Abstract
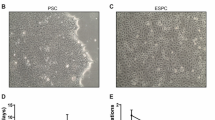
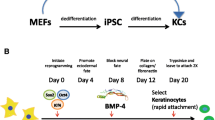
Direct reprogramming of somatic cells into induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) provides an opportunity to develop novel personalized treatment options for numerous diseases and to advance current approaches for cell-based drug discoveries and disease modeling. The ability to differentiate iPSCs into relevant cell types is an important prerequisite for the successful development of iPSC-based treatment and modeling strategies. Here, we describe a protocol for the efficient differentiation of human iPSCs into functional keratinocytes. The protocol employs treating iPSCs with retinoic acid and bone-morphogenetic protein-4 to induce differentiation toward a keratinocyte lineage, which is then followed by the growth of differentiated iPSCs on collagen type I- and collagen type IV-coated dishes to enrich for iPSC-derived keratinocytes.
An erratum to this chapter can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/7651_2014_79
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ColI:
-
Type I collagen
- ColIV:
-
Type IV collagen
- ESC:
-
Embryonic stem cell
- iPSC:
-
Induced pluripotent stem cell
- Krt14:
-
Keratin 14
- RA:
-
Retinoic acid
- BMP4:
-
Bone-morphogenetic protein-4
References
Takahashi K, Yamanaka S (2006) Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 126(4):663–676
Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, Narita M, Ichisaka T, Tomoda K, Yamanaka S (2007) Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell 131(5):861–872
Yu J, Vodyanik MA, Smuga-Otto K, Antosiewicz-Bourget J, Frane JL, Tian S, Nie J, Jonsdottir GA, Ruotti V, Stewart R, Slukvin II, Thomson JA (2007) Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from human somatic cells. Science 318(5858):1917–1920
Okita K, Ichisaka T, Yamanaka S (2007) Generation of germline-competent induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature 448(7151):313–317
Wernig M, Meissner A, Foreman R, Brambrink T, Ku M, Hochedlinger K, Bernstein BE, Jaenisch R (2007) In vitro reprogramming of fibroblasts into a pluripotent ES-cell-like state. Nature 448(7151):318–324
Yamanaka S (2007) Strategies and new developments in the generation of patient-specific pluripotent stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 1(1):39–49
Nishikawa S, Goldstein RA, Nierras CR (2008) The promise of human induced pluripotent stem cells for research and therapy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9(9):725–729
Yamanaka S (2009) A fresh look at iPS cells. Cell 137(1):13–17
Takahashi K (2012) Cellular reprogramming–lowering gravity on Waddington’s epigenetic landscape. J Cell Sci 125(Pt 11):2553–2560
Khavari PA (1997) Therapeutic gene delivery to the skin. Mol Med Today 3(12):533–538
DiGiovanna JJ, Robinson-Bostom L (2003) Ichthyosis: etiology, diagnosis, and management. Am J Clin Dermatol 4(2):81–95
Smith F (2003) The molecular genetics of keratin disorders. Am J Clin Dermatol 4(5):347–364
Bilousova G, Chen J, Roop DR (2011) Differentiation of mouse induced pluripotent stem cells into a multipotent keratinocyte lineage. J Invest Dermatol 131(4):857–864
Metallo CM, Ji L, de Pablo JJ, Palecek SP (2008) Retinoic acid and bone morphogenetic protein signaling synergize to efficiently direct epithelial differentiation of human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 26(2):372–380
Itoh M, Kiuru M, Cairo MS, Christiano AM (2011) Generation of keratinocytes from normal and recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa-induced pluripotent stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(21):8797–8802
Bain G, Kitchens D, Yao M, Huettner JE, Gottlieb DI (1995) Embryonic stem cells express neuronal properties in vitro. Dev Biol 168(2):342–357
Gambaro K, Aberdam E, Virolle T, Aberdam D, Rouleau M (2006) BMP-4 induces a Smad-dependent apoptotic cell death of mouse embryonic stem cell-derived neural precursors. Cell Death Differ 13(7):1075–1087
Bickenbach JR, Chism E (1998) Selection and extended growth of murine epidermal stem cells in culture. Exp Cell Res 244(1):184–195
Mills AA, Zheng B, Wang XJ, Vogel H, Roop DR, Bradley A (1999) p63 is a p53 homologue required for limb and epidermal morphogenesis. Nature 398(6729):708–713
Koster MI, Kim S, Mills AA, DeMayo FJ, Roop DR (2004) p63 is the molecular switch for initiation of an epithelial stratification program. Genes Dev 18(2):126–131
Warren L, Manos PD, Ahfeldt T, Loh YH, Li H, Lau F, Ebina W, Mandal PK, Smith ZD, Meissner A, Daley GQ, Brack AS, Collins JJ, Cowan C, Schlaeger TM, Rossi DJ (2010) Highly efficient reprogramming to pluripotency and directed differentiation of human cells with synthetic modified mRNA. Cell Stem Cell 7(5):618–630
Warren L, Ni Y, Wang J, Guo X (2012) Feeder-free derivation of human induced pluripotent stem cells with messenger RNA. Sci Rep 2:657
Liu Y, Song Z, Zhao Y, Qin H, Cai J, Zhang H, Yu T, Jiang S, Wang G, Ding M, Deng H (2006) A novel chemical-defined medium with bFGF and N2B27 supplements supports undifferentiated growth in human embryonic stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 346(1):131–139
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for funding support from the National Institutes of Health (R01AR059947 and P30 AR057212), the US Department of Defense (PR110793), the Foundation for Ichthyosis and Related Skin Types (F.I.R.S.T.), and the Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa Research Association (DEBRA) International.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Kogut, I., Roop, D.R., Bilousova, G. (2013). Differentiation of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells into a Keratinocyte Lineage. In: Turksen, K. (eds) Epidermal Cells. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1195. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/7651_2013_64
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/7651_2013_64
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-1223-0
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-1224-7
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols