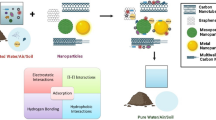
Abstract
The advancement in science and technology contributes directly or indirectly to the increase in waste and toxic materials in the environment. Thus it is required to clean up the contaminants of the environment by eco-friendly, sustainable, and economically adoptable technologies. Present treatment technologies, though efficient, cause several problems which make remediation processes complex. Bioremediation requires long treatment time, and it may not be effective if high contaminant concentrations that are toxic to microorganisms exist. The integration of nanomaterials and bioremediation has great potential to be effective, efficient, and sustainable. Thus use of nanotechnology for bioremediation is a new emerging field, playing an increasingly important role in addressing innovative and effective solutions to a vast range of environmental challenges. The use of nanomaterials for remediation/treatment results is more cost-effective and rapid than current conventional approaches due to their enhanced surface area, transport properties, and sequestration characteristics. Recently nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI), carbon nanotubes, and nano-fibers have been used for the remediation of a variety of contaminants including chlorinated compounds, hydrocarbons, organic compounds, and heavy metals.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson M, Osterlund L, Ljungstrom S, Palmqvist A (2002) Preparation of nanosize anatase and rutile TiO2 by hydrothermal treatment of microemulsions and their activity for photocatalytic wet oxidation of phenol. J Phys Chem B 106:10674–10679
Arkas M, Tsiourvas D, Paleos CM (2003) Functional dendrimeric “Nanosponges” for the removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from water. Chem Mater 15:2844–2847
Asilturk M, Sayýlkan F, Erdemoglu S, Akarsu M, Sayýlkan H, Erdemoglu M, Arpac E (2006) Characterization of hydrothermally synthesized nano-TiO2 crystallite and the photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B. J Hazard Mater B 129:164–170
Aziz N, Faraz M, Pandey R, Sakir M, Fatma T, Varma A, Barman I, Prasad R (2015) Facile algae-derived route to biogenic silver nanoparticles: synthesis, antibacterial and photocatalytic properties. Langmuir 31:11605–11612. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b03081
Aziz N, Pandey R, Barman I, Prasad R (2016) Leveraging the attributes of Mucor hiemalis-derived silver nanoparticles for a synergistic broad-spectrum antimicrobial platform. Front Microbiol 7:1984. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01984
Baker S, Satish S (2012) Endophytes: toward a vision in synthesis of nanoparticles for future therapeutic agents. Int J Bio-Inorg Hybd Nanomater 1:1–11
Bargar JR, Bernier-Latmani R, Giammar DE, Tebo BM (2008) Biogenic uraninite nanoparticles and their importance for uranium remediation. Elements 4:407–412
Bharati B, Sonkar AK, Singh N, Dash D, Chandana R (2017) Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of dyes under sunlight using biocompatible TiO2 nanoparticles. Mater Res Express 4(8):085503
Bhuyan T, Mishra K, Khanuja M, Prasad R, Varma A (2015) Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles from Azadirachta indica for antibacterial and photocatalytic applications. Mater Sci Semicond Process 32:55–61
Bina B, Pourzamani H, Rashidi A, Amin MM (2012) Ethylbenzene removal by carbon nanotubes from aqueous solution. J Environ Sci Public Health 2012:817187. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/817187
Buhleier E, Wehner W, Vogtle F (1978) Cascade and “nonskid chain- like” syntheses of molecular cavity topologies. Synthesis 2:155–158
Castillo VA, Barakat MA, Ramadan MH, Woodcock HL, Kuhn JN (2014) Metal ion remediation by polyamidoamine dendrimers: a comparison of metal ion, oxidation state, and titania immobilization. Int J Environ Sci Technol 11:1497–1502
Chen J, Liu M, Zhang L, Zhang J, Jin L (2003) Application of nano TiO2 towards polluted water treatment combined with electro-photochemical method. Water Res 37:3815–3820
Choe S, Chang YY, Hwang KY, Khim J (2000) Kinetics of reductive denitrification by nanoscale zero-valent iron. Chemosphere 41:1307–1311
Cundy AB, Hopkinson L, Whitby RLD (2008) Use of iron-based technologies in contaminated land and groundwater remediation: a review. Sci Total Environ 400:42–51
Dhillon GS, Brar SK, Kaur S, Verma M (2012) Green approach for nanoparticle biosynthesis by fungi: current trends and applications. Crit Rev Biotechnol 32:49–73
Diallo MS, Balogh L, Shafagati A, Johnson JH, Goddard WA, Tomalia DA (1999) Poly(amidoamine) Dendrimers:Â A New Class of High Capacity Chelating Agents for Cu(II) Ions. Environmental Science & Technology 33 (5):820–824
Dimitrov D (2006) Interactions of antibody conjugated nanoparticles with biological surfaces. Colloids Surf A 8:282–283
Feitz AJ, Joo SH, Guana J, Suna Q, Sedlak DL, Waite TD (2005) Oxidative transformation of contaminants using colloidal zerovalent iron. Colloids Surf A 265:88–94
Feng J, Lim TT (2005) Pathways and kinetics of carbon tetrachloride and chloroform reductions by nano-scale Fe and Fe/Ni particles: comparison with commercial micro-scale Fe and Zn. Chemosphere 59:1267–1277
Feng J, Hu X, Yue PL, Zhu HY, Lu GQ (2003) Degradation of azo-dye orange II by a photoassisted Fenton reaction using a novel composite of iron oxide and silicate nanoparticles as a catalyst. Ind Eng Chem Res 42:2058–2066
Friedrich KA, Henglein F, Stimming U, Unkauf W (1998) Investigations of Pt particles on gold substrates by IR spectroscopy. Colloids Surf A 134:193–206
Grieger KD, Fjordøge A, Hartmann NB, Eriksson E, Bjerg PL, Baun A (2010) Environmental benefits and risks of zero-valent iron particles (nZVI) for in situ remediation: risk mitigation or trade-off? J Contam Hydrol 118:165–183
Guo R, Guo X, Yu D, Hu J (2012) Application research in water treatment of PAMAM dendrimer. Chem Ind Eng Prog 31:671–675
Hua S, Gong JL, Zeng GM, Yao FB, Guo M, Ou XM (2017) Remediation of organochlorine pesticides contaminated lake sediment using activated carbon and carbon nanotubes. Chemosphere 77:65–76
Ilisz I, Dombi A, Mogyorósi K, Dékány I (2004) Photocataltyic water treatment with different TiO2 nanoparticles and hydrophilic/hydrophobic. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 230:89–97
Ingale AG, Chaudhari AN (2013) Biogenic synthesis of nanoparticles and potential applications: an eco- friendly approach. J Nanomed Nanotechnol 4:165–171
Johnson A, Merilis G, Hasting J, Palmer EM, Fitts JP, Chidambaram D (2013) Reductive degradation of organic compounds using microbial nanotechnology. J Electrochem Soc 160:G27–G31
Joo SH, Zhao D (2007) Destruction of lindane and atrazine using stabilized iron nanoparticles under aerobic and anaerobic conditions: effects of catalyst and stabilizer. Chemosphere 70:418–425
Joshi N, Jain N, Pathak A, Singh J, Prasad R, Upadhyaya CP (2018) Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Carissa carandas berries and its potential antibacterial activities. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 86:682–689. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-018-4666-2
Kanatzidis MG, Poeppelmeier KR (2007) Report from the third workshop on future directions of solid-state chemistry: the status of solid-state chemistry and its impact in the physical sciences. Prog Solid State Chem 36:1–133
Kanel SR, Manning B, Charlet L, Choi H (2005) Removal of arsenic (III) from groundwater by nanoscale zero-valent iron. Environ Sci Technol 39:1291–1298
Kanel SR, Greneche JM, Choi H (2006) Arsenic (V) removal from groundwater using nano scale zero-valent iron as a colloidal reactive barrier material. Environ Sci Technol 40:2045–2050
Karn B, Kuiken T, Otto M (2009) Nanotechnology and in situ remediation: a review of the benefits and potential risks. Environ Health Perspect 117:1823–1831
Kavitha KS, Syed B, Rakshith D, Kavitha HU, Yashwantha Rao HC, Harini BP, Satish S (2013) Plants as green source towards synthesis of nanoparticles. Int Res J Bio Sci 2:66–76
Kharissova OV, Dias Rasika HV, Kharisov BI, Pérez BO, Pérez Jiménez VM (2013) The greener synthesis of nanoparticles. Trends Biotechnol 31:240–248
Kshitij CJ, Zhuonan L, Hema V, Mallikarjuna N, Sharmila MK, Mesfin T (2016) Carbon nanotube based groundwater remediation: the case of trichloroethylene. Molecules 21:953–967
Lee C, Kim JY, Lee WI, Nelson KL, Yoon J, Sedlak DL (2008) Bactericidal effect of zero-valent iron nanoparticles on Escherichia coli. Environ Sci Technol 42:4927–4933
Li XQ, Zhang WX (2007) Iron nanoparticles: the core shell structure and unique properties for Ni(II) sequestration. Langmuir 22:4638–4642
Li YH, Wang S, Wei J, Zhang X, Xu C, Luan Z, Wu D, Wei B (2002) Lead adsorption on carbon nanotubes. Chem Phy Lett 357:263–266
Li YH, Dinga J, Luanb Z, Dia Z, Zhua Y, Xua C, Wu D, Wei B (2003a) Competitive adsorption of Pb2+ Cu2+ and Cd2+ ions from aqueous solutions by multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Carbon 41:2787–2792
Li YH, Wang S, Luan Z, Ding J, Xu C, Wu D (2003b) Adsorption of cadmium(II) from aqueous solution by surface oxidized carbon nanotubes. Carbon 41:1057–1062
Li YH, Di Z, Ding J, Wu D, Luan Z, Zhu Y (2005) Adsorption thermodynamic, kinetic and desorption studies of Pb2+ on carbon nanotubes. Water Res 39:605–609
Li Y, Liu F, Xia B (2010) Removal of copper from aqueous solution by carbon nanotube/calcium alginate composites. J Hazard Mater 177:876–880
Lien HL, Zhang WX (2001) Nanoscale iron particles for complete reduction of chlorinated ethenes. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 191:97–105
Lin DH, Xing BS (2007) Phytotoxicity of nanoparticles: inhibition of seed germination and root growth. Environ Poll 150:243–250
Liou YH, Lo SL, Lin CJ, Hu CY, Kuan WH, Weng SC (2005) Methods for accelerating nitrate reduction using zerovalent iron at near-neutral pH: effects of H2-reducing pretreatment and copper deposition. Environ Sci Technol 39:9643–9648
Lu C, Chung YL, Chang KF (2005) Adsorption of trihalomethanes from water with carbon nanotubes. Water Res 39:1183–1189
Machado S, Pinto SL, Grosso JP, Nouws HPA, Albergaria JT, Delerue-Matos C (2013) Green production of zero-valent iron nanoparticles using tree leaf extracts. Sci Total Environ 445:1–8
Makarova OV, Rajh T, Thurnauer MC, Martin A, Kemme PA, Cropek D (2000) Surface modification of TiO2 nanoparticles for photochemical reduction of nitrobenzene. Environ Sci Technol 34:4797–4803
Mansoori GA, Rohani-Bastami T, Ahmadpour A, Eshaghi Z (2008) Environmental application of nanotechnology. Annu Rev Nano Res 2:1–73
Mauter MS, Elimelech M (2008) Environmental applications of carbon-based nanomaterials. Environ Sci Technol 42:5843–5859
Newkome GR, Yao ZQ, Baker GR, Gupta VK (1985) Cascade molecules: a new approach to micelles. J Org Chem 50:2003–2004
Oberdörster G, Oberdörster E, Oberdörster J (2005) Nanotoxicology: An Emerging Discipline Evolving from Studies of Ultrafine Particles. Environmental Health Perspectives 113 (7):823–839
Paek SM, Jung H, Lee YJ, Park M, Hwang SJ, Choy JH (2006) Exfoliation and reassembling route to mesoporous titania nanohybrids. Chem Mater 18:1134–1140
Paknikar KM, Nagpal V, Pethkar AV, Rajwade JM (2005) Degradation of lindane from aqueous solutions using iron sulfide nanoparticles stabilized by biopolymers. Technol Adv Mater 6:370–374
Ponder SM, Darab JG, Mallouk TE (2000) Remediation of Cr(VI) and Pb(II) aqueous solutions using supported, nanoscale zero-valent iron. Environ Sci Technol 34:2564–2569
Prasad R (2014) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles in photosynthetic plants. J Nanopart 2014:963961. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/963961
Prasad R (2017) Mycoremediation and environmental sustainability, vol 1. Springer International Publishing, Cham. (ISBN 978-3-319-68957-9) https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-3-319-68957-9
Prasad R (2018) Mycoremediation and environmental sustainability, vol 2. Springer International Publishing, Cham. (ISBN 978-3-319-77386-5). https://www.springer.com/us/book/9783319773858
Prasad R, Pandey R, Barman I (2016) Engineering tailored nanoparticles with microbes: quo vadis. WIREs Nanomed Nanobiotechnol 8:316–330. https://doi.org/10.1002/wnan.1363
Qiang Y, Sharma A, Paszczynski A, Meyer D (2007) Conjugates of magnetic nanoparticle-enzyme for bioremediation. Proc 2007 NSTI Nanotechnol Conf Trade Show 4:656–659
Rajan S (2011) Nanotechnology in groundwater remediation. Int J Environ Sci Dev 2:182–187
Ralph T, Yang G (2003) Adsorbents: fundamentals and applications. Wiley, New Jersey
Rao GP, Lu C, Su F (2007) Sorption of divalent metal ions from aqueous solutions by carbon nanotubes: a review. Sep Purif Technol 58:224–231
Rebecca MT, Michele LP, Amy MB (2015) Effect of dendrimeric composition on the removal of pyrene from water. SpringerPlus 4:511–522
Richard F (1960) There’s plenty of room at the bottom. California Institute of Technology. Caltech Eng Sci 23:22–36
Roco MC (2005) The emergence and policy implications of converging new technologies integrated from the nanoscale. J Nanopart Res 7:129–143
Ruffini-Castiglione M, Cremonini R (2009) Nanoparticles and higher plants. Caryologia 62:161–165
Sayes CM, Gobin AM, Ausman KD, Mendez J, West JL, Colvin VL (2005) Nano-C60 cytotoxicity is due to lipid peroxidation. Biomaterials 26:7587–7595
Sayles GD, You G, Wang M, Kupferle MJ (1997) DDT, DDD, and DDE dechlorination by zero-valent iron. Environ Sci Technol 31:3448–3454
Schrick B, Blough JL, Jones AD, Mallouk TE (2002) Hydrodechlorination of trichloroethylene to hydrocarbons using bimetallic nickel-iron nanoparticles. Chem Mater 14:5140–5147
Sharma CS, Sarkar S, Periyakaruppan A, Barr J, Wise K, Thomas R (2007) Single-walled carbon nanotubes induces oxidative stress in rat lungcepithelial cells. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 7:2466–2472
Shedbalkar U, Singh R, Wadhwani S, Gaidhani S, Chopade BA (2014) Microbial synthesis of gold nanoparticles: Current status and future prospects. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science 209:40–48
Stathatos E, Tsiourvas D, Lianos P (1999) Titanium dioxide films made from reverse micelles and their use for photo catalytic degradation of adsorbed dyes. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 149:49–56
Thatai S, Khurana P, Boken J (2014) Nanoparticles and core–shell nanocomposite based new generation water remediation materials and analytical techniques: a review. J Microchem 116:62–76
Thomas RT, Nair V, Sandhyarani N (2013) TiO2 nanoparticles assisted solid phase photocatalytic degradation of polythene film: a mechanistic investigation. Colloids Surf A 422:1–9
Tomalia DA (1994) Starburst/Cascade Dendrimers: Fundamental building blocks for a new nanoscopic chemistry set. Advanced Materials 6 (7-8):529–539
Tosco T, Papini MP, Viggi CC, Sethi R (2014) Nanoscale zero valent iron particles for groundwater remediation: a review. J Clean Prod 77:10–21
Tungittiplakorn W, Cohen C, Lion LW (2005) Engineered Polymeric Nanoparticles for Bioremediation of Hydrophobic Contaminants. Environmental Science & Technology 39 (5):1354–1358
Undre SB, Singh M, Kale RK (2013a) Interaction behaviour of trimesoyl chloride derived 1st tier dendrimers determined with structural and physicochemical properties required for drug designing. J Mol Liq 182:106–120
Undre SB, Singh M, Kale RK, Rizwan M (2013b) Silibinin binding and release activities moderated by interstices of trimesoyl, tridimethyl, and tridiethyl malonate first-tier dendrimers. J Appl Polymer Sci 130:3537–3554
Von der Kammer F, Ferguson P, Holden P, Masion A, Rogers K, Klaine S, Koelmans A, Horne N, Unrine J (2012) Analysis of nanomaterials in complex matrices (environment and biota): general considerations and conceptual case studies. Environ Toxicol Chem 31:32–49
Wang CB, Zhang WX (1997) Synthesizing nanoscale iron particles for rapid and complete dechlorination of TCE and PCBs. Environ Sci Technol 31:2154–2156
Watlington K (2005) U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. www.epa.gov www.clu-in.org
Xiong Z, Zhao D, Pan G (2007) Rapid and complete destruction of perchlorate in water and ion-exchange brine using stabilized zero-valent iron nanoparticles. Water Res 41:3497–3505
Xu J, Bhattacharyya SD (2005) Membrane based bimetallic nanoparticles for environmental remediation: synthesis and reactive properties. Environ Prog 24:358–366
Yan W, Herzing AA, Li XQ, Kiely CJ, Zhang WX (2010) Structural evolution of Pd-doped nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) in aqueous media and implications for particle ageing and reactivity. Environ Sci Technol 44:4288–4294
Yu JG, Zhao XH, Yang H, Chen XH, Yang Q, Yu LY, Jiang JH, Chen XQ (2014) Aqueous adsorption and removal of organic contaminants by carbon nanotubes. Sci Total Environ 483:241–251
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Bhandari, G. (2018). Environmental Nanotechnology: Applications of Nanoparticles for Bioremediation. In: Prasad, R., Aranda, E. (eds) Approaches in Bioremediation. Nanotechnology in the Life Sciences. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-02369-0_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-02369-0_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-02368-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-02369-0
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)