Abstract
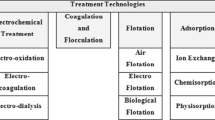
Large numbers of toxic and poisonous chemicals are released in our surroundings from different industries resulting in contamination of aqueous medium, atmosphere, and geosphere at an alarming level. Aqueous medium pollution that results from heavy metal has come into being as a severe environmental issue. Some poisonous metals include zinc, mercury, lead, chromium, cadmium, nickel, and copper, which are of particular concern in curing industrial wastewater. They are non-biodegradable in nature, make aggregate in living bodies and most of them are cancer-causing agents. A number of extensive industrial researches have been conducted for the safe removal of pollutants and metallic elements from industrial effluents and wastewater. There are many different ordinary treatment strategies that have been utilized to treat these aqueous phase toxins, such as flotation, ion-exchange, coagulation, reverse osmosis, electrolysis, and complexation.
The adsorption is more widely accepted, and more promising techniques can be utilized to eliminate certain types of pollutants by selecting appropriate adsorbent. It offers many advantages over other conventional methods and is accepted as one of the productive, effective, labor-saving, valuable, and reasonable methods. There are large number of adsorbents that have been used to adsorb heavy metals from aqueous media such as activated carbon, activated alumina, clays, zeolites, polymer clay-based nanoadsorbents, metal oxide-based nanoadsorbents, graphene, and carbon nanotubes; some other absorbents including chitosan, lignin, cellulose, starch, and fungi have also been used for safe removal of heavy metals. Agricultural wastes come from the growing and initially processed agricultural stuff, including organic products, vegetables, fruits meat, and dairy items, which nowadays have been used as economic and environment-friendly adsorbents. Agricultural wastes especially those that contain cellulose have a high biosorption capacity. Adsorbents from plant wastes can be used with or without modification for the reduction of a pollutant from aqueous media. Generally, chemical modification of plant wastes enhances their adsorption capacities as compared to unmodified. Rice husk in pristine form and in activated rice form is utilized for chromium (VI) removal. Different kinds of agricultural waste materials including peanut shells, soybean hulls, rice straw, bagasse, sugarcane, and walnut shells have been applied for lead adsorption. In some studies, rice and wheat bran were analyzed for cadmium adsorption, and excellent results were reported. Other studies showed the application of rice husk and rice polish in both pristine and composite forms for effective cadmium adsorption. The bark of some plants including Picea glehnii and Abies sachalinensis and biomass of dried plants (Parthenium) were checked for cadmium removal. Adsorption experiments performed using hazelnut shells, green shell, walnut shells, and peanut hulls exhibited good results toward cadmium adsorption. Some other adsorption studies conducted using activated carbon prepared coir pith, bagasse pith, and dates and peanut shells. Their cadmium adsorption capacity was found to be up to 98%. One study showed that tea-based adsorbent reduced almost 70% of the hexavalent chromium into Cr(III). In short, agricultural waste can be used as low-cost and most beneficial adsorbent for removal of heavy metals from aqueous media.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbaszadeh S, Alwi SRW, Webb C, Ghasemi N, Muhamad II (2016) Treatment of lead-contaminated water using activated carbon adsorbent from locally available papaya peel biowaste. J Clean Prod 118:210–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.01.054
Acharya J, Kumar U, Rafi PM (2018) Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater by chemically modified agricultural waste material as potential adsorbent-a review. Int J Curr Eng Technol 8(3):526–530. https://doi.org/10.14741/ijcet/v.8.3.6
Afroze S, Sen TK (2018) A review on heavy metal ions and dye adsorption from water by agricultural solid waste adsorbents. Water Air Soil Pollut 229(7):225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3869-z
Akbal F, Camcı S (2010) Comparison of electrocoagulation and chemical coagulation for heavy metal removal. Chem Eng Technol 33(10):1655–1664. https://doi.org/10.1002/ceat.201000091
Al-Saydeh SA, El-Naas MH, Zaidi SJ (2017) Copper removal from industrial wastewater: a comprehensive review. J Ind Eng Chem 56:35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2017.07.026
Alam MA, Shaikh WA, Alam MO, Bhattacharya T, Chakraborty S, Show B, Saha I (2018) Adsorption of as (III) and as (V) from aqueous solution by modified Cassia fistula (golden shower) biochar. Appl Water Sci 8(7):198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0839-y
Altaf F, Batool R, Ahmad MA, Raza R, Khan MA, Abbas G (2018) Novel vinyl-modified sepiolite-based polymer nanocomposites: synthesis and characterization. Iran Polym J 27(6):413–422. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-018-0619-4
Andreev YY, Safonov IA, Doub AV (2019) Application of scale of absolute surface potentials to the reactions of chemisorption and Electrocatalysis on metals. Part 2. Prot Metals Phys Chem Surf 55(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1134/S2070205119010039
Anirudhan T, Ramachandran M (2008) Synthesis and characterization of amidoximated polyacrylonitrile/organobentonite composite for cu (II), Zn (II), and cd (II) adsorption from aqueous solutions and industry wastewaters. Ind Eng Chem Res 47(16):6175–6184. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie070735d
Annadurai G, Juang R, Lee D (2003) Adsorption of heavy metals from water using banana and orange peels. Water Sci Technol 47(1):185–190. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2003.0049
Ansari M, Mahvi AH, Salmani MH et al (2018) Removal of cadmium from aqueous solutions by a synthesized activated carbon. J Environ Health Sustain Dev 3(3):593–605
Bhatnagar A, Sillanpää M (2010) Utilization of agro-industrial and municipal waste materials as potential adsorbents for water treatment—a review. Chem Eng J 157(2–3):277–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.01.007
Bilal M, Shah JA, Ashfaq T, Gardazi SMH, Tahir AA, Pervez A et al (2013) Waste biomass adsorbents for copper removal from industrial wastewater—a review. J Hazard Mater 263:322–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.07.071
Biswas S, Mishra U (2015) Continuous fixed-bed column study and adsorption modeling: removal of lead ion from aqueous solution by charcoal originated from chemical carbonization of rubber wood sawdust. J Chem 2015. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/907379
Budnik LT, Casteleyn L (2019) Mercury pollution in modern times and its socio-medical consequences. Sci Total Environ 654:720–734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.408
Bulut Y, Tez Z (2007) Adsorption studies on ground shells of hazelnut and almond. J Hazard Mater 149(1):35–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.03.044
Burakov AE, Galunin EV, Burakova IV, Kucherova AE, Agarwal S, Tkachev AG, Gupta VK (2018) Adsorption of heavy metals on conventional and nanostructured materials for wastewater treatment purposes: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 148:702–712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.11.034
Carolin CF, Kumar PS, Saravanan A, Joshiba GJ, Naushad M (2017) Efficient techniques for the removal of toxic heavy metals from aquatic environment: a review. J Environ Chem Eng 5(3):2782–2799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.05.029
Chen Q, Xu W, Ge Q (2018) Novel multicharge hydroacid complexes that effectively remove heavy metal ions from water in forward osmosis processes. Environ Sci Technol 52(7):4464–4471. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b06701
Crini G, Lichtfouse E, Wilson LD, Morin-Crini N (2019) Conventional and non-conventional adsorbents for wastewater treatment. Environ Chem Lett 17(1):195–213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-018-0786-8
Das N, Mathew L (2011) Chromium pollution and bioremediation: an overview. In: Biomanagement of metal-contaminated soils. Springer, pp 297–321. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-1914-9_13
Davis AP, Shokouhian M, Ni S (2001) Loading estimates of lead, copper, cadmium, and zinc in urban runoff from specific sources. Chemosphere 44(5):997–1009. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(00)00561-0
Demirbas A (2008) Heavy metal adsorption onto agro-based waste materials: a review. J Hazard Mater 157(2–3):220–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.01.024
Dubey SP, Gopal K (2007) Adsorption of chromium (VI) on low cost adsorbents derived from agricultural waste material: a comparative study. J Hazard Mater 145(3):465–470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.11.041
Fan S, Wang Y, Li Y, Tang J, Wang Z, Tang J et al (2017) Facile synthesis of tea waste/Fe 3 O 4 nanoparticle composite for hexavalent chromium removal from aqueous solution. RSC Adv 7(13):7576–7590. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA27781K
Farooq U, Kozinski JA, Khan MA, Athar M (2010) Biosorption of heavy metal ions using wheat based biosorbents–a review of the recent literature. Bioresour Technol 101(14):5043–5053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.02.030
Fernandez JA, Heeb MJ, Radtke K-P, Griffin MJ (1997) Potent blood coagulant activity of human semen due to prostasome-bound tissue factor. Biol Reprod 56(3):757–763. https://doi.org/10.1095/biolreprod56.3.757
Garg UK, Kaur M, Garg V, Sud D (2008) Removal of nickel (II) from aqueous solution by adsorption on agricultural waste biomass using a response surface methodological approach. Bioresour Technol 99(5):1325–1331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.02.011
Gautam RK, Mudhoo A, Lofrano G, Chattopadhyaya MC (2014) Biomass-derived biosorbents for metal ions sequestration: adsorbent modification and activation methods and adsorbent regeneration. J Environ Chem Eng 2(1):239–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2013.12.019
Golbad S, Khoshnoud P, Abu-Zahra N (2017) Hydrothermal synthesis of hydroxy sodalite from fly ash for the removal of lead ions from water. Int J Environ Sci Technol 14(1):135–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-016-1133-x
Gong X, Huang D, Liu Y, Zeng G, Wang R, Wei J et al (2018) Pyrolysis and reutilization of plant residues after phytoremediation of heavy metals contaminated sediments: for heavy metals stabilization and dye adsorption. Bioresour Technol 253:64–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.01.018
Gopalratnam VC, Bennett GF, Peters RW (1988) The simultaneous removal of oil and heavy metals from industrial wastewater by joint precipitation and air flotation. Environ Prog 7(2):84–92. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.3300070208
Guo X, Zhang S, Shan X-q (2008) Adsorption of metal ions on lignin. J Hazard Mater 151(1):134–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.05.065
Inbaraj BS, Sulochana N (2004) Carbonised jackfruit peel as an adsorbent for the removal of cd (II) from aqueous solution. Bioresour Technol 94(1):49–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2003.11.018
Inyang MI, Gao B, Yao Y, Xue Y, Zimmerman A, Mosa A et al (2016) A review of biochar as a low-cost adsorbent for aqueous heavy metal removal. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 46(4):406–433. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2015.1096880
Jain M, Yadav M, Kohout T, Lahtinen M, Garg VK, Sillanpää M (2018) Development of iron oxide/activated carbon nanoparticle composite for the removal of Cr (VI), cu (II) and cd (II) ions from aqueous solution. Water Res Indus 20:54–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wri.2018.10.001
Jain S, Jayaram RV (2010) Removal of basic dyes from aqueous solution by low-cost adsorbent: wood apple shell (Feronia acidissima). Desalination 250(3):921–927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2009.04.005
Kaliannan D, Palaninaicker S, Palanivel V, Mahadeo MA, Ravindra BN, Jae-Jin S (2019) A novel approach to preparation of nano-adsorbent from agricultural wastes (Saccharum officinarum leaves) and its environmental application. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(6):5305–5314. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3734-z
Kato K, Uchida E, Kang E-T, Uyama Y, Ikada Y (2003) Polymer surface with graft chains. Prog Polym Sci 28(2):209–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6700(02)00032-1
Kaya K, Pehlivan E, Schmidt C, Bahadir M (2014) Use of modified wheat bran for the removal of chromium (VI) from aqueous solutions. Food Chem 158:112–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.02.107
Kazemipour M, Ansari M, Tajrobehkar S, Majdzadeh M, Kermani HR (2008) Removal of lead, cadmium, zinc, and copper from industrial wastewater by carbon developed from walnut, hazelnut, almond, pistachio shell, and apricot stone. J Hazard Mater 150(2):322–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.04.118
Kuo C-JJ, Amy GL (1988) Factors affecting coagulation with aluminum sulfate—II. Dissolved organic matter removal. Water Res 22(7):863–872. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(88)90024-3
Kwikima MM, Lema MW (2017) Sorption characteristics of hexavalent chromium in the soil based on batch experiment and their implications to the environment. J Geosci Environ Prot 5(03):152. https://doi.org/10.4236/gep.2017.53011
Landaburu-Aguirre J, García V, Pongrácz E, Keiski RL (2009) The removal of zinc from synthetic wastewaters by micellar-enhanced ultrafiltration: statistical design of experiments. Desalination 240(1–3):262–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2007.11.077
Lim AP, Aris AZ (2014) A review on economically adsorbents on heavy metals removal in water and wastewater. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 13(2):163–181. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-013-9330-2
Liu J, Chen Y, Han T, Cheng M, Zhang W, Long J, Fu X (2019) A biomimetic SiO2@ chitosan composite as highly-efficient adsorbent for removing heavy metal ions in drinking water. Chemosphere 214:738–742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.09.172
Liu J, Ma Y, Xu T, Shao G (2010) Preparation of zwitterionic hybrid polymer and its application for the removal of heavy metal ions from water. J Hazard Mater 178(1–3):1021–1029. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.02.041
Ma H, Yang J, Gao X, Liu Z, Liu X, Xu Z (2019) Removal of chromium (VI) from water by porous carbon derived from corn straw: influencing factors, regeneration and mechanism. J Hazard Mater 369:550–560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.02.063
Matlock MM, Howerton BS, Atwood DA (2002) Chemical precipitation of heavy metals from acid mine drainage. Water Res 36(19):4757–4764. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00149-5
Mishra P, Patel R (2009) Removal of lead and zinc ions from water by low cost adsorbents. J Hazard Mater 168(1):319–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.02.026
Mohan D, Singh KP, Singh VK (2006) Trivalent chromium removal from wastewater using low cost activated carbon derived from agricultural waste material and activated carbon fabric cloth. J Hazard Mater 135(1–3):280–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.11.075
Morin-Crini N, Loiacono S, Placet V, Torri G, Bradu C, Kostić M et al (2019) Hemp-based adsorbents for sequestration of metals: a review. Environ Chem Lett 17(1):393–408. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-018-0812-x
Mortaheb HR, Kosuge H, Mokhtarani B, Amini MH, Banihashemi HR (2009) Study on removal of cadmium from wastewater by emulsion liquid membrane. J Hazard Mater 165(1–3):630–636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.10.039
Motaghi M, Ziarati P (2016) Adsorptive removal of cadmium and lead from Oryza sativa rice by banana peel as bio-sorbent. Biomed Pharmacol J 9(2):739–749. https://doi.org/10.13005/bpj/998
Naidoo S, Olaniran A (2014) Treated wastewater effluent as a source of microbial pollution of surface water resources. Int J Environ Res Public Health 11(1):249–270. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110100249
Ngah WW, Hanafiah M (2008) Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater by chemically modified plant wastes as adsorbents: a review. Bioresour Technol 99(10):3935–3948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.06.011
Nguyen TC, Loganathan P, Nguyen TV, Kandasamy J, Naidu R, Vigneswaran S (2018) Adsorptive removal of five heavy metals from water using blast furnace slag and fly ash. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(21):20430–20438. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9610-4
Noor NM, Othman R, Mubarak N, Abdullah EC (2017) Agricultural biomass-derived magnetic adsorbents: preparation and application for heavy metals removal. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 78:168–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2017.05.023
Okamoto M, Morita S, Taguchi H, Kim YH, Kotaka T, Tateyama H (2000) Synthesis and structure of smectic clay/poly (methyl methacrylate) and clay/polystyrene nanocomposites via in situ intercalative polymerization. Polymer 41(10):3887–3890. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-3861(99)00655-2
Pal B (2001) Granular ferric hydroxide for elimination of arsenic from drinking water. In: Technologies for arsenic removal from drinking water, 59–68
Patel P, Raju NJ, Reddy BSR, Suresh U, Sankar D, Reddy T (2018) Heavy metal contamination in river water and sediments of the Swarnamukhi River basin, India: risk assessment and environmental implications. Environ Geochem Health 40(2):609–623. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-017-0006-7
Pu S, Hou Y, Yan C, Ma H, Huang H, Shi Q et al (2018) In situ coprecipitation formed highly water-dispersible magnetic chitosan nanopowder for removal of heavy metals and its adsorption mechanism. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6(12):16754–16765. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b04028
Raman N, Sudharsan S, Pothiraj K (2012) Synthesis and structural reactivity of inorganic–organic hybrid nanocomposites–a review. J Saudi Chem Soc 16(4):339–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2011.01.012
Rehman R, Farooq S, Mahmud T (2019) Use of agro-waste Musa acuminata and Solanum tuberosum peels for economical sorptive removal of emerald green dye in ecofriendly way. J Clean Prod 206:819–826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.09.226
Saint-Jacques N, Brown P, Nauta L, Boxall J, Parker L, Dummer TJ (2018) Estimating the risk of bladder and kidney cancer from exposure to low-levels of arsenic in drinking water, Nova Scotia, Canada. Environ Int 110:95–104
Saka C, Şahin Ö, Küçük MM (2012) Applications on agricultural and forest waste adsorbents for the removal of lead (II) from contaminated waters. Int J Environ Sci Technol 9(2):379–394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-012-0041-y
Salahudeen N, Ahmed AS, Ala’a H, Dauda M, Waziri SM, Jibril BY, Al-Sabahi J (2015) Synthesis, characterization and adsorption study of nano-sized activated alumina synthesized from kaolin using novel method. Powder Technol 280:266–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2015.04.024
Samiey B, Cheng C-H, Wu J (2014) Organic-inorganic hybrid polymers as adsorbents for removal of heavy metal ions from solutions: a review. Materials 7(2):673–726. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7020673
Satapathy D, Natarajan G (2006) Potassium bromate modification of the granular activated carbon and its effect on nickel adsorption. Adsorption 12(2):147–154. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-006-0376-0
Say R, Birlik E, Erdemgil Z, Denizli A, Ersöz A (2008) Removal of mercury species with dithiocarbamate-anchored polymer/organosmectite composites. J Hazard Mater 150(3):560–564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.03.089
Setiawan BD, Rizqi O, Brilianti NF, Wasito H (2018) Nanoporous of waste avian eggshell to reduce heavy metal and acidity in water. Sustain Chem Pharm 10:163–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2018.10.002
Shah J, Jan MR, ul Haq A, Zeeshan M (2015) Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies for sorption of Ni (II) from aqueous solution using formaldehyde treated waste tea leaves. J Saudi Chem Soc 19(3):301–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2012.04.004
Shweta K, Jha H (2016) Synthesis and characterization of crystalline carboxymethylated lignin–TEOS nanocomposites for metal adsorption and antibacterial activity. Biores Bioproces 3(1):31. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-016-0107-7
Sillanpää M, Ncibi MC, Matilainen A, Vepsäläinen M (2018) Removal of natural organic matter in drinking water treatment by coagulation: a comprehensive review. Chemosphere 190:54–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.09.113
Singh K, Talat M, Hasan S (2006) Removal of lead from aqueous solutions by agricultural waste maize bran. Bioresour Technol 97(16):2124–2130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2005.09.016
Singh N, Gupta K (2016) Adsorption of heavy metals: a review. Int J Innov Res Sci Eng Technol 5(2)
Şölener M, Tunali S, Özcan AS, Özcan A, Gedikbey T (2008) Adsorption characteristics of lead (II) ions onto the clay/poly (methoxyethyl) acrylamide (PMEA) composite from aqueous solutions. Desalination 223(1–3):308–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2007.01.221
Streets DG, Lu Z, Levin L, ter Schure AF, Sunderland EM (2018) Historical releases of mercury to air, land, and water from coal combustion. Sci Total Environ 615:131–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.207
Sud D, Mahajan G, Kaur M (2008) Agricultural waste material as potential adsorbent for sequestering heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions–A review. Bioresour Technol 99(14):6017–6027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.11.064
Sun Y, Shah KJ, Sun W, Zheng H (2019) Performance evaluation of chitosan-based flocculants with good pH resistance and high heavy metals removal capacity. Sep Purif Technol 215:208–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.01.017
Tripathi A, Ranjan MR (2015) Heavy metal removal from wastewater using low cost adsorbents. J Bioremed Biodegr 6(6):1–5. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-6199.1000315
Ulusoy U, Şimşek S, Ceyhan Ö (2003) Investigations for modification of polyacrylamide-bentonite by phytic acid and its usability in Fe 3+, Zn 2+ and UO 2 2+ adsorption. Adsorption 9(2):165–175. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024297411400
Urgun-Demirtas M, Benda PL, Gillenwater PS, Negri MC, Xiong H, Snyder SW (2012) Achieving very low mercury levels in refinery wastewater by membrane filtration. J Hazard Mater 215:98–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.02.040
Vongdala N, Tran H-D, Xuan T, Teschke R, Khanh T (2019) Heavy metal accumulation in water, soil, and plants of municipal solid waste landfill in Vientiane, Laos. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16(1):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16010022
Wang X, Guo Y, Yang L, Han M, Zhao J, Cheng X (2012) Nanomaterials as sorbents to remove heavy metal ions in wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol, 2(7), 154. https://doi.org/10.4172/2161-0525.1000154
Xu J, Cao Z, Zhang Y, Yuan Z, Lou Z, Xu X, Wang X (2018) A review of functionalized carbon nanotubes and graphene for heavy metal adsorption from water: preparation, application, and mechanism. Chemosphere 195:351–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.061
Zhang D, Karki AB, Rutman D, Young DP, Wang A, Cocke D et al (2009) Electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanocomposite fibers reinforced with Fe3O4 nanoparticles: fabrication and property analysis. Polymer 50(17):4189–4198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2009.06.062
Zhang X, Yang L, Li Y, Li H, Wang W, Ye B (2012) Impacts of lead/zinc mining and smelting on the environment and human health in China. Environ Monit Assess 184(4):2261–2273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2115-6
Zhong X, Zhong C (2017) Mitochondrial biogenesis in response to chromium (VI) toxicity in human liver cells. Int J Mol Sci 18(9):1877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091877
Zhao Q, Wang Y, Cao Y, Chen A, Ren M, Ge Y et al (2014) Potential health risks of heavy metals in cultivated topsoil and grain, including correlations with human primary liver, lung and gastric cancer, in Anhui province, eastern China. Sci Total Environ 470:340–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.09.086
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Editor(s) (if applicable) and The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Sabir, A., Altaf, F., Batool, R., Shafiq, M., Khan, R.U., Jacob, K.I. (2021). Agricultural Waste Absorbents for Heavy Metal Removal. In: Inamuddin, Ahamed, M., Lichtfouse, E., Asiri, A. (eds) Green Adsorbents to Remove Metals, Dyes and Boron from Polluted Water. Environmental Chemistry for a Sustainable World, vol 49. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-47400-3_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-47400-3_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-47399-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-47400-3
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)