As(III)) as result of arsenate (As(V)) reduction under anaerobic conditions. Microorganisms play a crucial role in As speciation dynamics promoting redox transformation, methylation and volatilization processes. Various metabolic pathways, including As(V) reduction, As(III) efflux, and As(III)-thiol complexation govern As uptake, translocation, and loading into rice grains. The translocation of As from rice root to shoot leads to the accumulation of toxic As species in grains affecting rice quality and yield. The worst scenario of grain As is associated with the human exposure to high amounts of As via consumption of As-contaminated rice and related food products. Hence, this chapter provides an overview of (i) As speciation and transformation dynamics, (ii) As uptake mechanisms from root to shoot, (iii) As metabolic pathways over root, shoot and grain loading, and (iv) recommendations for future research. Such a widespread understanding of As dynamics in paddy rice ecosystems is crucial to develop sustainable As mitigation strategies and alleviate adverse impacts on global food safety and human health.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abedin M, Cotter-Howells J and Meharg AA (2002). Arsenic uptake and accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) irrigated with contaminated water. Plant Soil 240(2):311–319
Ackerman AH, Creed PA, Parks AN et al (2005) Comparison of a chemical and enzymatic extraction of arsenic from rice and an assessment of the arsenic absorption from contaminated water by cooked rice. Environ Sci Technol 39(14):5241–5246
Ahmed ZU, Panaullah GM, Gauch H et al (2011) Genotype and environment effects on rice (Oryza sativa L.) grain arsenic concentration in Bangladesh. Plant Soil 338(1):367–382
Althobiti RA, Sadiq NW, Beauchemin D (2018) Realistic risk assessment of arsenic in rice. Food Chem 257:230–236
Bachate S, Cavalca L, Andreoni V (2009) Arsenic-resistant bacteria isolated from agricultural soils of Bangladesh and characterization of arsenate-reducing strains. J Appl Microbiol 107(1):145–156
Bhattacharya P, Welch AH, Stollenwerk KG et al (2007) Arsenic in the environment: biology and chemistry. Elsevier 379:109–120
Bhattacharya P, Samal A, Majumdar J et al (2010a) Accumulation of arsenic and its distribution in rice plant (Oryza sativa L.) in Gangetic West Bengal, India. Paddy Water Environ 8(1):63–70
Bhattacharya P, Samal A, Majumdar J et al (2010b) Accumulation of arsenic and its distribution in rice plant (Oryza sativa L.) in Gangetic West Bengal, India. Paddy Water Environ 8(1):63–70
Biswas A, Biswas S, Santra SC (2014) Arsenic in irrigated water, soil, and rice: perspective of the cropping seasons. Paddy Water Environ 12(4):407–412
Burton ED, Johnston SG, Kocar BD (2014) Arsenic mobility during flooding of contaminated soil: the effect of microbial sulfate reduction. Environ Sci Technol 48(23):13660–13667
Carey A-M, Scheckel KG, Lombi E et al (2010) Grain unloading of arsenic species in rice. Plant Physiol 152(1):309–319
Chandrashekhar A, Chandrasekharam D, Farooq S (2016) Contamination and mobilization of arsenic in the soil and groundwater and its influence on the irrigated crops, Manipur Valley India. Environ Earth Sci 75(2):1–15
Chao D-Y, Chen Y, Chen J et al (2014) Genome-wide association mapping identifies a new arsenate reductase enzyme critical for limiting arsenic accumulation in plants. PLoS Biol 12(12):e1002009
Chen Y, Moore KL, Miller AJ et al (2015) The role of nodes in arsenic storage and distribution in rice. J Exp Bot 66(13):3717–3724
Chen H-L, Lee C-C, Huang W-J et al (2016a) Arsenic speciation in rice and risk assessment of inorganic arsenic in Taiwan population. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(5):4481–4488
Chen Z, Wang Y, Xia D et al (2016b) Enhanced bioreduction of iron and arsenic in sediment by biochar amendment influencing microbial community composition and dissolved organic matter content and composition. J Hazard Mater 311:20–29
Chen P, Li J, Wang H-Y et al (2017a) Evaluation of bioaugmentation and biostimulation on arsenic remediation in soil through biovolatilization. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(27):21739–21749
Chen Y, Sun S-K, Tang Z et al (2017b) The Nodulin 26-like intrinsic membrane protein OsNIP3; 2 is involved in arsenite uptake by lateral roots in rice. J Exp Bot 68(11):3007–3016
Chen C, Yang B, Shen Y et al (2021) Sulfate addition and rising temperature promote arsenic methylation and the formation of methylated thioarsenates in paddy soils. Soil Biol Biochem 154:108129
Chen C, Yang B, Gao A et al (2022a) Suppression of methanogenesis in paddy soil increases dimethylarsenate accumulation and the incidence of straighthead disease in rice. Soil Biol Biochem 169:108689
Chen M, Liu Y, Zhang D et al (2022b) Remediation of arsenic-contaminated paddy soil by iron oxyhydroxide and iron oxyhydroxide sulfate-modified coal gangue under flooded condition. Sci Total Environ 804:150199
Chhabra R, Goyal P, Singh T et al (2021). Understanding straighthead: a complex physiological disorder of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Acta Physiol Plant 43(10):1–14
Colmer T (2002) Aerenchyma and an inducible barrier to radial oxygen loss facilitate root aeration in upland, paddy and deep‐water rice (Oryza sativa L.). Ann Bot 91(2):301–309
Dahal BM, Fuerhacker M, Mentler A et al (2008) Arsenic contamination of soils and agricultural plants through irrigation water in Nepal. Environ Pollut 155(1):157–163
Dai J, Chen C, Gao A-X et al (2021) Dynamics of dimethylated monothioarsenate (DMMTA) in paddy soils and its accumulation in rice grains. Environ Sci Technol 55(13):8665–8674
Dai J, Tang Z, Gao AX et al (2022) Widespread occurrence of the highly toxic dimethylated monothioarsenate (DMMTA) in rice globally. Environ Sci Technol 56(6):3575–3586
Das S, Jean J-S, Chou M-L et al (2016) Arsenite-oxidizing bacteria exhibiting plant growth promoting traits isolated from the rhizosphere of Oryza sativa L.: implications for mitigation of arsenic contamination in paddies. J Hazard Mater 302:10–18
Dittmar J, Voegelin A, Roberts LC et al (2007) Spatial distribution and temporal variability of arsenic in irrigated rice fields in Bangladesh. 2. Paddy soil. Environ Sci Technol 41(17):5967–5972
Dittmar J, Voegelin A, Maurer F et al (2010) Arsenic in soil and irrigation water affects arsenic uptake by rice: complementary insights from field and pot studies. Environ Sci Technol 44(23):8842–8848
Dong DT, Yamaguchi N, Makino T et al (2014) Effect of soil microorganisms on arsenite oxidation in paddy soils under oxic conditions. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 60(3):377–383
Duan G-L, Hu Y, Schneider S et al (2015) Inositol transporters AtINT2 and AtINT4 regulate arsenic accumulation in Arabidopsis seeds. Nat Plants 2(1):1–6
Dwivedi S, Tripathi R, Tripathi P et al (2010) Arsenate exposure affects amino acids, mineral nutrient status and antioxidants in rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes. Environ Sci Technol 44(24):9542–9549.
Fleck AT, Mattusch J, Schenk MK (2013) Silicon decreases the arsenic level in rice grain by limiting arsenite transport. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 176(5):785–794
Fu Y, Chen M, Bi X et al (2011) Occurrence of arsenic in brown rice and its relationship to soil properties from Hainan Island. China. Environ Pollut 159(7):1757–1762
Geng A, Wang X, Wu L et al (2017a) Arsenic accumulation and speciation in rice grown in arsanilic acid-elevated paddy soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 137:172–178
Gu YD, Van Nostrand J, Wu L et al (2017) Bacterial community and arsenic functional genes diversity in arsenic contaminated soils from different geographic locations. PloS One 12(5):e0176696
Guo W, Zhang J, Teng M et al (2009) Arsenic uptake is suppressed in a rice mutant defective in silicon uptake. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 172(6):867–874
Halim M, Majumder R, Zaman M (2015) Paddy soil heavy metal contamination and uptake in rice plants from the adjacent area of Barapukuria coal mine, northwest Bangladesh. Arab J Geosci 8(6):3391–3401
Herath I, Vithanage M, Bundschuh J et al (2016) Natural arsenic in global groundwaters: distribution and geochemical triggers for mobilization. Curr Pollut Rep 2(1):68–89
Herath I, Kumarathilaka P, Bundschuh J et al (2020a) A fast analytical protocol for simultaneous speciation of arsenic by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC) hyphenated to inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) as a modern advancement in liquid chromatography approaches. Talanta 208:120457
Herath I, Zhao F-J, Bundschuh J et al (2020b) Microbe mediated immobilization of arsenic in the rice rhizosphere after incorporation of silica impregnated biochar composites. J Hazard Mater 398:123096
Horner NS, Beauchemin D (2013a) The effect of cooking and washing rice on the bio-accessibility of As, Cu, Fe, V and Zn using an on-line continuous leaching method. Anal Chim Acta 758:28–35
Hossain M, Jahiruddin M, Panaullah G et al (2008a) Spatial variability of arsenic concentration in soils and plants, and its relationship with iron, manganese and phosphorus. Environ Pollut 156(3):739–744
Hsu W-M, Hsi H-C, Huang Y-T et al (2012) Partitioning of arsenic in soil–crop systems irrigated using groundwater: a case study of rice paddy soils in southwestern Taiwan. Chemosphere 86(6):606–613
Huang H, Jia Y, Sun G-X et al (2012) Arsenic speciation and volatilization from flooded paddy soils amended with different organic matters. Environ Sci Technol 46(4):2163–2168
Huang Y, Miyauchi K, Endo G et al (2016) Arsenic contamination of groundwater and agricultural soil irrigated with the groundwater in Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Environ Earth Sci 75(9):1–7
Hundal H, Singh K, Singh D et al (2013) Arsenic mobilization in alluvial soils of Punjab, North-West India under flood irrigation practices. Environ Earth Sci 69(5):1637–1648
Jia Y, Huang H, Sun G-X et al (2012) Pathways and relative contributions to arsenic volatilization from rice plants and paddy soil. Environ Sci Technol 46(15):8090–8096
Jia Y, Bao P, Zhu Y-G (2015) Arsenic bioavailability to rice plant in paddy soil: influence of microbial sulfate reduction. J Soils Sediments 15(9):1960–1967
Jitaru P, Millour S, Roman M et al (2016) Exposure assessment of arsenic speciation in different rice types depending on the cooking mode. J Food Compos Anal 54:37–47
Kamiya T, Islam R, Duan G et al (2013a) Phosphate deficiency signaling pathway is a target of arsenate and phosphate transporter OsPT1 is involved in As accumulation in shoots of rice. Soil Sci Plant Nutrition 59(4):580–590
Kamiya T, Islam R, Duan G et al (2013b) Phosphate deficiency signaling pathway is a target of arsenate and phosphate transporter OsPT1 is involved in As accumulation in shoots of rice. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 59(4):580–590
Khan KM, Chakraborty R, Bundschuh J et al (2020) Health effects of arsenic exposure in Latin America: an overview of the past eight years of research. Sci Total Environ 710:136071
Kumar A, Basu S, Rishu AK et al (2022) Revisiting the mechanisms of arsenic uptake, transport and detoxification in plants. Environ Exp Botany 194:104730
Kumarathilaka P, Seneweera S, Meharg A et al (2018a) Arsenic accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) is influenced by environment and genetic factors. Sci Total Environ 642:485–496
Kumarathilaka P, Seneweera S, Meharg A et al (2018b) Arsenic speciation dynamics in paddy rice soil-water environment: sources, physico-chemical, and biological factors—a review. Water Res 140:403–414
Kumarathilaka P, Seneweera S, Ok YS et al (2019) Arsenic in cooked rice foods: assessing health risks and mitigation options. Environ Int 127:584–591
Lafferty BJ, Ginder-Vogel M, Sparks DL (2011) Arsenite oxidation by a poorly-crystalline manganese oxide. 3. Arsenic and manganese desorption. Environ Sci Technol 45(21):9218–9223
Lee S-G, Kang I, Seo M-N et al (2022) Exposure levels and contributing factors of various arsenic species and their health effects on Korean adults. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 82(3):391–402
Lentini C, Wankel S, Hansel C (2012) Enriched iron(III)-reducing bacterial communities are shaped by carbon substrate and iron oxide mineralogy. Front Microbiol 3
Li R-Y, Ago Y, Liu W-J et al (2009) The rice aquaporin Lsi1 mediates uptake of methylated arsenic species. Plant Physiol 150(4):2071–2080
Li X-M, Sun G-X, Chen S-C et al (2018) Molecular chemodiversity of dissolved organic matter in paddy soils. Environ Sci Technol 52(3):963–971
Li T, Liu Y, Lin S et al (2019) Soil pollution management in China: a brief introduction. Sustainability 11(3):556
Lihong W, Guilan D (2009) Effect of external and internal phosphate status on arsenic toxicity and accumulation in rice seedlings. J Environ Sci 21(3):346–351
Limmer MA, Seyfferth AL (2022) Altering the localization and toxicity of arsenic in rice grain. Sci Rep 12(1):5210
Liu E, Xie Z, Fang J et al (2022a) Nitrate-mediated biomigration and transformation of As/Fe in arsenic-bearing ferrihydrite. Appl Geochem 105204
Liu L, Yang Y-P, Duan G-L et al (2022b) The chemical-microbial release and transformation of arsenic induced by citric acid in paddy soil. J Hazard Mater 421:126731
Lomax C, Liu WJ, Wu L et al (2012) Methylated arsenic species in plants originate from soil microorganisms. New Phytol 193(3):665–672
Ma JF, Yamaji N, Mitani N et al (2008) Transporters of arsenite in rice and their role in arsenic accumulation in rice grain. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105(29):9931–9935
Ma L, Wang L, Jia Y et al (2016) Arsenic speciation in locally grown rice grains from Hunan Province, China: spatial distribution and potential health risk. Sci Total Environ 557–558:438–444
Mei X, Ye Z, Wong MH (2009) The relationship of root porosity and radial oxygen loss on arsenic tolerance and uptake in rice grains and straw. Environ Pollut 157(8–9):2550–2557
Mestrot A, Feldmann J, Krupp EM et al (2011a) Field fluxes and speciation of arsines emanating from soils. Environ Sci Technol 45(5):1798–1804
Mestrot A, Merle JK, Broglia A et al (2011b) Atmospheric stability of arsine and methylarsines. Environ Sci Technol 45(9):4010–4015
Mishra RK, Tiwari S, Patel A et al (2021a) Arsenic contamination, speciation, toxicity and defense strategies in plants. Brazilian J Bot 44(1):1–10
Mishra RK, Tiwari S, Patel A et al (2021b) Arsenic contamination, speciation, toxicity and defense strategies in plants. Brazilian J Bot 44(1):1–10
Mladenov N, Zheng Y, Simone B et al (2015) Dissolved organic matter quality in a shallow aquifer of Bangladesh: implications for arsenic mobility. Environ Sci Technol 49(18):10815–10824
Mondal D, Polya DA (2008) Rice is a major exposure route for arsenic in Chakdaha block, Nadia district, West Bengal, India: a probabilistic risk assessment. Appl Geochem 23(11):2987–2998
Mosa KA, Kumar K, Chhikara S et al (2012) Members of rice plasma membrane intrinsic proteins subfamily are involved in arsenite permeability and tolerance in plants. Transgenic Res 21(6):1265–1277
Murugaiyan V, Zeibig F, Anumalla M et al (2021) Arsenic stress responses and accumulation in rice. In: Rice improvement. Springer, Cham, pp 281–313
Naito S, Matsumoto E, Shindoh K et al (2015) Effects of polishing, cooking, and storing on total arsenic and arsenic species concentrations in rice cultivated in Japan. Food Chem 168:294–301
Pan Y, Koopmans GF, Bonten LT et al (2014) Influence of pH on the redox chemistry of metal (hydr) oxides and organic matter in paddy soils. J Soils Sediments 14(10):1713–1726
Pan D, Huang G, Yi J et al (2022) Foliar application of silica nanoparticles alleviates arsenic accumulation in rice grain: co-localization of silicon and arsenic in nodes. Environ Sci Nano
Panaullah GM, Alam T, Hossain MB et al (2009) Arsenic toxicity to rice (Oryza sativa L.) in Bangladesh. Plant Soil 317(1):31–39
Petursdottir AH, Sloth JJ, Feldmann J (2015) Introduction of regulations for arsenic in feed and food with emphasis on inorganic arsenic, and implications for analytical chemistry. Anal Bioanal Chem 407(28):8385–8396
Raab A, Williams PN, Meharg A et al (2007) Uptake and translocation of inorganic and methylated arsenic species by plants. Environ Chem 4(3):197–203
Rahman MA, Hasegawa H, Rahman MM et al (2007) Effect of arsenic on photosynthesis, growth and yield of five widely cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties in Bangladesh. Chemosphere 67(6):1072–1079
Rahman MA, Hasegawa H, Rahman M et al (2008) Straighthead disease of rice (Oryza sativa L.) induced by arsenic toxicity. Environ Exp Botany 62(1):54–59
Rahman MS, Abdul Mazid Miah M, Khaled HM et al (2010) Arsenic concentrations in groundwater, soils, and irrigated rice in southwestern Bangladesh. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 41(16):1889–1895
Rahaman S, Sinha AC, Mukhopadhyay D (2011) Effect of water regimes and organic matters on transport of arsenic in summer rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Environ Sci 23(4):633–639
Rahman MA, Siddique MAB, Khan R et al (2022) Mechanism of arsenic enrichment and mobilization in groundwater from southeastern Bangladesh: water quality and preliminary health risks assessment. Chemosphere 294:133556
Roberts LC, Hug SJ, Dittmar J et al (2007a) Spatial distribution and temporal variability of arsenic in irrigated rice fields in Bangladesh. 1. Irrigation water. Environ Sci Technol 41(17):5960–5966
Roberts LC, Hug SJ, Dittmar J et al (2007b) Spatial distribution and temporal variability of arsenic in irrigated rice fields in Bangladesh. 1. Irrigation water. Environ Sci Technol 41(17):5960–5966
Roychowdhury T (2008) Impact of sedimentary arsenic through irrigated groundwater on soil, plant, crops and human continuum from Bengal delta: special reference to raw and cooked rice. Food Chem Toxicol 46(8):2856–2864
Said-Pullicino D, Miniotti EF, Sodano M et al (2016) Linking dissolved organic carbon cycling to organic carbon fluxes in rice paddies under different water management practices. Plant Soil 401(1):273–290
Seyfferth AL, Webb SM, Andrews JC et al (2011) Defining the distribution of arsenic species and plant nutrients in rice (Oryza sativa L.) from the root to the grain. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 75(21):6655–6671
Shi S, Wang T, Chen Z et al (2016) OsHAC1; 1 and OsHAC1; 2 function as arsenate reductases and regulate arsenic accumulation. Plant Physiol 172(3):1708–1719
Shri M, Dave R, Diwedi S et al (2014) Heterologous expression of Ceratophyllum demersum phytochelatin synthase, CdPCS1, in rice leads to lower arsenic accumulation in grain. Scientific Rep 4(1):1–10
Shrivastava A, Barla A, Singh S et al (2017) Arsenic contamination in agricultural soils of Bengal deltaic region of West Bengal and its higher assimilation in monsoon rice. J Hazard Mater 324:526–534
Singh R, Parihar P, Prasad SM (2018) Simultaneous exposure of sulphur and calcium hinder As toxicity: Up-regulation of growth, mineral nutrients uptake and antioxidants system. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 161:318–331
Song W-Y, Yamaki T, Yamaji N et al (2014) A rice ABC transporter, OsABCC1, reduces arsenic accumulation in the grain. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111(44):15699–15704
Suda A, Baba K, Akahane I et al (2016) Use of water-treatment residue containing polysilicate-iron to stabilize arsenic in flooded soils and attenuate arsenic uptake by rice (Oryza sativa L.) plants. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 62(2):111–116
Sun J, Quicksall AN, Chillrud SN et al (2016) Arsenic mobilization from sediments in microcosms under sulfate reduction. Chemosphere 153:254–261
Tang Z, Chen Y, Chen F et al (2017a) OsPTR7 (OsNPF8. 1), a putative peptide transporter in rice, is involved in dimethylarsenate accumulation in rice grain. Plant Cell Physiol 58(5):904–913
Tang Z, Chen Y, Chen F et al (2017b) OsPTR7 (OsNPF8. 1), a putative peptide transporter in rice, is involved in dimethylarsenate accumulation in rice grain. Plant Cell Physiol 58(5):904–913
Tani Y, Miyata N, Ohashi M et al (2004) Interaction of inorganic arsenic with biogenic manganese oxide produced by a Mn-oxidizing fungus, strain KR21-2. Environ Sci Technol 38(24):6618–6624
Teasley WA, Limmer MA, Seyfferth AL (2017) How rice (Oryza sativa L.) responds to elevated as under different Si-rich soil amendments. Environ Sci Technol 51(18):10335–10343
Tiwari M, Sharma D, Dwivedi S et al (2014) Expression in A rabidopsis and cellular localization reveal involvement of rice NRAMP, OsNRAMP 1, in arsenic transport and tolerance. Plant Cell Environ 37(1):140–152
Villegas-Torres MF, Bedoya-Reina OC, Salazar C et al (2011) Horizontal arsC gene transfer among microorganisms isolated from arsenic polluted soil. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 65(1):147–152
Wang P, Sun G, Jia Y et al (2014) A review on completing arsenic biogeochemical cycle: microbial volatilization of arsines in environment. J Environ Sci 26(2):371–381
Wang P, Zhang W, Mao C et al (2016) The role of OsPT8 in arsenate uptake and varietal difference in arsenate tolerance in rice. J Exp Bot 67(21):6051–6059
Wang J, Halder D, Wegner L et al (2020a) Redox dependence of thioarsenate occurrence in paddy soils and the rice rhizosphere. Environ Sci Technol 54(7):3940–3950
Wang J, Kerl CF, Hu P et al (2020b) Thiolated arsenic species observed in rice paddy pore waters. Nat Geosci 13(4):282–287
WHO (2014) WHO Codex Alimentarius Commission-Geneva, 14–18 July 2014
Williams PN, Villada A, Deacon C et al (2007) Greatly enhanced arsenic shoot assimilation in rice leads to elevated grain levels compared to wheat and barley. Environ Sci Technol 41(19):6854–6859
Williams PN, Zhang H, Davison W et al (2011) Organic matter solid phase interactions are critical for predicting arsenic release and plant uptake in Bangladesh paddy soils. Environ Sci Technol 45(14):6080–6087
Wind T, Conrad R (1995) Sulfur compounds, potential turnover of sulfate and thiosulfate, and numbers of sulfate-reducing bacteria in planted and unplanted paddy soil. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 18(4):257–266
Wu C, Ye Z, Shu W et al (2011) Arsenic accumulation and speciation in rice are affected by root aeration and variation of genotypes. J Exp Bot 62(8):2889–2898
Xie X, Wang Y, Li J et al (2015) Effect of irrigation on Fe (III)–SO42− redox cycling and arsenic mobilization in shallow groundwater from the Datong basin, China: evidence from hydrochemical monitoring and modeling. J Hydrol 523:128–138
Xu X, McGrath S, Zhao F (2007) Rapid reduction of arsenate in the medium mediated by plant roots. New Phytol 176(3):590–599
Xu J, Shi S, Wang L et al (2017) OsHAC4 is critical for arsenate tolerance and regulates arsenic accumulation in rice. New Phytol 215(3):1090–1101
Yamaguchi N, Ohkura T, Takahashi Y et al (2014) Arsenic distribution and speciation near rice roots influenced by iron plaques and redox conditions of the soil matrix. Environ Sci Technol 48(3):1549–1556
Yan S, Wu F, Zhou S et al (2021a) Zinc oxide nanoparticles alleviate the arsenic toxicity and decrease the accumulation of arsenic in rice (Oryza sativa L.). BMC Plant Biol 21(1):1–11
Yan S, Wu F, Zhou S et al (2021b) Zinc oxide nanoparticles alleviate the arsenic toxicity and decrease the accumulation of arsenic in rice (Oryza sativa L.). BMC Plant Biol 21(1):1–11
Yan M, Zhu C, Song T et al (2022). Impact of different manure-derived dissolved organic matters on the fate of arsenic-antibiotic in co-contaminated paddy soils. Environ Pollut 119376
Yang X, Hinzmann M, Pan H et al (2022a) Pig carcass-derived biochar caused contradictory effects on arsenic mobilization in a contaminated paddy soil under fluctuating controlled redox conditions. J Hazard Mater 421:126647
Yang X, Shaheen SM, Wang J et al (2022b) Elucidating the redox-driven dynamic interactions between arsenic and iron-impregnated biochar in a paddy soil using geochemical and spectroscopic techniques. J Hazard Mater 422:126808
Ye W, Fan T, Lu H et al (2015) Arsenic speciation in xylem exudates of rice growing in arsenic-contaminated soil. Acta Agric Scand B Soil Plant Sci 65(8):697–701
Ye W, Zhang J, Fan T et al (2017a) Arsenic speciation in the phloem exudates of rice and its role in arsenic accumulation in rice grains. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 143:87–91
Ye Y, Li P, Xu T et al (2017b) OsPT4 contributes to arsenate uptake and transport in rice. Front Plant Sci 8:2197
Yuan Z-F, Gustave W, Boyle J et al (2021) Arsenic behavior across soil-water interfaces in paddy soils: coupling, decoupling and speciation. Chemosphere 269:128713
Yun S-W, Baveye PC, Kim K-B et al (2016) Effect of postmining land use on the spatial distribution of metal(loid)s and their transport in agricultural soils: analysis of a case study of Chungyang, South Korea. J Geochem Explor 170:157–166
Zhang S-Y, Zhao F-J, Sun G-X et al (2015) Diversity and abundance of arsenic biotransformation genes in paddy soils from southern China. Environ Sci Technol 49(7):4138–4146
Zhang J, Zou Q, Sun M et al (2022) Effect of applying persulfate on the accumulation of arsenic in rice plants grown in arsenic-contaminated paddy soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 1–11
Zhao FJ, Ma JF, Meharg A et al (2009) Arsenic uptake and metabolism in plants. New Phytol 181(4):777–794
Zhao FJ, Ago Y, Mitani N et al (2010) The role of the rice aquaporin Lsi1 in arsenite efflux from roots. New Phytol 186(2):392–399
Zhao F-J, Harris E, Yan J et al (2013a) Arsenic methylation in soils and its relationship with microbial arsM abundance and diversity, and As speciation in rice. Environ Sci Technol 47(13):7147–7154
Zhao F-J, Zhu Y-G, Meharg AA (2013b) Methylated arsenic species in rice: geographical variation, origin, and uptake mechanisms. Environ Sci Technol 47(9):3957–3966
Zheng R, Sun G, Zhu Y (2013) Effects of microbial processes on the fate of arsenic in paddy soil. Chin Sci Bull 58(2):186–193
Zhou S, Liu Z, Sun G et al (2022) Simultaneous reduction in cadmium and arsenic accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) by iron/iron-manganese modified sepiolite. Sci Total Environ 810:152189
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Herath, I., Lin, C., Bundschuh, J. (2023). Arsenic Dynamics in Paddy Rice Ecosystems and Human Exposure. In: Niazi, N.K., Bibi, I., Aftab, T. (eds) Global Arsenic Hazard. Environmental Science and Engineering. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16360-9_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16360-9_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-16359-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-16360-9
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)