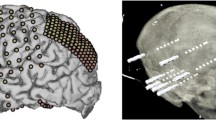
Abstract
Intracerebral EEG, performed in patients during presurgical evaluation of epilepsy, provides a unique opportunity for recording directly from brain structures in humans. From a neuroscientific point of view, this allows investigating brain networks at a mesoscopic scale, with high spatial precision and time-frequency sensitivity. From a methodological perspective, this provides a “ground truth” to which MEG results can be compared. As brain activity fluctuates across sessions and across time within a session, it is necessary to record the signals simultaneously in order to ensure that the same signals are captured in both depth (SEEG) and surface (MEG) measurements. In this chapter, we introduce the practical challenges that are encountered for recording MEG and intracerebral EEG together, as well as the new venues offered by this unique combination of invasive and noninvasive recordings in humans.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alarcon G, Guy CN, Binnie CD, Walker SR, Elwes RD, Polkey CE (1994) Intracerebral propagation of interictal activity in partial epilepsy: implications for source localisation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 57:435–449
Andrzejak RG, David O, Gnatkovsky V, Wendling F, Bartolomei F, Francione S et al (2015) Localization of epileptogenic zone on pre-surgical intracranial EEG recordings: toward a validation of quantitative signal analysis approaches. Brain Topogr 28(6):832–837
Attal Y, Bhattacharjee M, Yelnik J, Cottereau B, Lefèvre J, Okada Y, et al. (2007) Modeling and detecting deep brain activity with MEG & EEG. Conference proceedings: annual international conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society Conference 2007, pp 4937–4940
Badier JM, Dubarry AS, Gavaret M, Chen S, Trebuchon AS, Marquis P et al (2017) Technical solutions for simultaneous MEG and SEEG recordings: towards routine clinical use. Physiol Meas 38:N118–NN27
Baillet S (2003) Challenging MEG source imaging with simultaneous depth recordings in epilepsy. International Congress of the International Society for Brain Electromagnetic Topography (ISBET2003). Santa Fe
Balderston NL, Schultz DH, Baillet S, Helmstetter FJ (2013) How to detect amygdala activity with magnetoencephalography using source imaging. J Vis Exp (76)
Bancaud J, Angelergues R, Bernouilli C, Bonis A, Bordas-Ferrer M, Bresson M et al (1970) Functional stereotaxic exploration (SEEG) of epilepsy. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 28:85–86
Bartolomei F, Trebuchon A, Bonini F, Lambert I, Gavaret M, Woodman M et al (2016) What is the concordance between the seizure onset zone and the irritative zone? A SEEG quantified study. Clin Neurophysiol 127:1157–1162
Bartolomei F, Lagarde S, Wendling F, McGonigal A, Jirsa V, Guye M et al (2017) Defining epileptogenic networks: contribution of SEEG and signal analysis. Epilepsia 58:1131–1147
Bénar C-G, Grova C, Kobayashi E, Bagshaw AP, Aghakhani Y, Dubeau F et al (2006) EEG-fMRI of epileptic spikes: concordance with EEG source localization and intracranial EEG. NeuroImage 30:1161–1170
Bénar C-G, Schön D, Grimault S, Nazarian B, Burle B, Roth M et al (2007) Single-trial analysis of oddball event-related potentials in simultaneous EEG-fMRI. Hum Brain Mapp 28:602–613
Brovelli A, Chicharro D, Badier JM, Wang H, Jirsa V (2015) Characterization of cortical networks and corticocortical functional connectivity mediating arbitrary visuomotor mapping. J Neurosci 35:12643–12658
Cohen D, Cuffin BN, Yunokuchi K, Maniewski R, Purcell C, Cosgrove GR et al (1990) MEG versus EEG localization test using implanted sources in the human brain. Ann Neurol 28:811–817
Coito A, Plomp G, Genetti M, Abela E, Wiest R, Seeck M et al (2015) Dynamic directed interictal connectivity in left and right temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 56(2):207–217
Dalal SS, Baillet S, Adam C, Ducorps A, Schwartz D, Jerbi K et al (2009) Simultaneous MEG and intracranial EEG recordings during attentive reading. NeuroImage 45:1289–1304
Dalal SS, Jerbi K, Bertrand O, Adam C, Ducorps A, Schwartz D et al (2013) Simultaneous MEG-intracranial EEG: new insights into the ability of MEG to capture oscillatory modulations in the neocortex and the hippocampus. Epilepsy Behav 2013
Daunizeau J, Grova C, Marrelec G, Mattout J, Jbabdi S, Pélégrini-Issac M et al (2007) Symmetrical event-related EEG/fMRI information fusion in a variational Bayesian framework. NeuroImage 36:69–87
de Curtis M, Avanzini G (2001) Interictal spikes in focal epileptogenesis. Prog Neurobiol 63:541–567
Debener S, Ullsperger M, Siegel M, Fiehler K, von Cramon DY, Engel AK (2005) Trial-by-trial coupling of concurrent electroencephalogram and functional magnetic resonance imaging identifies the dynamics of performance monitoring. J Neurosci 25:11730–11737
Dubarry AS, Badier JM, Trebuchon-Da Fonseca A, Gavaret M, Carron R, Bartolomei F et al (2014) Simultaneous recording of MEG, EEG and intracerebral EEG during visual stimulation: from feasibility to single-trial analysis. NeuroImage 99:548–558
Gavaret M, Dubarry AS, Carron R, Bartolomei F, CG B, Trébuchon A (2016) Simultaneous SEEG-MEG-EEG recordings overcome the SEEG limited spatial sampling. Epilepsy Res 128(67):72
Gotman J (1991) Relationships between interictal spiking and seizures: human and experimental evidence. Can J Neurol Sci 18:573–576
Jirsa VK, Proix T, Perdikis D, Woodman MM, Wang H, Gonzalez-Martinez J et al (2017) The virtual epileptic patient: individualized whole-brain models of epilepsy spread. NeuroImage 145(Pt B):377–388
Kahane P, Landré E, Minotti L, Francione S, Ryvlin P (2006) The Bancaud and Talairach view on the epileptogenic zone: a working hypothesis. Epileptic Disord 8(Suppl 2):S16–S26
Kakisaka Y, Kubota Y, Wang ZI, Piao Z, Mosher JC, Gonzalez-Martinez J et al (2012) Use of simultaneous depth and MEG recording may provide complementary information regarding the epileptogenic region. Epileptic Disord 14:298–303
Koessler L, Cecchin T, Colnat-Coulbois S, Vignal JP, Jonas J, Vespignani H et al (2015) Catching the invisible: mesial temporal source contribution to simultaneous EEG and SEEG recordings. Brain Topogr 28:5–20
Krieg J, Koessler L, Jonas J, Colnat-Coulbois S, Vignal JP, Benar CG et al (2017) Discrimination of a medial functional module within the temporal lobe using an effective connectivity model: a CCEP study. NeuroImage 161:219–231
Lachaux JP, George N, Tallon-Baudry C, Martinerie J, Hugueville L, Minotti L et al (2005) The many faces of the gamma band response to complex visual stimuli. NeuroImage 25:491–501
Lopes da Silva F, Van Rotterdam A (2005) Biophysical aspects of EEG and magnetoencephalogram generation. In: Electroencephalography: basic principles, clinical applications, and related fields. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore
Malinowska U, Badier JM, Gavaret M, Bartolomei F, Chauvel P, Benar CG (2014) Interictal networks in magnetoencephalography. Hum Brain Mapp 35:2789–2805
Matsumoto R, Nair DR, LaPresto E, Bingaman W, Shibasaki H, Luders HO (2007) Functional connectivity in human cortical motor system: a cortico-cortical evoked potential study. Brain 130:181–197
Merlet I, Gotman J (1999) Reliability of dipole models of epileptic spikes. Clin Neurophysiol 110:1013–1028
Merlet I, Gotman J (2001) Dipole modeling of scalp electroencephalogram epileptic discharges: correlation with intracerebral fields. Clin Neurophysiol 112:414–430
Migliorelli C, Alonso JF, Romero S, Nowak R, Russi A, Mananas MA (2017) Automated detection of epileptic ripples in MEG using beamformer-based virtual sensors. J Neural Eng 14:046013
Mikuni N, Nagamine T, Ikeda A, Terada K, Taki W, Kimura J et al (1997) Simultaneous recording of epileptiform discharges by MEG and subdural electrodes in temporal lobe epilepsy. NeuroImage 5:298–306
Oishi M, Otsubo H, Kameyama S, Morota N, Masuda H, Kitayama M et al (2002) Epileptic spikes: magnetoencephalography versus simultaneous electrocorticography. Epilepsia 43:1390–1395
Oswal A, Jha A, Neal S, Reid A, Bradbury D, Aston P et al (2016) Analysis of simultaneous MEG and intracranial LFP recordings during deep brain stimulation: a protocol and experimental validation. J Neurosci Methods 261:29–46
Petkoski S, Palva JM, Jirsa VK (2018) Phase-lags in large scale brain synchronization: methodological considerations and in-silico analysis. PLoS Comput Biol 14:e1006160
Pizzo F, Roehri N, Medina Villalon S, Trebuchon A, Chen S, Lagarde S et al (2019) Deep brain activities can be detected with magnetoencephalography. Nat Commun 10:971
Ponten SC, Bartolomei F, Stam CJ (2007) Small-world networks and epilepsy: graph theoretical analysis of intracerebrally recorded mesial temporal lobe seizures. Clin Neurophysiol 118:918–927
Rampp S, Kaltenhauser M, Weigel D, Buchfelder M, Ingmar Blumcke I, Dorfler A et al (2010) MEG correlates of epileptic high gamma oscillations in invasive EEG. Epilepsia 51:1638–1642
Roehri N, Pizzo F, Lagarde S, Lambert I, Nica A, McGonigal A et al (2018) High-frequency oscillations are not better biomarkers of epileptogenic tissues than spikes. Ann Neurol 83:84–97
Rosenow F, Lüders H (2001) Presurgical evaluation of epilepsy. Brain 124:1683–1700
Santiuste M, Nowak R, Russi A, Tarancon T, Oliver B, Ayats E et al (2008) Simultaneous magnetoencephalography and intracranial EEG registration: technical and clinical aspects. J Clin Neurophysiol 25:331–339
Shigeto H, Morioka T, Hisada K, Nishio S, Ishibashi H, Kira D et al (2002) Feasibility and limitations of magnetoencephalographic detection of epileptic discharges: simultaneous recording of magnetic fields and electrocorticography. Neurol Res 24:531–536
Shirozu H, Hashizume A, Masuda H, Fukuda M, Ito Y, Nakayama Y et al (2016) Spatiotemporal accuracy of gradient magnetic-field topography (GMFT) confirmed by simultaneous magnetoencephalography and intracranial electroencephalography recordings in patients with intractable epilepsy. Front Neural Circ 10:65
Sutherling WW, Akhtari M, Mamelak AN, Mosher J, Arthur D, Sands S et al (2001) Dipole localization of human induced focal afterdischarge seizure in simultaneous magnetoencephalography and electrocorticography. Brain Topogr 14:101–116
Tallon-Baudry C, Bertrand O, Henaff MA, Isnard J, Fischer C (2005) Attention modulates gamma-band oscillations differently in the human lateral occipital cortex and fusiform gyrus. Cereb Cortex 15:654–662
Tao JX, Ray A, Hawes-Ebersole S, Ebersole JS (2005) Intracranial EEG substrates of scalp EEG interictal spikes. Epilepsia 46:669–676
Urrestarazu E, Chander R, Dubeau F, Gotman J (2007) Interictal high-frequency oscillations (100–500 Hz) in the intracerebral EEG of epileptic patients. Brain 130:2354–2366
van Klink N, Hillebrand A, Zijlmans M (2016) Identification of epileptic high frequency oscillations in the time domain by using MEG beamformer-based virtual sensors. Clin Neurophysiol 127:197–208
van Mierlo P, Carrette E, Hallez H, Raedt R, Meurs A, Vandenberghe S et al (2013) Ictal-onset localization through connectivity analysis of intracranial EEG signals in patients with refractory epilepsy. Epilepsia 54:1409–1418
Wennberg R, Valiante T, Cheyne D (2011) EEG and MEG in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy: where do the spikes really come from. Clin Neurophysiol 122:1295–1313
Wilke C, Worrell G, He B (2011) Graph analysis of epileptogenic networks in human partial epilepsy. Epilepsia 52:84–93
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Section Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry
Bénar, CG., Badier, JM. (2019). Simultaneous Recordings of MEG and Intracerebral EEG. In: Supek, S., Aine, C. (eds) Magnetoencephalography. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00087-5_58
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00087-5_58
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-00086-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-00087-5
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesReference Module Biomedical and Life Sciences