Abstract
The quantity of sludges in Morocco generated by the treatment of industrial effluents achieved a value of 39,656 Tons per year in 2000 and is estimated at 80,000 Tons per year in 2020. These residual sludges represent a real threat to the environment and their elimination is one of the major challenges in order to find a solution that is both economic and ecological. There are several ways for eliminating this type of waste, however the appropriate choice of disposal method should be dependent both on the origin and nature of sludges, the additional value of the resulting product and its impact on the environment. In Morocco, the most widespread solution is their landfilling.
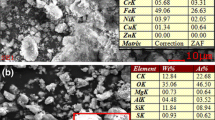
The use of local resources as aggregates or as supplementary cementitious materials is one of the important facets of sustainable development and the circular economy for the construction area. In this context, the use of residual sludge as cementitious additives in the construction field, a great consumer of materials, is one of the most suitable alternative solutions for the valorization of this type of waste. In fact, the use of supplementary cementitious materials contributes to the improvement of the technical performance of cementitious materials (mortars and concretes) on the one hand, and on the other hand, their introduction into cement contributes to save energy by reducing the consumption of clinker and, consequently, solving the environmental problems related to the emission of carbon dioxide released during the manufacturing of Portland cement. This work deals with the valorization of a wastewater treatment plant sludge generated by a local sanitary ceramic products industry in cementitious building materials. The objective is to study the effect of incorporating the thermally activated industrial sludge as a substitute binder for Portland cement in ordinary concrete. An evaluation of the mechanical properties by compressive strength tests was conducted. The durability performances of concrete with the studied sludge in a marine environment were also evaluated by several tests, including the porosity accessible to water, the mass variation and the mechanical resistance of the concrete exposed to chemical aggressions.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadi, B., Al-Khaja, W.: Utilization of paper waste sludge in the building construction industry. Resour Conserv Recycl, 32, 105–13 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-3449(01)00051-9
ASTM: C 125 Standard Terminology Relating to Concrete and Concrete Aggregates. American Society for Testing and materials (2007)
Lamrani, S., Allal, L.B., Ammari, M., Boutamou, S., Azmani, A.: Thermal activation of an industrial sludge for a possible valorization. MATEC Web Conf. 11, 01022 (2014)
Lamrani, S., Benallal, L., Ammari, M.: Valorization of an industrial sludge as an artificial pozzolan in cementitious materials. Int. J. Eng. Res. Appl. 6, 28–40 (2016)
NF EN 12620: NF EN 12620+A1 - Granulats pour béton (2008)
Dreux, G., Festa, J.: Nouveau guide du béton: composants et propriétés (1995)
Aïtcin, P.C.: The durability characteristics of high performance concrete: a review. Cem. Concr. Compos. 25, 409–420 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0958-9465(02)00081-1
Vicat, L.: Recherches sur les causes physiques de destruction des composés hydrauliques par l’eau de mer. Bulletin de la société d’encouragement pour l’industrie nationale (1857)
Rich, A.: Dessalement de l’eau de mer par congelation sur paroi froide : aspect thermodynamique et influence des conditions operatoires. Thèse de Doctorat de L’universite Claude Bernard Lyon 1- France (2011)
Nicolas, R.S.: Approche performantielle des bétons avec métakaolins obtenus par calcination flash. Thèse de doctorat de l’université de Toulouse (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lamrani, S., El Ayadi, H., Belmokhtar, N., Ammari, M., Ben Allal, L. (2022). Integration of an Industrial Waste in the Manufacturing of a Cementitious Construction Material. In: Kacprzyk, J., Balas, V.E., Ezziyyani, M. (eds) Advanced Intelligent Systems for Sustainable Development (AI2SD’2020). AI2SD 2020. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1417. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-90633-7_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-90633-7_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-90632-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-90633-7
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)