Abstract
Antimicrobial agents are vital to fight infectious diseases which are pooling up day by day. The treatment of microbial infections is increasingly getting convoluted by the ability of microorganisms to develop resistance towards a wide range of antimicrobial agents. Resistance is most often an evolutionary process taking place either through lateral gene transfer or during antibiotic therapy, thereby contributing to the emergence of diseases that were under good control for many years.
Further, drug resistance enforces high-dose administration of antibiotics leading to adverse side effects and intolerable toxicity. This has prompted the search for alternative strategies to treat microbial infections either by controlling their growth or by preventing the formation of bacterial biofilms. Recently tremendous developments in the field of nanotechnology have been recorded with nanoscale materials emerging as novel antimicrobial agents.
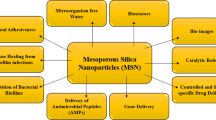
Nanotechnology is an interdisciplinary area of science with promising interests across the globe steering into nanoindustrial revolution with innumerable applications. The enormous diversity of the nanoparticles that exhibit new and enhanced size-dependent properties compared to their bulk material are being exploited as antimicrobials for treating infectious diseases. Numerous nanodevices like carbon nanotubes, quantum dots, and polymeric micelles have been reported as potential antibacterial candidates. In the present scenario, mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) are emerging for their widespread applications as antibacterial and antibiofilm agents. MSNs are constituted of an amorphous silica matrix with ordered porous molecular sieves characterized by periodic arrangements of uniformly sized mesopores (diameter between 2 and 50 nm). MSNs with uniform and tailorable pore dimensions with high surface areas are currently being employed in a number of applications such as wastewater remediation, indoor air cleaning, bio-catalysis, drug delivery, CO2 capture, bioanalytical sample preparation, pervaporation membrane improvement, etc. MSNs with their unique properties like chemical stability, surface functionality, and biocompatibility are used in quorum quenching as well as prospective antibacterial agents. The present book chapter deals with MSNs and their applications as possible antibacterial and antibiofilm agents.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albanese A, Tang PS, Chan WCW (2012) The effect of nanoparticle size, shape, and surface chemistry on biological systems. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 14:1–16
Allahverdiyev AM, Kon KV, Abamor ES, Bagirova M, Rafailovich M (2011) Coping with antibiotic resistance: combining nanoparticles with antibiotics and other antimicrobial agents. Expert Rev Anti-Infect Ther 9:1035–1052
Ammer MR, Zaman S, Khalid M, Bilal M, Erum S, Huang D, Che S (2016) Optimization of antibacterial activity of Eucalyptus tereticornis leaf extracts against Escherichia coli through response surface methodology. J Radiat Res Appl Sci 9(4):376–385
An N, Lin H, Yang C, Zhang T, Tong R, Chen Y, Qu F (2016) Gated magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles for intracellular enzyme-triggered drug delivery. Mater Sci Eng 69:292–300
Ashraf MA, Khan AM, Ahmad M, Sarfraz M (2015) Effectiveness of silica-based sol-gel microencapsulation method for odorants and flavors leading to sustainable environment. Front Chem 3:42
Aziz N, Fatma T, Varma A, Prasad R (2014) Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Scenedesmus abundans and evaluation of their antibacterial activity. J Nanopart 2014:689419. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/689419
Aziz N, Faraz M, Pandey R, Sakir M, Fatma T, Varma A, Barman I, Prasad R (2015) Facile algae-derived route to biogenic silver nanoparticles: synthesis, antibacterial and photocatalytic properties. Langmuir 31:11605–11612. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b03081
Aziz N, Pandey R, Barman I, Prasad R (2016) Leveraging the attributes of Mucor hiemalis-derived silver nanoparticles for a synergistic broad-spectrum antimicrobial platform. Front Microbiol 7:1984. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01984
Aziz N, Faraz M, Sherwani MA, Fatma T, Prasad R (2019) Illuminating the anticancerous efficacy of a new fungal chassis for silver nanoparticle synthesis. Front Chem 7:65. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2019.00065
Bagwe RP, Hilliard LR, Tan W (2006) Surface modification of silica nanoparticles to reduce aggregation and nonspecific binding. Langmuir 22:4357–4362
Balaure PC, Boarca B, Popescu RC, Savu D, Trusca R, Vasile BS,, Grumezescu AM, Holban AM, Bolocan A, Andronescu E (2017) Bioactive mesoporous silica nanostructures with anti-microbial and anti-biofilm properties. Int J Pharm 531:35–46
Balouiri M, Sadiki M, Ibnsouda SK (2016) Methods for in vitro evaluating antimicrobial activity: a review. J Pharm Anal 6(2):71–79
Bayir S, Barras A, Boukherroub R, Szunerits S, Raehm L, Richeter S, Durand J (2018) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for recent photodynamic therapy applications. Photochem Photobiol Sci 17(11):1651–1674. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8PP00143J
Bein KMT (2017) Talented mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Chem Mater 29(1):371–388
Bobo D, Robinson KJ, Islam J, Thurecht KJ, Corrie SR (2016) Nanoparticle-based medicines: a review of FDA-approved materials and clinical trials to date. Pharm Res 33:2373–2387
Chan AC, Cadena MB, Townley HE, Fricker MD, Thompson IP (2016) Effective delivery of volatile biocides employing mesoporous silicates for treating biofilms. J R Soc Interface 14:20160650
Chen CY, Burkett SL, Li HX, Davis ME (1993) Ordered mesoporous and macro porous inorganic film and membrane. Microporous Mater 2:27–34
Cheng G, Dai M, Ahmed S, Hao H, Wang X, Yuan Z (2016) Antimicrobial drugs in fighting against antimicrobial resistance. Front Microbiol 7(470):1–11
Cicily J (2017) Biomedical applications of mesoporous silica particles. University of Iowa, PhD thesis, p 2017
Coenye T, Nelis HJ (2010) In vitro and in vivo model systems to study microbial biofilm formation. J Microbiol Methods 83(2):89–105
Fruijtier-Pölloth C (2012) The toxicological mode of action and the safety of synthetic amorphous silica-a nanostructured material. Toxicology 294:61–79
Grumezescu AM, Andronescu E, Ficai A, Voicu G, Cocos O, Chifiriuc MC (2013) Eugenia caryophyllata essential oil- SiO2 biohybrid structure for the potentiation of antibiotics’ activity. Rom J Mater 43(2):160–166
Gupta S, Variyar PS (2016) Nanoencapsulation of essential oils for sustained release: application as therapeutics and antimicrobials. In: Mihai Grumezescu A (ed) Nanotechnology in the agri-food industry. Academic, Amsterdam, pp 641–672. (Encapsulations.)
Gurunathan S, Han JW, Deug-Nam KW, Kim J-H (2014) Enhanced antibacterial and anti-biofilm activities of silver nanoparticles against Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. Nanoscale Res Lett 9:373
Hom C, Lu J, Liong M, Luo H, Li Z, Zink JI, Tamanoi F (2010) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles facilitate delivery of siRNA to shutdown signaling pathways in mammalian cells. Small 6:1185–1190
Huang X, Young NP, Townley HE (2013) Characterization and comparison of mesoporous silica particles for optimized drug delivery. Nanomater Nanotechnol 4:1. https://doi.org/10.5772/58290
Hudson SP, Padera RF, Langer R, Kohane DS (2008) The biocompatibility of mesoporous silicates. Biomaterials 29:4045–4055
Ispas C, Sokolov I, Andreescu S (2009) Enzyme functionalized mesoporous silica for bioanalytical applications. Anal Bioanal Chem 393:543–554
Jorge J, Verelst M, de Castro GR, Martines MAU (2016) Synthesis parameters for control of mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs). Biointerface Res Appl Chem 6(5):1520–1524
Juan L. Paris, M. Victoria Cabañas, Miguel Manzano, María Vallet-Regí (2015) Polymer-Grafted mesoporous silica nanoparticles as ultraso/cund-responsive drug carriers ACS nano 9(11):11023–11033
Kar S (2016) Development of nano mullite based mesoporous silica biocer with incorporated bacteria for arsenic remediation. Ceram Silik 60(3):1–10
Kong B, Seog JH, Graham LM, Lee SB (2011) Experimental considerations on the cytotoxicity of nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 6(5):929–941
Kavanagh F (1992) Analytical microbiology-II. Academic, New York, pp 241–243
Lakshmi P, Sravani K, Swetha MK, Jhansi Rani S, Kollu P, Parine NR, Murali Krishna R, Pammi S (2017) Diospyros assimilis root extract assisted bio synthesized silver nanoparticles and their evaluation of antimicrobial activity. IETnanotechnology 12(2):133–137
Lee B-Y, Li Z, Clemens DL, Dillon BJ, Hwang AA, Zink JI (2016) Redox-triggered release of moxifloxacin from mesoporous silica nanoparticles functionalized with disulfide snap tops enhances efficacy against pneumonic tularemia in mice. Small 12(27):3690–3702
Li L, Wang H (2013) Enzyme-coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles as efficient antibacterial agents in vivo. Adv Healthc Mater 2(10):1351–1360
Li Z, Jonathan CB, Aleksandr Bosoy J, Stoddart F, Jeffrey IZ (2012) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in biomedical applications. Chem Soc Rev 41:2590–2605
Malone M, Goeres DM, Gosbell I, Vickery K, Jensen S, Stoodley P (2017) Approaches to biofilm-associated infections: the need for standardized and relevant biofilm methods for clinical applications. Expert Rev Anti-Infect Ther 15(2):147–156
Merezeanu N, Gheorghe I, Popa M, Chifiriuc MC, Lazar V, Pantea O, Banu O, Bolocan A, Grigore R, Beresteanu VS (2016) Virulence and resistance features of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from patients with cardiovascular diseases. Biointerface Res Appl Chem 6(2):1117–1121
Moller K, Kobler J, Bein T (2007) Colloidal suspensions of nanometer-sized mesoporous silica. Adv Funct Mater 17(4):605–612
Obeidat M, Shatnawi M, Al-alawi M, Al-Zubi E, Al-Dmoor H, Al-Qudah M, El-Qudah J, Otri I et al (2012) Antimicrobial activity of crude extracts of some plant leaves. Res J Microbiol 7:59–67
Paul Catalin Balaure, Bianca Boarca, Roxana Cristina Popescu, Diana Savu, Roxana Trusca, Bogdan Stefan Vasile, Alexandru Mihai Grumezescu, Alina Holban, Alexandra Bolocan, Ecaterina Andronescu (2017) Bioactive mesoporous silica nanostructures with anti-microbial and anti-biofilm properties. Int J Pharm 531:35–46
Percival SL, Bowler R, Woods EJ (2008) Assessing the effect of an antimicrobial wound dressing on biofilms. Wound Repair Regen 16:52–57
Portin L (2012) Layer by layer assembly of the polyelectrolyte on mesoporous silicon. In: Biosciences. University of Eastern Finland, Finland, pp 1–59
Prasad R, Pandey R, Barman I (2016) Engineering tailored nanoparticles with microbes: quo vadis. WIREs Nanomed Nanobiotechnol 8:316–330. https://doi.org/10.1002/wnan.1363
Prasad R, Pandey R, Varma A, Barman I (2017) Polymer based nanoparticles for drug delivery systems and cancer therapeutics. In: Kharkwal H, Janaswamy S (eds) Natural polymers for drug delivery. CAB International, UK, pp 53–70
Qi G, Li L, Yu F, Wang H (2013) Vancomycin-modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles for selective recognition and killing of pathogenic Gram-positive bacteria over macrophage-like cells. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:10874–10881
Reema N, Usha YN, Ashok MR, Garg S (2018) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles: a comprehensive review on synthesis and recent advances. Pharmaceutics 10(3):118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030118
Renwick MJ, Brogan DM, Mossialos E (2016) A systematic review and critical assessment of incentive strategies for discovery and development of novel antibiotics. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 69(2):73–88
Sahoo B, Devi KS, Dutta S, Maiti TK, Pramanik P, Dhara D (2015) Biocompatible mesoporous silica-coated superparamagnetic manganese ferrite nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery and MR imaging applications. Nanomedicine 11(2):313–327
Sakai-Kato K, Hasegawa T, Takaoka A, Kato M, Toyo’oka T, Utsunomiya-Tate N (2011) Controlled structure and properties of silicate nanoparticle networks for incorporation of biosystem components. Nanotechnology 22:205–702
Saladino ML, Rubino S, Colomba P, Girasolo MA, Chillura Martino DF, Demirbag C, Caponetti E (2016) Pt(II) complex @mesoporous silica: preparation, characterization and study of release. Biointerface Res Appl Chem 6(6):1621–1626
Sen Karaman D, Sarwar S, Desai D, Björk E, Magnus Odén P, Chakrabarti J, Rosenholm M, Chakraborti S (2016) Shape engineering boosts antibacterial activity of chitosan-coated mesoporous silica nanoparticle doped with silver: a mechanistic investigation. J Mater Chem 4(19):3292–3304
Sharmila Devi S, Shanmuga Priya S, Sujitha MV (2016) Synthesis of mesoporous silica nanoparticles and drug loading for Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 8(5):196–201
Song Y, Li Y, Qien X, Liu Z (2017) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for stimuli-responsive controlled drug delivery: advances, challenges, and outlook. Int J Nanomed 12:87–110
Sousa FL, Santos M, Rocha SM, Trindade T (2014) Encapsulation of essential oils in SiO2 microcapsules and release behaviour of volatile compounds. J Microencapsul 31(7):627–635
Spataru CI, Ianchis R, Petcu C, Nistor CL, Purcar V, Trica B, Nitu SG, Somoghi R, Alexandrescu E, Oancea F, Donescu D (2016) Synthesis of non-toxic silica particles stabilized by molecular complex oleic-acid/sodium oleate. Int J Mol Sci 17(11):19–36
Tarn D, Ashley CE, Xue M, Carnes EC, Zink JI, Brinker CJ (2013) Mesoporous silica nanoparticle nanocarriers: biofunctionality and biocompatibility. Acc Chem Res 46:792–801
Tozuka Y, Wongmekiat A, Kimura K, Moribe K, Yamamura S, Yamamoto K (2005) Effect of pore size of FSM-16 on the entrapment of Flurbiprofen in mesoporous structures. Chem Pharm Bull 53:974–977
Trewyn GB, Giri S, Igor IS, Victor SYL (2007) Mesoporous silica nanoparticle based controlled release, drug delivery, and biosensor systems. Chem Commun 2007:3236–3245
Ventola CL (2015) The antibiotic resistance crisis: part 1: causes and threats. Pharm Ther 40(4):277–283
Wang F, Guo C, Yang L-R, Liu CZ (2010) Magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles: fabrication and their laccase immobilization performance. Bioresour Technol 101:8931–8935
Wang Y, Zhao Q, Han N, Bai L, Li J, Liu J, Che E, Hu L, Zhang Q, Jiang T, Wang S (2015) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in drug delivery and biomedical applications. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med Mol Med 11(2):313–327
Webster TJ, Seil I (2012) Antimicrobial applications of nanotechnology: methods and literature. Int J Nanomedicine 7:2767–2781
Worthington RJ, Richards JJ, Melander C (2012) Small molecule control of bacterial biofilms. Org Biomol Chem 10(37):7457
Wu W, Ye C, Xiao H, Sun X, Qu W, Li X, Chen M, Li J (2016) Hierarchical mesoporous silica nanoparticles for tailorable drug release. Int J Pharm 511(1):65–72
Xia TA, Kovochich M, Liong M, Meng H, Kabehie S, George S, Zink JI, Nel AE (2009) Polyethyleneimine coating enhances the cellular uptake of mesoporous silica nanoparticles and allows safe delivery of siRNA and DNA constructs. ACS Nano 3:3273–3286
Xu C, Hea Y, Lia Z, Yusilawatic AN, Ye Q (2018) Nanoengineered hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles for the delivery of anteimicrobial protein into biofilm. J Mater Chem B 6:1899–1902
Zhang Y, Yuan Q, Chen T, Zhang X, Tan YCW (2012) DNA-capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles as an ion-responsive release system to determine the presence of mercury in aqueous solutions. Anal Chem 84(4):1956–1962
Zhang Y, Liu X, Wang Y, Jiang P, Quek SY (2016) Antibacterial activity and mechanism of cinnamon essential oil against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Food Control 59:282–289
Zhao Q, Han N, Bai L, Li J, Liu J, Che E, Hu L, Zhang Q, Jiang T, Wang S (2017) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in drug delivery and biomedical applications. Nanomedicine 11(2):313–327
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Lakshmi, P., Pola, S. (2020). Mesoporous Silica Nanomaterials as Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Agents. In: Prasad, R., Siddhardha, B., Dyavaiah, M. (eds) Nanostructures for Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Applications. Nanotechnology in the Life Sciences. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-40337-9_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-40337-9_16
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-40336-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-40337-9
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)