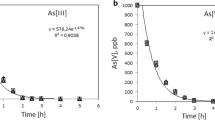
Abstract
According to WHO, 140 million peoples across the world are under the threat of arsenic poisoning. This call for technological intervention to remove arsenic from contaminated water and the availability of suitable point-of-use treatment may be a suitable option. A domestic filter was designed for removal of arsenic from water having both arsenic and iron at higher concentration. The ferro-cement filter consists of a sand-clay-rice husk candle in the upper chamber for iron removal. The second chamber houses a bed of Activated Alumina (AA) within a polypropylene container. This candle essentially functions on the principle of oxidation of iron to insoluble ferric hydroxide precipitates and their removal by the candle. Ferric hydroxide has a keen affinity towards both trivalent and pentavalent arsenic. Therefore, the candle is observed to remove significant arsenic along with iron. The activated alumina bed subsequently acts as a polishing unit to remove further residual arsenic.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sahani, N., Lee, J.Y., Xu, H., Ciardelli, M., Gaillard, J.F.: Role of Fe II and phosphate in arsenic uptake by coprecipitation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 71(13), 3193–3210 (2007)
Sarkar, S., Gupta, A., Biswas, R.K., Deb, A.K., Greenleaf, J.E., Sengupta, A.K.: Well-head arsenic removal units in remote villages of Indian subcontinent: field results and performance evaluation. Water Res. 39(10), 2196–2206 (2005)
Gupta, V.K., Saini, V.K., Jain, N.: Adsorption of As (III) from aqueous solution by iron oxide coated sand. J. Coll. Intr. 288(1), 55–60 (2005)
Jeong, Y., Fan, M., Singh, S., Chuang, C., Saha, B., Leeuwen, J.H.: Evaluation of iron oxide and aluminium oxide as potential arsenic (V) adsorbents. Chem. Eng. Process. 46(10), 1030–1039 (2007)
Hering, J.G., Elimelech, M.: Arsenic Removal by Enhanced Coagulation and Membrane Processes. American Water Works Association Research Foundation Report, Denver (1996)
Kumar, P.T., Chaudhuri, S., Khilar, K.C., Mahajan, S.P.: Removal of arsenic from water by electrocoagulation. Chemosphere 55(9), 1245–1252 (2004)
Pierce, M.L., Moore, C.B.: Adsorption of arsenite and arsenate on amorphous iron hydroxide. Water Res. 16(7), 1247–1253 (1982)
APHA: Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 18th edn. APHA, AWWA and WEF, Washington DC (1992)
Acknowledgement
The authors are thankful to United Nation International Children’s Emergency Fund (UNICEF), Kolkata, India for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Koner, S., Gupta, A. (2020). Enhanced Removal of Arsenic Through a Low Cost Domestic Filter Designed by Innovative Technology. In: Dawn, S., Balas, V., Esposito, A., Gope, S. (eds) Intelligent Techniques and Applications in Science and Technology. ICIMSAT 2019. Learning and Analytics in Intelligent Systems, vol 12. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-42363-6_41
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-42363-6_41
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-42362-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-42363-6
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)