Abstract
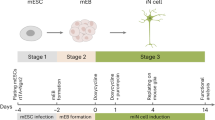
Forced expression of specific neuronal transcription factors in mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) can lead to their direct conversion into functional neurons. Direct neuronal reprogramming has become a powerful tool to characterize individual factors and molecular mechanisms involved in forced and normal neurogenesis and to generate neuronal cell types for in vitro studies. Here we provide a detailed protocol for the isolation of MEFs devoid of neural tissue and their direct reprogramming into functional neurons by overexpression of neuronal reprogramming factors (Ascl1, Brn2, and Myt1l) using lentiviral vectors. This method enables quick and efficient generation of mouse neurons in vitro for versatile functional and mechanistic characterization.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Masserdotti G, Gascón S, Götz M (2016) Direct neuronal reprogramming: learning from and for development. Development 143:2494–2510. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.092163
Colasante G, Rubio A, Massimino L, Broccoli V (2019) Direct neuronal reprogramming reveals unknown functions for known transcription factors. Front Neurosci 13:283. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.00283
Vierbuchen T, Ostermeier A, Pang ZP et al (2010) Direct conversion of fibroblasts to functional neurons by defined factors. Nature 463:1035–1041. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08797
Wapinski OL, Vierbuchen T, Qu K et al (2013) Hierarchical mechanisms for direct reprogramming of fibroblasts to neurons. Cell 155:621–635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.09.028
Mall M, Kareta MS, Chanda S et al (2017) Myt1l safeguards neuronal identity by actively repressing many non-neuronal fates. Nature 544:245–249. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature21722
Luo C, Lee QY, Wapinski O et al (2019) Global DNA methylation remodeling during direct reprogramming of fibroblasts to neurons. elife 8:e40197. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.40197
Chanda S, Ang CE, Davila J et al (2014) Generation of induced neuronal cells by the single reprogramming factor ASCL1. Stem Cell Reports 3:282–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2014.05.020
Adrian-Segarra JM, Weigel B, Mall M (2021) Combining cell fate reprogramming and protein engineering to study transcription factor functions. In: Ahlenius H (ed) Neural reprogramming: methods and protocols. Methods in molecular biology, vol 2352. Springer, New York
Drouin-Ouellet J, Pircs K, Barker RA et al (2017) Direct neuronal reprogramming for disease modeling studies using patient-derived neurons: what have we learned? Front Neurosci 11:530. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2017.00530
Pang ZP, Yang N, Vierbuchen T et al (2011) Induction of human neuronal cells by defined transcription factors. Nature 476:220–223. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10202
Zhang Y, Pak C, Han Y et al (2013) Rapid single-step induction of functional neurons from human pluripotent stem cells. Neuron 78:785–798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2013.05.029
Yang N, Chanda S, Marro S et al (2017) Generation of pure GABAergic neurons by transcription factor programming. Nat Methods 14:621–628. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.4291
Pruett SB, Obiri N, Kiel JL (1989) Involvement and relative importance of at least two distinct mechanisms in the effects of 2-mercaptoethanol on murine lymphocytes in culture. J Cell Physiol 141:40–45. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.1041410107
DuBridge RB, Tang P, Hsia HC et al (1987) Analysis of mutation in human cells by using an Epstein-Barr virus shuttle system. Mol Cell Biol 7:379–387. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.7.1.379
Pear WS, Nolan GP, Scott ML, Baltimore D (1993) Production of high-titer helper-free retroviruses by transient transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90:8392–8396. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.90.18.8392
Xu J (2005) Preparation, culture, and immortalization of mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Curr Protoc Mol Biol 28(1):1–8
Elegheert J, Behiels E, Bishop B et al (2018) Lentiviral transduction of mammalian cells for fast, scalable and high-level production of soluble and membrane proteins. Nat Protoc 13:2991–3017. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-018-0075-9
Xie Q, Xinyong G, Xianjin C, Yayu W (2013) PEI/DNA formation affects transient gene expression in suspension Chinese hamster ovary cells via a one-step transfection process. Cytotechnology 65:263–271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-012-9483-9
Higashikawa F, Chang L (2001) Kinetic analyses of stability of simple and complex retroviral vectors. Virology 280:124–131. https://doi.org/10.1006/viro.2000.0743
Murray EJ (1991) Gene transfer and expression protocols. Humana Press, Clifton, NJ
Kutner RH, Zhang X-Y, Reiser J (2009) Production, concentration and titration of pseudotyped HIV-1-based lentiviral vectors. Nat Protoc 4:495–505. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2009.22
Kumar M, Keller B, Makalou N, Sutton RE (2001) Systematic determination of the packaging limit of lentiviral vectors. Hum Gene Ther 12:1893–1905. https://doi.org/10.1089/104303401753153947
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Adrian-Segarra, J.M., Weigel, B., Mall, M. (2021). Isolation and Neuronal Reprogramming of Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts. In: Ahlenius, H. (eds) Neural Reprogramming. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2352. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1601-7_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1601-7_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-1600-0
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-1601-7
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols