Abstract
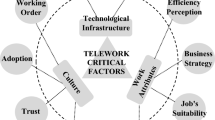
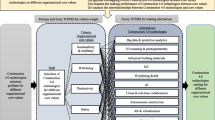
The COVID 19 pandemic has affected the daily routine of all people, both in their family and work environments, globally. As a result, many companies in practically all the productive sectors of the countries have required to rethink several critical aspects of the business itself so as not to be absorbed by the crisis, avoid as much as possible losses in financial, human, technological resources, etc., and even disappear. In these challenging times that we live in, the corporate technology platform must provide remote connection facilities to employees. Thus, Teleworking is facilitated in a safe, flexible way, which does not delay the processes and business goals. To define this technological roadmap, it is essential to review the current specialized components, the network infrastructure, and recommendations to improve and optimize existing processes. Concerning the application of integrated methodologies for evaluating Teleworker’s technological conditions during the COVID-19, some studies have been found related to health and safety conditions, growth in the implementation of this modality, and future trends in teleworking. However, the approach to technological requirements in teleworking during the COVID-19 pandemic is still limited and not sufficiently studied. To address this challenge, this paper presents an integrated framework based on the application of Fuzzy AHP, TOPSIS, and multivariate methods for the evaluation of technological conditions of teleworkers during the COVID-19 in the construction sector. The methodology’s design is based on the international guidelines and pertinent scientific literature in Telework. The results obtained evidence that the criteria “Infrastructure,” “Digital Connectivity Services,” “Applications,” and “Users” are relevant in the evaluation of technological conditions for Telework due to the few differences in their relative weights.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lopez-Leon, S., Forero, D.A., Ruiz-DIáz, P.: Recommendations for working from home during the COVID-19 pandemic (and beyond). Work (2020). https://doi.org/10.3233/WOR-203187
Riva, G., Mantovani, F., Wiederhold, B.K.: Positive technology and COVID-19. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2020.29194.gri
Fana, M., Milasi, S., Napierala, J., Fernandez-Macias, E., Vazquez, I.G.: Telework, work organisation and job quality during the COVID-19 crisis: a qualitative study. In: J RC Working Papers Series on Labour, Education and Technology (2020). https://ideas.repec.org/p/ipt/laedte/202011.html. Accessed 29 June 2021
Hernandez, L., Jimenez, G., Baloco, C., Jimenez, A., Hernandez, H.: Characterization of the use of the internet of things in the institutions of higher education of the city of barranquilla and its metropolitan area. In: Stephanidis, C. (ed.) HCI 2018. CCIS, vol. 852, pp. 17–24. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-92285-0_3
Garcia-Contreras, R., Muñoz-Chavez, P., Valle-Cruz, D., Rubalcaba-Gomez, E., Becerra-Santiago, J.: Teleworking in times of COVID-19. some lessons for the public sector from the emergent implementation during the pandemic period: teleworking in times of COVID-19. In: ACM International Conference Proceeding Series, pp. 376–385 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1145/3463677.3463700
Belzunegui-Eraso, A., Erro-Garcés, A.: Teleworking in the context of the Covid-19 crisis. Sustainability 12(9), 1–18 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/su12093662
Lopez, M.R.: Telework decision strategy: a systematic review. Dissertation Abstracts International Section A Humanities and Social Sciences, vol. 82, no. 1-A (2021)
Kawashima, T., et al.: The relationship between fever rate and telework implementation as a social distancing measure against the COVID-19 pandemic in Japan. Publ. Health (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.puhe.2020.05.018
Suranti, N.M.Y.: Variations of models and learning platforms for prospective teachers during the COVID-19 pandemic period. Indones. J. Teach. Educ. (2020)
Tokarchuk, O., Gabriele, R., Neglia, G.: Teleworking during the COVID-19 crisis in Italy: evidence and tentative interpretations. Sustainability 13(4), 1–12 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/su13042147
Hallman, D.M., Januario, L.B., Mathiassen, S.E., Heiden, M., Svensson, S., Bergstrom, G.: Working from home during the COVID-19 outbreak in Sweden: effects on 24-h time-use in office workers. BMC Publ. Health 21(1) (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-021-10582-6
Wang, L., Alexander, C.A.: Cyber security during the COVID-19 pandemic. AIMS Electron. Electr. Eng. 5(2), 146–157 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3934/ELECTRENG.2021008
Medina-Rodríguez, C.E., Casas-Valadez, M.A., Faz-Mendoza, A., Castañeda-Miranda, R., Gamboa-Rosales, N.K., López-Robles, J.R.: The cyber security in the age of telework: a descriptive research framework through science mapping. In: 2020 International Conference on Data Analytics for Business and Industry: Way Towards a Sustainable Economy (ICDABI), pp. 1–5 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDABI51230.2020.9325633
Hernandez, L., et al.: Optimization of a WiFi wireless network that maximizes the level of satisfaction of users and allows the use of new technological trends in higher education institutions. In: Streitz, N., Konomi, S. (eds.) HCII 2019. LNCS, vol. 11587, pp. 144–160. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-21935-2_12
Jimenez-Delgado, G., Balmaceda-Castro, N., Hernández-Palma, H., de la Hoz-Franco, E., García-Guiliany, J., Martinez-Ventura, J.: An integrated approach of multiple correspondences analysis (MCA) and fuzzy AHP method for occupational health and safety performance evaluation in the land cargo transportation. In: Duffy, V.G. (ed.) HCII 2019. LNCS, vol. 11581, pp. 433–457. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-22216-1_32
Rueda, D., Balmaceda, N.: Analisis de Correspondencias Multiples aplicado a la prueba Saber Pro 2017 en el programa de matematicas de las universidades del Departamento del Atlantico (2019)
Abdulgader, F.S., Eid, R., Rouyendegh, B.D.: Development of decision support model for selecting a maintenance plan using a fuzzy MCDM approach: a theoretical framework. Appl. Comput. Intell. Soft Comput. (2018)
Abdullah, L., Zulkifli, N., Integration of fuzzy AHP and interval type-2 fuzzy DEMATEL: an application to human resource management. Expert Syst. Appl. 42(9), 4397–4409 (2015)
Duque Porras, J., Fonseca, L.A.P.: Reward, social support and general health in Colombian teleworkers. a mixed study. In: Black, N.L., Neumann, W.P., Noy, I. (eds.) IEA 2021. LNNS, vol. 219, pp. 123–130. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-74602-5_19
Hernandez, L., Jimenez, G.: Characterization of the current conditions of the ITSA data centers according to standards of the green data centers friendly to the environment. In: Silhavy, R., Senkerik, R., Kominkova Oplatkova, Z., Prokopova, Z., Silhavy, P. (eds.) CSOC 2017. AISC, vol. 574, pp. 329–340. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-57264-2_34
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Hernandez-Collantes, L. et al. (2021). An Integrated Framework Based on Fuzzy AHP-TOPSIS and Multiple Correspondences Analysis (MCA) for Evaluate the Technological Conditions of the Teleworker in Times of Pandemic: A Case Study. In: Stephanidis, C., et al. HCI International 2021 - Late Breaking Papers: HCI Applications in Health, Transport, and Industry. HCII 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13097. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-90966-6_32
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-90966-6_32
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-90965-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-90966-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)