Abstract
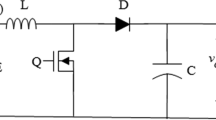
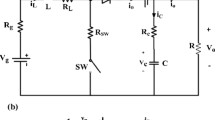
The large-signal averaged model of a coupled-inductor double-boost converter is developed and analysed in this paper. Due to the large current fluctuations, the differential system is deduced by averaging the circuit equations of the operation modes over a switching period. Generic expressions that permit to calculate the current commutation intervals as function of the averaged state variables are also found to complete the model. Resistive losses are introduced into an equivalent averaged circuit leading to a more realistic scenario. The proposed state-space model is used for studying voltage conversion ratios, transients and frequency-domain responses of the converter as well as for designing a control loop that regulates the output voltage. Numerical simulations and experimental measurements corroborate the obtained results.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lessa TF, de Castro PD, Josias de Paula W, de Sousa Oliveira JD (2015) Survey on non-isolated high-voltage step-up dc–dc topologies based on the boost converter. IET Power Electron 8(10):2044–2057
Forouzesh M, Siwakoti YP, Gorji SA, Blaabjerg F, Lehman B (2017) Step-up DC–DC converters: a comprehensive review of voltage-boosting techniques, topologies and applications. IEEE Trans Power Electron 32(12):9143–9178
Hu X, Gong C (2014) A high voltage gain dc–dc converter integrating coupled-inductor and diode-capacitor techniques. IEEE Trans Power Electron 29(2):789–800
Ajami A, Ardi H, Farakhor A (2015) A novel high step-up DC/DC converter based on integrating coupled inductor and switched-capacitor techniques for renewable energy applications. IEEE Trans Power Electron 30(8):4255–4263
Alencar Freitas AA, Lessa Tofoli F, Mineiro Sá Júnior E, Daher S, Antunes FLM (2015) High-voltage gain dc–dc boost converter with coupled inductors for photovoltaic systems. IET Power Electron 8(10):1885–1892
Patidar K, Umarikar AC (2016) A step-up PWM DC–DC converter for renewable energy applications. Int J Circuit Theory Appl 44(4):817–832
Sri Revathi B, Prabhakar M (2018) Modular high-gain DC-DC converter for renewable energy microgrids. Electr Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-017-0673-5
Van de Sype DM, De Gusseme K, Renders B, Van den Bossche AP, Melkebeek JA (2005) A single switch boost converter with high conversion ratio. Proc IEEE Appl Power Electron Conf (APEC) 3:1581–1587
Zhao Q, Lee FC (2003) High-efficiency, high step-up dc–dc converters. IEEE Trans Power Electron 18(1):65–73
Berkovich Y, Axelrod B (2011) Switched-coupled inductor cell for DC–DC converters with very large conversion ratio. IET Power Electron 4(3):309–315
Chen S-M, Lao M-L, Hsieh Y-H, Liang T-J, Chen K-H (2015) A novel switched-coupled-inductor dc–dc step-up converter and its derivatives. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 51(1):309–314
Nguyen TV, Petit P, Aillerie M, Salame Ch, Charles J-P (2015) Efficiency of magnetic coupled boost DC–DC converters mainly dedicated to renewable energy systems: influence of the coupling factor. Int J Circuit Theory Appl 43(8):1042–1062
Erickson RW, Maksimovic D (2004) Fundamentals of power electronics. Springer, New York
Kazimierczuk MK (2008) Pulse-width modulated DC–DC power converters. Wiley, Chichester
Forouzesh M, Siwakoti YP, Blaabjerg F, Hasanpour S (2016) Small-signal modeling and comprehensive analysis of magnetically coupled impedance-source converters. IEEE Trans Power Electron 31(11):7621–7641
Ayachit A, Siwakoti YP, Galigekere VP, Kazimierczuk MK, Blaabjerg F (2018) Steady-state and small-signal analysis of A-source converter. IEEE Trans Power Electron 33(8):7118–7131
Chan C-Y, Chincholkar SH, Jiang W (2017) Adaptive current-mode control of a high step-up DC–DC converter. IEEE Trans Power Electron 32(9):7297–7305
Leyva-Ramos J, Mota-Varona R, Ortiz-Lopez MG, Diaz-Saldierna LH, Langarica-Cordoba D (2017) Control strategy of a quadratic boost converter with voltage multiplier cell for high-voltage gain. IEEE J Emerg Sel Top Power Electron 05(4):1761–1770
Sun J, Mitchell DM, Gruel MF, Krein PT, Bass RM (2001) Averaged modeling of PWM converters operating in discontinuous conduction mode. IEEE Trans Power Electron 16(4):482–492
Davoudi A, Jatskevich J (2006) Numerical state-space averaged-value modeling of PWM DC–DC converters operating in DCM and CCM. IEEE Trans Power Electron 21(4):1003–1012
Dwari S, Jayawant S, Beechner T et al (2006) Dynamics characterization of coupled-inductor boost dc–dc converters. In: Proceedings IEEE workshop control and modelling for power electronics (COMPEL), pp 264–269
Krein PT, Bentsman J, Bass RM, Lesieutre BC (1990) On the use of averaging for the analysis of power electronic systems. IEEE Trans Power Electron 5(2):182–190
D’Amico MB, González SA (2017) A small-signal averaged model of a coupled-inductor boost converter. In: Proceedings IEEE Latin American symposium on circuits and systems (LASCAS 2017)
Acknowledgements
Authors acknowledge the financial support of SGCyT at the Universidad Nacional del Sur, Universidad Nacional de La Plata, CONICET and ANPCyT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendices
Appendix A
The solution of set of linear equations defined in Subsection 3.2 is given by
Notice that \(Ip_{12}\) is equivalent to (6) since both expressions arise in the same set of equations (Table 2). But, additional relations given by the average of the currents are used here to find \(d_1\) and \(d_2\) values.
Appendix B
Considering that \(L_{1M}= L_1 + M\), \(L_{2M}= L_2 + M\), \(L_p=L_1+L_2\), \(L_n=L_1-L_2\), \(L_{d}= d L_2 + M\) and \(L_\alpha =M[\alpha +L_1(L_2+M)]\), the polynomials that permit to calculate \(d_1\) and \(d_2\) as a function of the average state-space variables are
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
D’Amico, M.B., González, S.A. Modelling and dynamical analysis of a DC–DC converter with coupled inductors. Electr Eng 101, 67–80 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-019-00757-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-019-00757-1