Abstract
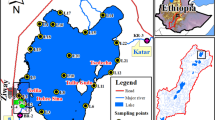
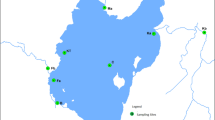
Environmental carrying capacity is a measure of competence of a lake to accommodate pollution inputs without degrading water quality. In the research reported here, we identified the factors influencing the environmental carrying capacity of Vellayani Lake or VL (a typical tropical freshwater lake), Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala State, India. R-mode factor analysis is used to identify the factors controlling the carrying capacity of the lake, whereas hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) helped to classify the lake. The carrying capacity of the lake is low with respect to alkalinity, due to ion deficiency, and is potentially reactive to sudden changes in pH. Eutrophic condition exists in the entire lake system. Acidic factor, mineralization factor, fertilizer factor (P & K), evaporation factor and organic pollution factor are the controllers of VL water quality during the pre-monsoon period. The same factors (but not evaporation factor) and an additional runoff factor control the water quality during monsoon. In the post-monsoon, the aforesaid factors (other than runoff, alkalinity) and soil erosion factor influence the water quality. Hence, managers of the lake system need to also focus on combating acidic factor during pre- and post-monsoons and runoff during monsoon. Smaller areal extent and shallow depth of VL, reduced outflow from it, less rainfall, presence of lateritic rock and soil and absence of limestone strata in the catchment are the chief elements affecting the acidic factor of Vellayani Lake.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abhijna, U. G., Ratheesh, R., & Biju, K. (2012). Distribution and diversity of aquatic insects of Vellayani Lake in Kerala. Journal of Environmental Biology, 34, 605–611.
Adam, G., Barbieri, P., Picciotto, A., & Reisenhofer, E. (2008). Principal factor analysis as applied in environmental chemistry: the study of eutrophication in a shallow lake. Toxicological and Environmental Chemistry, 61, 99–108.
Allott, T. E. H., Curtis, C. J., Hall, J., Harriman, R., & Battarbee, R. W. (1995). The impact of nitrogen deposition on upland surface waters in Great Britain: a regional assessment of nitrate leaching. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 85, 297–302.
Anazawa, K., & Ohmori, H. (2005). The hydrochemistry of surface waters in Andesitic Volcanic area, Norikura volcano, Central Japan. Chemosphere, 59, 605–615.
Anonymous (1991). Indian standard for drinking water specification. IS 10500:1991.
Anonymous (2002). Four township environmental carrying capacity study. Project No: 51830106, Progressive AE, 1811 4 Mile Road, NE Grand Rapids, MI-49525-244 616/361-2664.
APHA (2012). Standard methods for examination of water and waste water. Washington: American Public Health Association, 22nd edition.
Ashley, R. P., & Lloyd, J. W. (1978). An example of the use of factor analysis and cluster analysis in ground water chemistry interpretation. Journal of Hydrology, 39, 355–364.
CESS (2000). Conservation of Vellayani Lake in Trivandrum district as drinking water source—detailed study. Project report submitted to the Kerala Water Authority. Trivandrum. Centre for Earth Science Studies, Thiruvananthapuram-695031.
Chapman, D. (1997). Water quality assessment. A guide to the use of biota, sediments and water in environmental monitoring. Second edition, E & FN Spon, London. P.
Davis, J. C. (1986). Statistics and data analysis in geology, second edition (p. 646). New York: Wiley.
Dawdy, D. R., & Feth, J. H. (1967). Applications of factor analysis in study of chemistry of groundwater quality, Mojave River Valley, California. Water Resources Research, 3, 505–510.
De Ceballos, B. S. O., Koning, A., & De Olivera, J. F. (1998). Dam reservoir eutrophication: a simplified technique for a fast diagnosis of an environmental degradation. Water Research, 32(11), 3477–3483.
Douglas, E. B., & Leo, W. N. (1977). Hydrochemical relationships using partial correlation coefficients. Water Resources Bulletin, 13(4), 843–846.
Feth, J. H. (1966). Nitrogen compounds in natural water—a review. Water Resources Research, 2, 41–58. files.dnr.state.mn.us/assistance/nrplanning/bigpicture/cwcs/habitats/16.pdf.
Gao, J. X. (2001). Methods and application of ecological carrying capacity. Beijing: Environment and Science Press.
Granina, L., Müller, B., & Wehrli, B. (2004). Origin and dynamics of Fe and Mn sedimentary layers in Lake Baikal. Chemical Geology, 205(1), 55–72.
Harman, H. H. (1960). Modern factor analysis. Chicago: The University of Chicago Press.
Helena, B., Pardo, R., Vega, M., Barrado, E., Fernandez, J. M., & Fernandez, L. (2000). Temporal evolution of groundwater composition in an alluvial aquifer (Pisuergariver, Spain) by principal component analysis. Water Research, 34(3), 807–816.
Jayaprakash, M., Giridharan, L., Venugopal, T., Krishna Kumar, S. P., & Periakali, P. (2008). Characterization and evaluation of the factors affecting the geochemistry of groundwater in Neyveli Tamil Nadu, India. Environmental Geology, 54, 855–867.
Jørgensen, S. E. (1976). A eutrophication model for a lake. Ecological Modelling, 2(2), 147–165. lakes.chebucto.org/DATA/morphology.html.
KSPCB (2015). Water and Air Quality Directory, 2015. Kerala State Pollution Control Board, Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala.
Lau, S. S. S., & Lane, S. N. (2002). Biological and chemical factors influencing shallow lake eutrophication: a long-term study. The Science of the Total Environment, 288, 167–181.
Lawniezak, A. (2011). Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium resorption efficiency and proficiency of four emergent macrophytes from nutrient rich wetlands. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 20(5), 1227–1234.
Li, Q. L., Wang, L. G., Zhang, H. Z., & Yan, X. X. (2004). Research and prospect on theoretical framework of water environmental bearing capacity. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 2, 87–89.
Malvi, U. R. (2011). Interaction of micro nutrients with special reference to potassium. Karnataka Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 24(1), 106–109.
Miller, C. V., Denis, J. M., Ator, S. W., & Brakebill, G. W. (1997). Nutrients in streams during base flow in selected environmental settings of the Potomac River basin. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 33, 1155–1171.
Momen, B., Zehr, G. P., Boylen, C. W., & Sutherland, J. W. (1999). Determinants of summer nitrate concentration in a set of Adirondack Lakes, New York. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 111, 19–28.
Nikanorov, A. M., & Brazhnikova, L. V. (2009). Water chemical composition of rivers, lakes and wetlands. Encyclopedia of life support systems, types and properties of water, 2, 42–79
Padisák, J., & Reynolds, C. S. (2003). Shallow lakes: the absolute, the relative, the functional and the pragmatic. Hydrobiologia, 506(1–3), 1–11.
Papatheodorou, G., Demopoulou, G., & Lambrakis, N. (2006). A long-term study of temporal hydrochemical data in a shallow lake using multivariate statistical techniques. Ecological Modelling, 193, 759–776.
Patil, J. V., Ekhande, A. P., & Padate, G. S. (2011). Study of Lotus Lake: its abiotic factors their correlation with reference to seasonal changes and altitude. Annals of Biological Research, 2(4), 44–56.
Rao, S. Y. R., Reddy, T. V. K., & Nayudu, P. T. (1996). Groundwater quality in the Niva river basin, Chittoor district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environmental Geology, 32(1), 56–63.
Recknagel, F., French, M., Harkonen, P., & Yabunaka, K. I. (1997). Artificial neural network approach for modelling and prediction of algal blooms. Ecological Modelling, 96(1), 11–28.
Reeder, S. W., Hitchon, B., & Levinson, A. A. (1972). Hydrogeochemistry of the surface waters of the Mackenzie River drainage basin, Canada—I. Factors controlling inorganic composition. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 36, 825–865.
Reimann, C., Filzmoser, P., & Garrett, R. G. (2002). Factor analysis applied to regional geochemical data: problems and possibilities. Applied Geochemistry, 17, 185–206.
Reisenhofer, E., Picciotto, A., & Li, D. (1995). A factor analysis approach to the study of the eutrophication of a shallow, temperate lake (San Daniele, north eastern Italy). Analytica Chimica Acta, 306, 99–106.
Reyment, R., & Joreskog, K. G. (1996). Applied factor analysis in natural sciences. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Scheffer, M. (1998). Ecology of shallow lakes (p. 61). London: Chapman and Hall.
Sheela, A. M., Letha, J., Sabu Joseph (2010). Environmental status of a tropical lake system. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, Springer, 180(1–4), 422–449, doi:10.1007/s10661-010-1707-5, 3-12-2010.
Sheela, A. M., Letha, J., Sabu Joseph, Sheeja, R. V., Justus, J. (2011). Influence of lake morphology on water quality. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, Springer, 182(1–4), 443–454, doi:10.1007/s10061-01-1888-y
Sheela, A. M., Letha, J., Sabu Joseph, Jobin Thomas, & Sanal Kumar, S. P., (2012). Water quality assessment of a tropical coastal lake system using multivariate-cluster, principal component and factor analysis. Lakes and Reservoir Management, USA, Taylor and Francis Group 17, 143–159
Sheela A.M., Letha, J., Sabu Joseph, Justus, J., Jobin Thomas (2014). Multivariate analysis of the sediment quality of a tropical coastal lake system. Lakes and Reservoir: Research and Management, Wiley Publishers Asia Limited, 19, 306–317.
Simeonov, V., Sarbu, C., Massart, D., & Tsakovski, S. (2001). Danube River water data modelling by multivariate data analysis. Mikrochimica Acta, 137, 243–248.
Singh, A., Meetei, N. S., & Meitei, L. B. (2013). Seasonal variation of some physic-chemical characteristics of three major rivers in Imphal, Manipur: a comparative evaluation. Current World Environment: An International Research Journal of Environmental Sciences, 8(1), 93–102.
Soman, K., Chattopadhyay, M., Chattopadhyay, S., & Krishnan Potti, G. (2002). Occurrence and water resource potential of freshwater lakes in South Kerala and their relation to the Quaternary geological evolution of the Kerala coast. Memoir of Geological Society of India, 49, 21.
Somlyay, L. & Straten, G.V. (1986). Modeling and managing shallow lake eutrophication, Executive report-10, International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis, a-2361, Austria.
Sorenson, D. L., McCarthy, M. K., Middle Brooks, E. J., & Porcella, D. B. (1977). Suspended and dissolved solids effect on fresh water biota: a review. Oregon: Corvallis Environmental Research Laboratory.
Suk, H., & Lee, K. (1999). Characterization of a ground water hydrochemical system through multivariate analysis: clustering into ground water zones. Ground Water, 37(3), 358–366.
Tan, C. O., & Beklioglu, M. (2005). Catastrophic-like shifts in shallow Turkish lakes: a modeling approach. Ecological Modelling, 183(4), 425–434.
Usunoff, E. J., & Guzman, A. G. (1989). Multivariate analysis in hydrochemistry—an example of the use of factor and correspondence analysis. Ground Water, 17, 27–34.
Wang, S. C. (2001). Analysis and regulation on water environmental carrying capacity. China Water Resources, 11, 9–12.
Werner, D. (1977). The biology of diatoms. Berkeley: University of California Press.
Widerlund, A., Roos, P., Gunneriusson, L., Ingri, J., & Holmström, H. (2002). Early diagenesis and isotopic composition of lead in Lake Laisan, Northern Sweden. Chemical Geology, 189(3), 183–197.
Yidana, S. M., Ophori, D., & Banoeng-Yakubo, B. (2008). A multivariate statistical analysis of surface water chemistry data—the Ankobra Basin, Ghana. Journal of Environmental Management, 86, 80–87.
Yu, S., Shang, J., Zhao, J., & Guo, H. (2003). Factor analysis and dynamics of water quality of the Songhua River, Northeast China. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 144, 159–169.
Zhang, J., Jørgensen, S. E., Beklioglu, M., & Ince, O. (2003). Hysteresis in vegetation shift—Lake Mogan prognoses. Ecological Modelling, 164(2), 227–238.
Zhu, Y. H., Drake, S., Lu, H. S., & Xia, J. (2010). Analysis of temporal and spatial differences in eco-environmental carrying capacity related to water in the Haihe River Basin. Water Resources Management, 24, 1089–1105.
Acknowledgments
This research project is funded by the Dept. of Science and Technology, Govt. of India (Project No. DST-N0. SR/S3/ENGF-01/2002 Dtd. 19 August 2009; Project code – DST-206/SP-1). Dr. K.P. Thrivikramaji (Former Prof. & Head, Dept. of Geology, Univ. of Kerala, India) is thankfully acknowledged for editing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mullakkezhil Reghunathan, V., Joseph, S., Warrier, C.U. et al. Factors affecting the environmental carrying capacity of a freshwater tropical lake system. Environ Monit Assess 188, 615 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5636-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5636-1