Abstract
Background
Coronal deformity correction with total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is an important feature in the treatment of osteoarthritis (OA). The hypothesis of this study was that bone morphology would be different in varus and valgus deformity, both before osteoarthritis development as well as during and after the disease process of OA.
Materials and methods
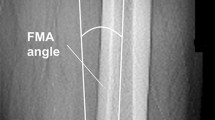
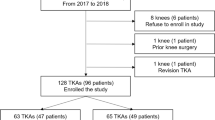
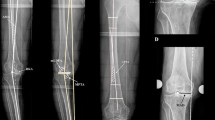
Retrospective study with measurements on preoperative and postoperative full leg standing radiographs of 96 patients who underwent TKA. The included patients were selected for this study because they had an OA knee on one side and a non-arthritic knee on the contralateral side presenting the same type of alignment as the to-be-operated knee (varus or valgus alignment on both sides). The control group of 46 subjects was a group of patients with neutral mechanical alignment who presented for ligamentous problems. A single observer measured mechanical alignment, anatomical alignment, anatomical–mechanical femoral angle and intra-articular bone morphology parameters with an accuracy of 1°.
Results
Varus OA group has less distal femoral valgus (mLDFA 89°) than control group (87°) and valgus OA group (mLDFA 85°). Varus OA group has same varus obliquity as control group (MPTA 87°) but more than valgus OA group (MPTA 90°). Joint Line Congruency Angle (JLCA) is 3°open on lateral side in varus and medially open in valgus OA group (2°). The non-arthritic valgus group presents a constitutional mechanical valgus of 184° Hip–Knee–Ankle (HKA) angle.
Discussion
Varus deformity in OA as measured with an HKA angle (HKA) <177° is a combination of distal femoral wear, tibial varus obliquity and lateral joint line opening. Valgus deformity in OA with an HKA > 183° is a combination of femoral distal joint line obliquity and wear combined with medial opening due to medial collateral ligament stretching. The clinical importance of bone morphotype analysis is that it shows the intra-articular potential of alignment correction when mechanical axis cuts are performed.
Conclusion
Bone morphology in varus and valgus deformity is different before and after osteoarthritis. Perpendicular cuts to mechanical axes do not necessarily lead to neutral mechanical axis. Constitutional mechanical valgus was observed as 184° HKA angle before the development of OA.
Level of evidence
Level IV study.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel M, Oussedik S, Parratte S, Lustig S, Haddad FS (2014) Coronal alignment in total knee replacement: historical review, contemporary analysis, and future direction. Bone Joint J 96-B(7):857–862
Allen MM, Pagnano MW (2016) Neutral mechanical alignment: Is it Necessary? Bone Joint J 98-b(1 Suppl A):81–83
Athwal KK, Daou HE, Kittl C, Davies AJ, Deehan DJ, Amis AA (2015) The superficial medial collateral ligament is the primary medial restraint to knee laxity after cruciate-retaining or posterior-stabilised total knee arthroplasty: effects of implant type and partial release. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. doi:10.1007/s00167-015-3796-0
Bellemans J, Colyn W, Vandenneucker H, Victor J (2012) The Chitranjan Ranawat award: is neutral mechanical alignment normal for all patients? The concept of constitutional varus. Clin Orthop Relat Res 470(1):45–53
Boettner F, Renner L, Arana Narbarte D, Egidy C, Faschingbauer M (2016) Total knee arthroplasty for valgus osteoarthritis: the results of a standardized soft-tissue release technique. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. doi:10.1007/s00167-016-4054-9
Bowman A, Shunmugam M, Watts AR, Bramwell DC, Wilson C, Krishnan J (2016) Inter-observer and intra-observer reliability of mechanical axis alignment before and after total knee arthroplasty using long leg radiographs. Knee 23(2):203–208
Brouwer RW, Jakma TS, Bierma-Zeinstra SM, Ginai AZ, Verhaar JA (2003) The whole leg radiograph: standing versus supine for determining axial alignment. Acta Orthop Scand 74(5):565–568
Calliess T, Bauer K, Stukenborg-Colsman C, Windhagen H, Budde S, Ettinger M (2016) PSI kinematic versus non-PSI mechanical alignment in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. doi:10.1007/s00167-016-4136-8
Cherian JJ, Kapadia BH, Banerjee S, Jauregui JJ, Issa K, Mont MA (2014) Mechanical, anatomical, and kinematic axis in TKA: concepts and practical applications. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med 7(2):89–95
Cooke TD, Li J, Scudamore RA (1994) Radiographic assessment of bony contributions to knee deformity. Orthop Clin North Am 25(3):387–393
De Muylder J, Victor J, Cornu O, Kaminski L, Thienpont E (2015) Total knee arthroplasty in patients with substantial deformities using primary knee components. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 23(12):3643–3659
Fahlman L, Sangeorzan E, Chheda N, Lambright D (2014) Older Adults without Radiographic Knee Osteoarthritis: Knee Alignment and Knee Range of Motion. Clin Med Insights Arthritis Musculoskelet Disord 7:1–11
Fang D, Ritter M, Davis K (2009) Coronal alignment in total knee arthroplasty: just how important is it? J Arthroplasty 24(6 Suppl):39–43
Hawi N, Yarboro S, Suero EM, Liodakis E, Meller R, Krettek C, Citak M (2014) Laser method for intraoperative evaluation of lower extremity alignment: comparison of a novel technique to CT and a conventional method. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 134(5):645–650
Hsu RW, Himeno S, Coventry MB, Chao EY (1990) Normal axial alignment of the lower extremity and load-bearing distribution at the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res 255:215–227
Hungerford DS, Krackow KA (1985) Total joint arthroplasty of the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res 192:23–33
Insall JN, Binazzi R, Soudry M, Mestriner LA (1985) Total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 192:13–22
Ishii Y, Noguchi H, Matsuda Y, Kiga H, Takeda M, Toyabe S (2009) Preoperative laxity in osteoarthritis patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop 33(1):105–109
Kawakami H, Sugano N, Yonenobu K, Yoshikawa H, Ochi T, Hattori A, Suzuki N (2004) Effects of rotation on measurement of lower limb alignment for knee osteotomy. J Orthop Res 22(6):1248–1253
Kennedy WR, White RP (1987) Unicompartmental arthroplasty of the knee. Postoperative alignment and its influence on overall results. Clin Orthop Relat Res 221:278–285
Kornilov N, Kulyaba T, Petukhov A, Ignatenko V, Thienpont E (2015) Computer navigation helps achieving appropriate gap balancing and restoration of alignment in total knee arthroplasty for fixed valgus knee osteoarthritis irrespective of the surgical approach. Acta Orthop Belg 81(4):673–681
Krackow KA, Pepe CL, Galloway EJ (1990) A mathematical analysis of the effect of flexion and rotation on apparent varus/valgus alignment at the knee. Orthopedics 13(8):861–868
Magnussen RA, Weppe F, Demey G, Servien E, Lustig S (2011) Residual varus alignment does not compromise results of TKAs in patients with preoperative varus. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469(12):3443–3450
Moreland JR, Bassett LW, Hanker GJ (1987) Radiographic analysis of the axial alignment of the lower extremity. J Bone Joint Surg Am 69(5):745–749
Nam D, Vajapey S, Haynes JA, Barrack RL, Nunley RM (2016) Does use of a variable distal femur resection angle improve radiographic alignment in primary total knee arthroplasty? J Arthroplasty 10.1016/j.arth.2016.01.070
Paley D, Tetsworth K (1992) Mechanical axis deviation of the lower limbs. Preoperative planning of uniapical angular deformities of the tibia or femur. Clin Orthop Relat Res 280:48–64
Parratte S, Pagnano MW, Trousdale RT, Berry DJ (2010) Effect of postoperative mechanical axis alignment on the fifteen-year survival of modern, cemented total knee replacements. J Bone Joint Surg Am 92(12):2143–2149
Paternostre F, Schwab P, Thienpont E (2014) The difference between weight-bearing and non-weight-bearing alignment in patient-specific instrumentation planning. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. doi:10.1007/s00167-013-2687-5
Pfitzner T, von Roth P, Perka C, Matziolis G (2014) Intramedullary control of distal femoral resection results in precise coronal alignment in TKA. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 134(4):459–465
Ritter MA, Faris PM, Keating EM, Meding JB (1994) Postoperative alignment of total knee replacement. Its effect on survival. Clin Orthop Relat Res 299:153–156
Sharma L, Song J, Felson DT, Cahue S, Shamiyeh E, Dunlop DD (2001) The role of knee alignment in disease progression and functional decline in knee osteoarthritis. Jama 286(2):188–195
Specogna AV, Birmingham TB, Hunt MA, Jones IC, Jenkyn TR, Fowler PJ, Giffin JR (2007) Radiographic measures of knee alignment in patients with varus gonarthrosis: effect of weightbearing status and associations with dynamic joint load. Am J Sports Med 35(1):65–70
Stucinskas J, Robertsson O, Lebedev A, Wingstrand H, Smailys A, Tarasevicius S (2016) Measuring long radiographs affects the positioning of femoral components in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 136(5):693–700
Thippanna RK, Kumar MN (2016) Lateralization of femoral entry point to improve the coronal alignment during total knee arthroplasty in patients with bowed femur. J Arthroplasty. 10.1016/j.arth.2016.02.057
van Raaij TM, Brouwer RW, Reijman M, Bierma-Zeinstra SM, Verhaar JA (2009) Conventional knee films hamper accurate knee alignment determination in patients with varus osteoarthritis of the knee. Knee 16(2):109–111
Victor JM, Bassens D, Bellemans J, Gursu S, Dhollander AA, Verdonk PC (2014) Constitutional varus does not affect joint line orientation in the coronal plane. Clin Orthop Relat Res 472(1):98–104
Willcox NM, Clarke JV, Smith BR, Deakin AH, Deep K (2012) A comparison of radiological and computer navigation measurements of lower limb coronal alignment before and after total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 94(9):1234–1240
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
E. Thienpont: Royalties from Medacta, Zimmer Biomet; Consultancy fees from Depuy-Synthes, Lima, Medacta, Zimmer Biomet; Board function in Belgian Knee Society, European Knee Society. PE Schwab: nothing to disclose. O. Cornu: nothing to disclose. J. Bellemans: Royalties from Smith & Nephew; Consultancy fees from Corin, Smith & Nephew, Stryker; Stock from Stryker; Publisher royalties from Springer, Acco; Board function in European Knee Society. J. Victor: Royalties from Smith & Nephew; Consultancy fees from Corin, Smith & Nephew, Zimmer Biomet; Research support from Corin, Depuy-Synthes, Smith & Nephew, Zimmer Biomet; Board functions in European Knee Society, BVOT.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thienpont, E., Schwab, P.E., Cornu, O. et al. Bone morphotypes of the varus and valgus knee. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 137, 393–400 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-017-2626-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-017-2626-x