Abstract
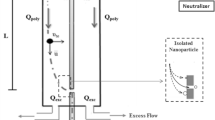
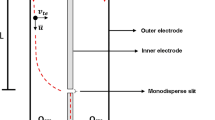
Nanotechnology characterizes an important area in engineering due to various applications that can be found, such as electronics and pharmaceutical industries, development of air filters, among others. From the environmental point of view, because nanometric particles provide special characteristics to the products, emission of these particles into the air must be limited. Among the approaches proposed in the literature, the electrical mobility technique is an emerging strategy used to ensure an aerosol stream with monodispersed particles. This technique is based on the ability of a charged particle to cross an electrical field. Thus, depending on the size of the particles, the bigger ones will arrive later in the central electrode than the smaller ones, and only a narrow band of sizes will be collected in a slit located at the bottom of the equipment. In order to characterize the relation between the monodispersed and polydispersed aerosol stream, an inverse problem is formulated and solved by using differential evolution. The objective function consists of determining transfer functions that minimize the sum of difference between predicted and experimental concentrations of NaCl obtained by a differential mobility analyzer. The results demonstrated that the proposed methodology was able to obtain a good approximation for two classical transfer functions.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kauffeldt, T., Kleinwechter, H., Schmidt-Ott, A.: Absolute on-line measurement of the magnetic moment of aerosol particles. Chem. Eng. Commun. 151(1), 169–185 (1995)
Gonzalez, D., Nasibulin, A.G., Jiang, H., Queipo, P.: Electrospraying of ferritin solutions for the production of monodisperse iron oxide nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. Commun. 194, 901–912 (2007)
Lee, H., You, S., Pikhitsa, P.V., Kim, J., Kwon, S., Woo, C.G., Choi, M.: Three-dimensional assembly of nanoparticles from charged aerosols. Nano Lett. 11(1), 119–124 (2011)
Pui, D.Y.H, Chen, D.R.: Nanometer particles: a new frontier for multidisciplinary research. J. Aerosol Sci. 28, 539–554 (1997)
Shi, J., Votruba, A.R., Farokhzad, O.C., Langer, R.: Nanotechnology in drug delivery and tissue engineering: from discovery to applications. Nano Lett. 10, 3223–3230 (2010)
Seto, T., Kawakami, Y., Suzuki, N., Hirasawa, M., Aya, N.: Laser synthesis of uniform silicon single nanodots. Nano Lett. 6, 315–318 (2001)
Rosati, J.A., Leith, D., Kim, C.S.: Aerosol Sci. Technol. 37, 528–535 (2003)
Intra, P., Tippayawong, N.: Brownian diffusion effect on nanometer aerosol classification in electrical mobility spectrometer. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 26(1), 269–276 (2009)
Luond, F., Schlatter, J.: Improved monodispersity of size selected aerosol particles with a new charging and selection scheme for tandem DMA setup. J. Aerosol Sci. 62, 40–55 (2013)
Kievit, O., Weiss, M., Verheijen, P.J.T., Marijnissen, J.C.M., Scarlett, B.: The online chemical analysis of single particles using aerosol beams and time of flight mass spectrometry. Chem. Eng. Commun. 151(1), 79–100 (1995)
Zhao, Z.M., Pfeffer, R.: A semi-empirical approach to predict the total collection efficiency of electrostatic precipitators. Chem. Eng. Commun. 148–150(1), 315–331 (1995)
Hagwood, C.: The DMA transfer function with Brownian motion a trajectory/Monte-Carlo approach. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 30(1), 40–61 (1999)
Martinsson, B.G., Karlsson, M.N.A., Frank, G.: Methodology to estimate the transfer function of individual differential mobility analyzers. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 35(4), 815–823 (2001)
Seol, K.S., Yabumoto, J., Takeuchi, K.: A differential mobility analyzer with adjustable column length for wide particle-size-range measurements. Aerosol Sci. 33, 1481–1492 (2002)
Karlsson, M.N.A., Martinsson, B.G.: Methods to measure and predict the transfer function size dependence of individual DMAs. Aerosol Sci. 34, 603–625 (2003)
Song, D.K., Lee, H.M., Chang, H., Kim, S.S., Shimada, M., Okuyama, K.: Performance evaluation of long differential mobility analyzer (LDMA) in measurements of nanoparticles. Aerosol Sci. 37, 598–615 (2006)
Song, D.K., Dhaniyala, S.: Nanoparticle cross-flow differential mobility analyzer (NCDMA): theory and design. Aerosol Sci. 38, 964–979 (2007)
Ramechecandane, S., Beghein, C., Allard, F., Bombardier, P.: Modelling ultrafine/nano particle dispersion in two differential mobility analyzers (M-DMA and L-DMA). Build. Environ. 46, 2255–2266 (2011)
Cai, R., Chen, D-R., Hao, J., Jiang, J.: A miniature cylindrical differential mobility analyzer for sub-3 nm particle sizing. J. Aerosol Sci. 106, 111–119 (2017)
Dalcin, M.G., Nunes, D.M., Damasceno, J.J.R., Arouca, F.O.: Project and construction of a differential mobility analyzer to produce monosized nanoparticles materials. Sci. Forum 802, 197–202 (2014)
Storn, R., Price, K.: Differential evolution: a simple and efficient adaptive scheme for global optimization over continuous spaces. International Computer Science Institute, 12, pp. 1–16 (1995)
Camargo, E.C.M.: Performance evaluation of a low cost electrostatic analyzer for classification of nanoparticles sizes. Federal University de Uberlândia (2019, In Portuguese)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support from FAPEMIG and CNPq agencies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Borges, L.C., Camargo, E.C.d.M., Damasceno, J.J.R., Arouca, F.d.O., Lobato, F.S. (2020). Determination of Nano-aerosol Size Distribution Using Differential Evolution. In: Llanes Santiago, O., Cruz Corona, C., Silva Neto, A., Verdegay, J. (eds) Computational Intelligence in Emerging Technologies for Engineering Applications. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol 872. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-34409-2_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-34409-2_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-34408-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-34409-2
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)