Abstract
Motion planning or trajectory planning, respectively, refers to the design of an open-loop control to achieve desired trajectories for the system states or outputs. Given distributed parameter systems that are governed by partial differential equations (PDEs), this requires to take into account the spatial-temporal system dynamics. In this case flatness-based techniques provide a systematic motion planning approach, which is based on the parametrization of any system variable by means of a flat or basic output. With this, the motion planning problem can be solved rather intuitively as is illustrated subsequently for linear and semi-linear PDEs. In addition constraints on system input or states can be taken into account systematically by introducing a dynamic optimization problem for the computation of the flat output trajectory.
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
Expressions are for the sake of simplicity in the following only written for the input parametrization. The state parametrization follows accordingly.
- 2.
Classically stationary solutions are to be defined in terms of stationary input values
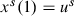 .
.
Bibliography
Andrej J, Meurer T (2018) Flatness-based constrained optimal control of reaction-diffusion systems. In: American control conference (ACC), Milwaukee, pp 2539–2544
Boas R (1954) Entire functions. Academic, New York
Böhm T, Meurer T (2017) Trajectory planning and tracking control for the temperature distribution in a deep drawing tool. Control Eng Pract 64:127–139
Delaleau E, Rudolph J (1998) Control of flat systems by quasi-static feedback of generalized states. Int J Control 71(5):745–765 https://doi.org/10.1080/002071798221551
Fliess M, Lévine J, Martin P, Rouchon P (1995) Flatness and defect of non–linear systems: introductory theory and examples. Int J Control 61:1327–1361
Fliess M, Mounier H, Rouchon P, Rudolph J (1997) Systèmes linéaires sur les opérateurs de Mikusiński et commande d’une poutre flexible. ESAIM Proceedings 2:183–193
Fliess M, Lévine J, Martin P, Rouchon P (1999) A Lie-Bäcklund approach to equivalence and flatness of nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans Autom Control 44(5): 922–937
Freudenthaler G, Meurer T (2016) PDE–based tracking control for multi-agent deployment. IFAC–PapersOnLine 49(18):582–587; 10th IFAC symposium on nonlinear control systems (NOLCOS 2016), Monterey, 23–25 Aug 2016
Kater A, Meurer T (2019) Motion planning and tracking control for coupled flexible beam structures. Control Eng Pract 84:389–398
Knüppel T, Woittennek F, Rudolph J (2010) Flatness-based trajectory planning for the shallow water equations. In: Proceedings of 49th IEEE conference on decision and control (CDC), Altanta, pp 2960–2965
Meurer T (2011) Flatness–based trajectory planning for diffusion–reaction systems in a Parallelepipedon – a spectral approach. Automatica 47(5):935–949
Meurer T (2013) Control of higher–dimensional PDEs: flatness and backstepping designs. Communications and control engineering series. Springer
Meurer T, Andrej J (2018) Flatness-based model predictive control of linear diffusion–convection–reaction processes. In: IEEE conference on decision and control (CDC), Miami Beach, pp 527–532
Meurer T, Krstic M (2011) Finite–time multi–agent deployment: a nonlinear PDE motion planning approach. Automatica 47(11):2534–2542
Meurer T, Kugi A (2009) Trajectory planning for boundary controlled parabolic PDEs with varying parameters on higher-dimensional spatial domains. IEEE T Automat Control 54(8):1854–1868
Petit N, Rouchon P (2001) Flatness of heavy chain systems. SIAM J Control Optim 40(2):475–495
Petit N, Rouchon P (2002) Dynamics and solutions to some control problems for water-tank systems. IEEE Trans Autom Control 47(4):594–609
Qi J, Vazquez R, Krstic M (2015) Multi–agent deployment in 3–D via PDE control. IEEE Trans Autom Control 60(4):891–906
Rodino L (1993) Linear partial differential operators in Gevrey spaces. World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd., Singapore
Rouchon P (2001) Motion planning, equivalence, and infinite dimensional systems. Int J Appl Math Comp Sci 11:165–188
Rudolph J (2003a) Beiträge zur flachheitsbasierten Folgeregelung linearer und nichtlinearer Systeme endlicher und unendlicher Dimension. Berichte aus der Steuerungs– und Regelungstechnik, Shaker–Verlag, Aachen
Rudolph J (2003b) Flatness Based Control of Distributed Parameter Systems. Berichte aus der Steuerungs– und Regelungstechnik, Shaker–Verlag, Aachen
Rudolph J, Woittennek F (2008) Motion planning and open loop control design for linear distributed parameter systems with lumped controls. Int J Control 81(3):457–474
Schörkhuber B, Meurer T, Jüngel A (2013) Flatness of semilinear parabolic PDEs – a generalized Cauchy-Kowalevski approach. IEEE T Automat Control 58(9):2277–2291
Schröck J, Meurer T, Kugi A (2013) Motion planning for Piezo–actuated flexible structures: modeling, design, and experiment. IEEE T Control Sys Tech 21(3): 807–819
Woittennek F, Mounier H (2010) Controllability of networks of spatially one-dimensional second order p.d.e. – an algebraic approach. SIAM J Control Optim 48(6):3882–3902
Woittennek F, Rudolph J (2003) Motion planning for a class of boundary controlled linear hyperbolic PDE’s involving finite distributed delays. ESAIM: Control Optim Calcul Var 9:419–435
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Section Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer-Verlag London Ltd., part of Springer Nature
About this entry
Cite this entry
Meurer, T. (2020). Motion Planning for PDEs. In: Baillieul, J., Samad, T. (eds) Encyclopedia of Systems and Control. Springer, London. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4471-5102-9_14-2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4471-5102-9_14-2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, London
Print ISBN: 978-1-4471-5102-9
Online ISBN: 978-1-4471-5102-9
eBook Packages: Springer Reference EngineeringReference Module Computer Science and Engineering
Publish with us
Chapter history
-
Latest
Motion Planning for PDEs- Published:
- 20 November 2019
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4471-5102-9_14-2
-
Original
Motion Planning for PDEs- Published:
- 14 March 2014
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4471-5102-9_14-1





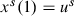 .
.