Abstract
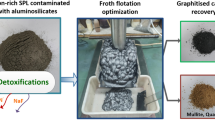
Froth flotation is a low-cost SPL recycling technique, which separates carbon in spent potlining (SPL) from other components. The carbon is enriched in the flotation concentrate since it has outstanding hydrophobicity, and cryolite is enriched in the flotation tailing. During the process, NaF in SPL dissolves in water and can be recovered by evaporation and crystallization, whilst cyanides are decomposed. The recycling efficiency is evaluated by flotation index which is greatly affected by the collecting agent . In this study, the effects of types, dosing times, dosage and emulsification of collecting agent on the flotation index were studied. The optimized collecting agent was adopted in a quadruple-roughing double-cleaning closed-circuit experiment. The results indicated that carbon grade and recovery of concentrate were higher than 80% and 95%, respectively, while the NaAl11O17 and Na3AlF6 were successfully concentrated in the floatation tailing.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Robshaw, S. Tukra, D.B. Hammond, G.J. Leggett, M.D. Ogden (2019) Highly efficient fluoride extraction from simulant leachate of spent potlining via La-loaded chelating resin. An equilibrium study. Journal of hazardous materials 361: 200–209.
G. Ospina, M.I. Hassan (2017) Spent Pot Lining Characterization Framework. JOM 69: 1–7.
G. Holywell, R. Breault (2013) An Overview of Useful Methods to Treat, Recover, or Recycle Spent Potlining. JOM 65: 1441–1451.
G. Sun, G. Zhang, J. Liu, W. Xie, F. Evrendilek, M. Buyukada (2019) (Co-) combustion behaviors and products of spent potlining and textile dyeing sludge. Journal of Cleaner Production 224: 384–395.
C. Ghenai, A. Inayat, A. Shanableh, E. Al-Sarairah, I. Janajreh (2019) Combustion and emissions analysis of Spent Pot lining (SPL) as alternative fuel in cement industry. Science of The Total Environment 684: 519–526.
G. Sun, G. Zhang, J. Liu, W. Xie, J. Kuo, X. Lu, M. Buyukada, F. Evrendilek, S. Sun (2019) Thermogravimetric and mass-spectrometric analyses of combustion of spent potlining under N2/O2 and CO2/O2 atmospheres. Waste management 87: 237–249.
I.V. Flores, F. Fraiz, R.A.L. Junior, M.C. Bagatini (2019) Evaluation of spent pot lining (SPL) as an alternative carbonaceous material in ironmaking processes. Journal of Materials Research & Technology 8(1): 33–40.
L. Gao, S. Mostaghel, S. Ray, K. Chattopadyay (2016) Using SPL (Spent Pot-Lining) as an Alternative Fuel in Metallurgical Furnaces. Metallurgical & Materials Transactions E 3: 1–10.
X. Jin, Z. Liuyun, Y. Jie, Y. Zhen, T. Lei, W. Zhian, Z. Zhenhua (2018) Co-utilization of spent pot-lining and coal gangue by hydrothermal acid-leaching method to prepare silicon carbide powder. Journal of Cleaner Production 204: 848–860.
N. Li, Y. Jiang, X. Lv, L. Gao, K. Chattopadhyay (2019) Vacuum Distillation-Treated Spent Potlining as an Alternative Fuel for Metallurgical Furnaces. JOM: 1–8.
L. Birry, S. Leclerc, S. Poirier (2016) The LCL&L process: A sustainable solution for the treatment and recycling of spent potlining. Light Metals 2016: 467–471.
D.F. Lisbona, K.M. Steel (2008) Recovery of fluoride values from spent pot-lining: Precipitation of an aluminium hydroxyfluoride hydrate product. Separation & Purification Technology 61: 182–192.
Z.N. Shi, L.I. Wei, H.U. Xian-Wei, B.J. Ren, B.L. Gao (2012) Recovery of carbon and cryolite from spent pot lining of aluminium reduction cells by chemical leaching. Transactions of the Nonferrous Metals Society of China 22: 222–227.
S.B. Sleap, B.D. Turner, S.W. Sloan (2015) Kinetics of fluoride removal from spent pot liner leachate (SPLL) contaminated groundwater. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering 3: 2580–2587.
J. Xiao, J. Yuan, Z. Tian, K. Yang, Z. Yao, B. Yu, L. Zhang (2018) Comparison of ultrasound-assisted and traditional caustic leaching of spent cathode carbon (SCC) from aluminum electrolysis. Ultrasonics sonochemistry 40: 21–29.
J. Yuan, J. Xiao, F. Li, B. Wang, Z. Yao, B. Yu, L. Zhang (2018) Co-treatment of spent cathode carbon in caustic and acid leaching process under ultrasonic assisted for preparation of SiC. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry 41: 608–618.
D. Yu, V. Mambakkam, A.H. Rivera, D. Li, K. Chattopadhyay (2015). Spent Potlining (SPL): A myriad of opportunities. Aluminium International Today.
V.V. Kondrat’ev, E.P. Rzhechitskii, S.G. Shakhrai, A.I. Karlina, I.A. Sysoev (2016) Recycling of Electrolyzer Spent Carbon-Graphite Lining with Aluminum Fluoride Regeneration. Metallurgist 60: 571–575.
L. Nan, X. Gang, X.W. Zu, Q.H. Yan, X.L. Rong (2014) Recycle of Spent Potlining with Low Carbon Grade by Floatation. Advanced Materials Research 881–883: 1660–1664.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Science Foundation of Yunnan Provincial Department of Education (Grant No. 2019J0644).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society
About this paper
Cite this paper
Li, N., Gao, L., Chattopadhyay, K. (2020). Experimental Study on the Collecting Agent for Spent Potlining Flotation Index Optimization. In: Tomsett, A. (eds) Light Metals 2020. The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36408-3_171
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36408-3_171
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-36407-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-36408-3
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)