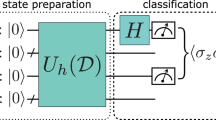
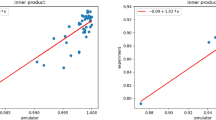
Abstract
There is an intrinsic link between operations that can be performed on a quantum computer and kernel methods. This has inspired the development of quantum-kernel-based classifiers that exploit the ability of quantum computers to efficiently perform operations in large Hilbert spaces. This work performs a proof of principle demonstration of a quantum-kernel-based classifier applied to the binary classification of various non-linearly separable datasets. For each classification task, a quantum device provided by the IBM Quantum (IBMQ) platform is used to estimate a kernel matrix. A number of novel strategies comprised of combinations of existing post-processing methods are then applied to the matrix to mitigate the effects of noise from the quantum device, readout error and account for the effects of finite sampling. The application of certain strategies is shown to improve the quality of the kernel matrices estimated by the quantum device. The raw and post-processed kernel matrices are fed into a classical support vector machines (SVM) that learns a model to perform the classification. For each classification task, the classifiers exhibits high accuracies that are comparable to the classifiers that use ideal, simulated kernel matrices. The classifiers that use certain post-processed kernel matrices exhibit higher accuracies than the classifiers that use the raw kernel matrices. This demonstrates the effectiveness of quantum-kernel-based classifiers in the Noisy Intermediate Scale Quantum (NISQ) computing era as well as the power of certain of post-processing strategies.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
A brief introduction to quantum computing and kernels can be found in Sections A and B, respectively, of the Supplementary Material [29].
- 2.
References
Li, W., Deng, D.-L.: Recent advances for quantum classifiers. arXiv preprint arXiv:2108.13421 (2021)
Schuld, M., Petruccione, F.: Supervised Learning with Quantum Computers, vol. 17. Springer (2018)
Zoufal, C., Lucchi, A., Woerner, S.: Quantum generative adversarial networks for learning and loading random distributions. NPJ Quant. Inf. 5(1), 1–9 (2019)
Romero, J., Olson, J.P., Aspuru-Guzik, A.: Quantum autoencoders for efficient compression of quantum data. Quant. Sci. Technol. 2(4), 045001 (2017)
Dunjko, V., Briegel, H.J.: Machine learning & artificial intelligence in the quantum domain: a review of recent progress. Rep. Prog. Phys. 81(7), 074001 (2018)
Ciliberto, C.: Quantum machine learning: a classical perspective. Proc. R. Soci. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 474(2209), 20170551 (2018)
Killoran, N., Bromley, T.R., Miguel Arrazola, J., Schuld, M., Quesada, N., Lloyd, S.: Continuous-variable quantum neural networks. Phys. Rev. Res. 1(3), 033063 (2019)
Schuld, M., Sinayskiy, I., Petruccione, F.: The quest for a quantum neural network. Quant. Inf. Process. 13(11), 2567–2586 (2014)
Farhi, E., Neven, H.: Classification with quantum neural networks on near term processors. arXiv preprint arXiv:1802.06002 (2018)
Lu, S., Braunstein, S.L.: Quantum decision tree classifier. Quant. Inf. Process. 13(3), 757–770 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-013-0687-5
Lloyd, S., Mohseni, M., Rebentrost, P.: Quantum algorithms for supervised and unsupervised machine learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1307.0411 (2013)
Wiebe, N., Kapoor, A., Svore, K.: Quantum algorithms for nearest-neighbor methods for supervised and unsupervised learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1401.2142 (2014)
Rebentrost, P., Mohseni, M., Lloyd, S.: Quantum support vector machine for big data classification. Phys. Rev. Lett. 113(13), 130503 (2014)
Chatterjee, R., Yu, T.: Generalized coherent states, reproducing kernels, and quantum support vector machines. arXiv preprint arXiv:1612.03713 (2016)
Schuld, M., Fingerhuth, M., Petruccione, F.: Implementing a distance-based classifier with a quantum interference circuit. EPL (Europhys. Lett.) 119(6), 60002 (2017)
Schuld, M., Killoran, N.: Quantum machine learning in feature Hilbert spaces. Phys. Rev. Lett.122(4), 040504 (2019)
Havlíček, V., et al.: Supervised learning with quantum-enhanced feature spaces. Nature 567(7747), 209–212 (2019)
Blank, C., Park, D.K., Kevin Rhee, J.-K., Petruccione, F.: Quantum classifier with tailored quantum kernel. NPJ Quant. Inf. 6(1), 1–7 (2020)
Liu, Y., Arunachalam, S., Temme, K.: A rigorous and robust quantum speed-up in supervised machine learning. Nat. Phys. 1–5 (2021)
Huang, H.-Y., et al.: Power of data in quantum machine learning. Nat. Commun. 12(1), 1–9 (2021)
Bittel, L., Kliesch, M.: Training variational quantum algorithms is np-hard. Phy. Rev. Lett.127(12), 120502 (2021)
Bartkiewicz, K., Gneiting, C., Černoch, A., Jiráková, K., Lemr, K., Nori, F.: Experimental kernel-based quantum machine learning in finite feature space. Sci. Rep. 10(1), 1–9 (2020)
Kusumoto, T., Mitarai, K., Fujii, K., Kitagawa, M., Negoro, M.: Experimental quantum kernel machine learning with nuclear spins in a solid. arXiv preprint arXiv:1911.12021 (2019)
Peters, E.: Machine learning of high dimensional data on a noisy quantum processor. arXiv preprint arXiv:2101.09581 (2021)
Hubregtsen, T.: Training quantum embedding kernels on near-term quantum computers. arXiv preprint arXiv:2105.02276 (2021)
Wang, X., Du, Y., Luo, Y., Tao, D.: Towards understanding the power of quantum kernels in the NISQ era. arXiv preprint arXiv:2103.16774 (2021)
Asfaw, A., et al.: Learn quantum computation using Qiskit (2020)
Suzuki, Y., et al.: Analysis and synthesis of feature map for kernel-based quantum classifier. Quant. Mach. Intell. 2(1), 1–9 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42484-020-00020-y
Mahashakti Pillay, S., Sinayskiy, I., Jembere, E., Petruccione,F.: Implementing-quantum-kernel-based-classifiers-in-the-NISQ-Era-Supp-Material. 11 (2021). https://git.io/JX8cp
Nielsen, M., Chuang, I.: Quantum Computation and Quantum Information, 10th Anniversary edition. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2010)
Roth, V., Laub, J., Kawanabe, M., Buhmann, J.M.: Optimal cluster preserving embedding of nonmetric proximity data. IEEE Trans. Patt. Anal. Mach. Intell. 25(12), 1540–1551 (2003)
Wu, G., Chang, E.Y., Zhang, Z.: An analysis of transformation on non-positive semidefinite similarity matrix for kernel machines. In: Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Machine Learning, vol. 8. Citeseer (2005)
Graepel, T., Herbrich, R., Bollmann-Sdorra, P., Obermayer, K.: Classification on pairwise proximity data. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 11, 438–444 (1999)
Abraham, H., et al.: Qiskit: an open-source framework for quantum computing (2019)
Bergholm, V., et al.: Automatic differentiation of hybrid quantum-classical computations (2020)
Pedregosa, F., et al.: Scikit-learn: machine learning in python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 12, 2825–2830 (2011)
Acknowlegdements
This work is based upon research supported by the South African Research Chair Initiative, Grant No. 64812 of the Department of Science and Innovation and the National Research Foundation of the Republic of South Africa. Support from the CSIR DSI-Interbursary Support (IBS) Programme is gratefully acknowledged. Support from the Center of Artificial Intelligence Research is appreciated. We would like to thank Mr I. J. David for his assistance in proof reading the manuscript. We acknowledge the use of IBM Quantum services for this work. The views expressed are those of the authors and do not reflect the official policy or position of IBM or the IBM Quantum team.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Pillay, S.M., Sinayskiy, I., Jembere, E., Petruccione, F. (2022). Implementing Quantum-Kernel-Based Classifiers in the NISQ Era. In: Jembere, E., Gerber, A.J., Viriri, S., Pillay, A. (eds) Artificial Intelligence Research. SACAIR 2021. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1551. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-95070-5_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-95070-5_17
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-95069-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-95070-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)