Abstract
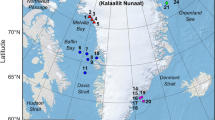
The project conducts application-oriented research on impacts of underwater noise on marine vertebrates in the North and Baltic Seas. In distinct subprojects, the hearing sensitivity of harbor porpoises and gray seals as well as the acoustic tolerance limit of harbor porpoises to impulsive noise from pile driving and stress reactions caused by anthropogenic noise is investigated. Animals are equipped with DTAGs capable of recording the actual surrounding noise field of free-swimming harbor porpoises and seals. Acoustic noise mapping including porpoise detectors in the Natura 2000 sites of the North and Baltic Seas will help to fully understand current noise impacts.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asselin S, Hammill MO, Barrette C (1993) Underwater vocalizations of ice breeding grey seals. Can J Zool 71:2211–2219
Bibikov NG (1992) Auditory brainstem responses in the harbour porpoise (Phocoena phocoena). In: Thomas JA, Kastelein RA, Supin AY (eds) Marine mammal sensory systems. Plenum, New York, pp 197–211
Jewett DL, Williston JS (1971) Auditory-evoked far fields averaged from the scalp of humans. Brain 94:681–696
Lucke K, Siebert U, Lepper PA, Blanchet MA (2009) Temporary shift in masked hearing thresholds in a harbor porpoise (Phocoena phocoena) after exposure to seismic airgun stimuli. J Acoust Soc Am 125:4060–4070
Müller S, Lehnert K, Seibel H, Driver J, Ronnenberg K, Teilmann J, van Elk C, Kristensen J, Everaarts E, Siebert U (2013) Evaluation of immune and stress status in harbour porpoises (Phocoena phocoena): can hormones and mRNA expression levels serve as indicators to assess stress? BMC Vet Res 9:145. doi:10.1186/1746-6148-9-145
Popov VV, Supin AY (1990) Auditory brain stem responses in characterization of dolphin hearing. J Comp Physiol A 166:385–393
Ralls K, Forelli P, Gish S (1985) Vocalisation and vocal mimicry in captive harbor seals, Phoca vitulina. Can J Zool 63:1050–1056
Ridgway SH, Bullock TH, Carder DA, Seeley RL, Woods D, Galambos R (1981) Auditory brainstem response in dolphins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:1943–1947
Ruser A, Dähne M, Sundermeyer J, Lucke K, Houser D, Driver J, Kuklik I, Rosenberger T, Siebert U (2014) Evoked potential audiograms of grey seals (Halichoerus grypus) from the North and Baltic Seas. PLoS ONE 9:e90824. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0090824
Szymanski MD, Bain DE, Kiehl K, Pennington S, Wong S, Henry KR (1999) Killer whale (Orcinus orca) hearing: auditory brainstem response and behavioral audiograms. J Acoust Soc Am 106:1134–1141
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the German Federal Agency for Nature Conservation (BfN). We thank Mark Johnson (Sea Mammal Research Unit, University of St. Andrews, St. Andrews, UK), the German Oceanographic Museum (Stralsund, Germany), and all other people who were involved for their assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this paper
Cite this paper
Liebschner, A. et al. (2016). Impacts of Underwater Noise on Marine Vertebrates: Project Introduction and First Results. In: Popper, A., Hawkins, A. (eds) The Effects of Noise on Aquatic Life II. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 875. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2981-8_76
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2981-8_76
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-2980-1
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-2981-8
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)