Abstract
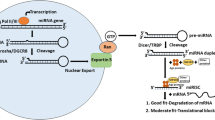
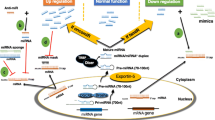
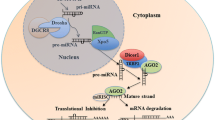
MicroRNA (miRNA) is a nonprotein coding small RNA molecule that negatively regulates gene expression by degradation of mRNA or suppression of mRNA translation. MiRNA plays important roles in physiological processes such as cellular development, differentiation, proliferation, apoptosis, and stem cell self-renewal. Studies show that the deregulation of miRNA expression is closely associated with tumorigenicity, invasion, and metastasis. The functionality of miRNAs may act as oncogenes or tumor suppressors during tumor initiation and progression. miRNomes in almost all types of cancers started to develop the regulatory network of miRNA::mRNA interaction in the view of systems biology. Experimental evidence demonstrates that the modulation of specific miRNA alterations in cancer cells using miRNA replacement or anti-miRNA technologies can restore miRNA activities and repair the gene regulatory network and signaling pathways, in turn, reverse the phenotype of cancerous cells. Numerous animal studies for miRNA-based therapy offer the hope of targeting miRNAs as alternative cancer treatment. Developing the small molecules to interfere with miRNAs could be of great pharmaceutical interest in the future. Interestingly, specific miRNA is capable of reprogramming the cancer cells into a pluriopotent embryonic stem cell-like state (mirPS), which could be induced into tissue-specific mature cell types. This chapter will present the various strategies of modulation of miRNAs in vitro and in vivo.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kato, M., and Slack, F. J. (2008) MicroRNAs: small molecules with big roles – C. elegans to human cancer, Biol Cell 100, 71–81.
Lee, R. C., Feinbaum, R. L., and Ambros, V. (1993) The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14, Cell 75, 843–854.
Reinhart, B. J., Slack, F. J., Basson, M., Pasquinelli, A. E., Bettinger, J. C., Rougvie, A. E., Horvitz, H. R., and Ruvkun, G. (2000) The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans, Nature 403, 901–906.
Lagos-Quintana, M., Rauhut, R., Lendeckel, W., and Tuschl, T. (2001) Identification of novel genes coding for small expressed RNAs, Science 294, 853–858.
Lau, N. C., Lim, L. P., Weinstein, E. G., and Bartel, D. P. (2001) An abundant class of tiny RNAs with probable regulatory roles in Caenorhabditis elegans, Science 294, 858–862.
Lee, R. C., and Ambros, V. (2001) An extensive class of small RNAs in Caenorhabditis elegans, Science 294, 862–864.
Bartel, D. P. (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function, Cell 116, 281–297.
Kim, V. N., and Nam, J. W. (2006) Genomics of microRNA, Trends Genet 22, 165–173.
Hutvagner, G., and Zamore, P. D. (2002) A microRNA in a multiple-turnover RNAi enzyme complex, Science 297, 2056–2060.
Wu, W., Sun, M., Zou, G. M., and Chen, J. (2006) MicroRNA and cancer: Current status and prospective, Int J Cancer 120, 953–960.
He, L., Thomson, J. M., Hemann, M. T., Hernando-Monge, E., Mu, D., Goodson, S., Powers, S., Cordon-Cardo, C., Lowe, S. W., Hannon, G. J., and Hammond, S. M. (2005) A microRNA polycistron as a potential human oncogene, Nature 435, 828–833.
O’Donnell, K. A., Wentzel, E. A., Zeller, K. I., Dang, C. V., and Mendell, J. T. (2005) c-Myc-regulated microRNAs modulate E2F1 expression, Nature 435, 839–843.
Zhu, S., Wu, H., Wu, F., Nie, D., Sheng, S., and Mo, Y. Y. (2008) MicroRNA-21 targets tumor suppressor genes in invasion and metastasis, Cell Res 18, 350–359.
Hua, Z., Lv, Q., Ye, W., Wong, C. K., Cai, G., Gu, D., Ji, Y., Zhao, C., Wang, J., Yang, B. B., and Zhang, Y. (2006) MiRNA-directed regulation of VEGF and other angiogenic factors under hypoxia, PLoS ONE 1, e116.
Yu, F., Yao, H., Zhu, P., Zhang, X., Pan, Q., Gong, C., Huang, Y., Hu, X., Su, F., Lieberman, J., and Song, E. (2007) let-7 regulates self renewal and tumorigenicity of breast cancer cells, Cell 131, 1109–1123.
Calin, G. A., Sevignani, C., Dumitru, C. D., Hyslop, T., Noch, E., Yendamuri, S., Shimizu, M., Rattan, S., Bullrich, F., Negrini, M., and Croce, C. M. (2004) Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101, 2999–3004.
Calin, G. A., Liu, C. G., Sevignani, C., Ferracin, M., Felli, N., Dumitru, C. D., Shimizu, M., Cimmino, A., Zupo, S., Dono, M., Dell’Aquila, M. L., Alder, H., Rassenti, L., Kipps, T. J., Bullrich, F., Negrini, M., and Croce, C. M. (2004) MicroRNA profiling reveals distinct signatures in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemias, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101, 11755–11760.
Cimmino, A., Calin, G. A., Fabbri, M., Iorio, M. V., Ferracin, M., Shimizu, M., Wojcik, S. E., Aqeilan, R. I., Zupo, S., Dono, M., Rassenti, L., Alder, H., Volinia, S., Liu, C. G., Kipps, T. J., Negrini, M., and Croce, C. M. (2005) miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2, Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102, 13944–13949.
Johnson, S. M., Grosshans, H., Shingara, J., Byrom, M., Jarvis, R., Cheng, A., Labourier, E., Reinert, K. L., Brown, D., and Slack, F. J. (2005) RAS is regulated by the let-7 microRNA family, Cell 120, 635–647.
Park, S. M., Shell, S., Radjabi, A. R., Schickel, R., Feig, C., Boyerinas, B., Dinulescu, D. M., Lengyel, E., and Peter, M. E. (2007) Let-7 prevents early cancer progression by suppressing expression of the embryonic gene HMGA2, Cell Cycle 6, 2585–2590.
Ota, A., Tagawa, H., Karnan, S., Tsuzuki, S., Karpas, A., Kira, S., Yoshida, Y., and Seto, M. (2004) Identification and characterization of a novel gene, C13orf25, as a target for 13q31-q32 amplification in malignant lymphoma, Cancer Res 64, 3087–3095.
Hayashita, Y., Osada, H., Tatematsu, Y., Yamada, H., Yanagisawa, K., Tomida, S., Yatabe, Y., Kawahara, K., Sekido, Y., and Takahashi, T. (2005) A polycistronic microRNA cluster, miR-17-92, is overexpressed in human lung cancers and enhances cell proliferation, Cancer Res 65, 9628–9632.
Takakura, S., Mitsutake, N., Nakashima, M., Namba, H., Saenko, V. A., Rogounovitch, T. I., Nakazawa, Y., Hayashi, T., Ohtsuru, A., and Yamashita, S. (2008) Oncogenic role of miR-17-92 cluster in anaplastic thyroid cancer cells, Cancer Sci 99, 1147–1154.
Hossain, A., Kuo, M. T., and Saunders, G. F. (2006) Mir-17-5p regulates breast cancer cell proliferation by inhibiting translation of AIB1 mRNA, Mol Cell Biol 26, 8191–8201.
Lu, Z., Liu, M., Stribinskis, V., Klinge, C. M., Ramos, K. S., Colburn, N. H., and Li, Y. (2008) MicroRNA-21 promotes cell transformation by targeting the programmed cell death 4 gene, Oncogene 27, 4373–4379.
Meng, F., Henson, R., Wehbe-Janek, H., Ghoshal, K., Jacob, S. T., and Patel, T. (2007) MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer, Gastroenterology 133, 647–658.
Zhu, S., Si, M. L., Wu, H., and Mo, Y. Y. (2007) MicroRNA-21 targets the tumor suppressor gene tropomyosin 1 (TPM1), J Biol Chem 282, 14328–14336.
Asangani, I. A., Rasheed, S. A., Nikolova, D. A., Leupold, J. H., Colburn, N. H., Post, S., and Allgayer, H. (2008) MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer, Oncogene 27, 2128–2136.
Frankel, L. B., Christoffersen, N. R., Jacobsen, A., Lindow, M., Krogh, A., and Lund, A. H. (2008) Programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) is an important functional target of the microRNA miR-21 in breast cancer cells, J Biol Chem 283, 1026–1033.
Gabriely, G., Wurdinger, T., Kesari, S., Esau, C. C., Burchard, J., Linsley, P. S., and Krichevsky, A. M. (2008) MiR-21 promotes glioma invasion by targeting MMP regulators, Mol Cell Biol 28(17), 5369–5380.
Sayed, D., Rane, S., Lypowy, J., He, M., Chen, I. Y., Vashistha, H., Yan, L., Malhotra, A., Vatner, D., and Abdellatif, M. (2008) MicroRNA-21 targets Sprouty2 and promotes cellular outgrowths, Mol Biol Cell 19(8), 3272–3282.
Yu, S. L., Chen, H. Y., Chang, G. C., Chen, C. Y., Chen, H. W., Singh, S., Cheng, C. L., Yu, C. J., Lee, Y. C., Chen, H. S., Su, T. J., Chiang, C. C., Li, H. N., Hong, Q. S., Su, H. Y., Chen, C. C., Chen, W. J., Liu, C. C., Chan, W. K., Chen, W. J., Li, K. C., Chen, J. J., and Yang, P. C. (2008) MicroRNA signature predicts survival and relapse in lung cancer, Cancer Cell 13, 48–57.
Lewis, B. P., Shih, I. H., Jones-Rhoades, M. W., Bartel, D. P., and Burge, C. B. (2003) Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets, Cell 115, 787–798.
Wang, V., and Wu, W. (2009) MicroRNA-based therapeutics for cancer, BioDrugs 23, 15–23.
Takamizawa, J., Konishi, H., Yanagisawa, K., Tomida, S., Osada, H., Endoh, H., Harano, T., Yatabe, Y., Nagino, M., Nimura, Y., Mitsudomi, T., and Takahashi, T. (2004) Reduced expression of the let-7 microRNAs in human lung cancers in association with shortened postoperative survival, Cancer Res 64, 3753–3756.
Weidhaas, J. B., Babar, I., Nallur, S. M., Trang, P., Roush, S., Boehm, M., Gillespie, E., and Slack, F. J. (2007) MicroRNAs as potential agents to alter resistance to cytotoxic anticancer therapy, Cancer Res 67, 11111–11116.
Johnson, C. D., Esquela-Kerscher, A., Stefani, G., Byrom, M., Kelnar, K., Ovcharenko, D., Wilson, M., Wang, X., Shelton, J., Shingara, J., Chin, L., Brown, D., and Slack, F. J. (2007) The let-7 microRNA represses cell proliferation pathways in human cells, Cancer Res 67, 7713–7722.
Esquela-Kerscher, A., Trang, P., Wiggins, J. F., Patrawala, L., Cheng, A., Ford, L., Weidhaas, J. B., Brown, D., Bader, A. G., and Slack, F. J. (2008) The let-7 microRNA reduces tumor growth in mouse models of lung cancer, Cell Cycle 7, 759–764.
Trang, P., Medina, P. P., Wiggins, J. F., Ruffino, L., Kelnar, K., Omotola, M., Homer, R., Brown, D., Bader, A. G., Weidhaas, J. B., and Slack, F. J. (2010) Regression of murine lung tumors by the let-7 microRNA, Oncogene 29(11), 1580–1587.
Xiao, J., Yang, B., Lin, H., Lu, Y., Luo, X., and Wang, Z. (2007) Novel approaches for gene-specific interference via manipulating actions of microRNAs: examination on the pacemaker channel genes HCN2 and HCN4, J Cell Physiol 212, 285–292.
Chung, K. H., Hart, C. C., Al-Bassam, S., Avery, A., Taylor, J., Patel, P. D., Vojtek, A. B., and Turner, D. L. (2006) Polycistronic RNA polymerase II expression vectors for RNA interference based on BIC/miR-155, Nucleic Acids Res 34, e53.
McLaughlin, J., Cheng, D., Singer, O., Lukacs, R. U., Radu, C. G., Verma, I. M., and Witte, O. N. (2007) Sustained suppression of Bcr-Abl-driven lymphoid leukemia by microRNA mimics, Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104, 20501–20506.
Liang, Z., Wu, H., Reddy, S., Zhu, A., Wang, S., Blevins, D., Yoon, Y., Zhang, Y., and Shim, H. (2007) Blockade of invasion and metastasis of breast cancer cells via targeting CXCR4 with an artificial microRNA, Biochem Biophys Res Commun 363, 542–546.
Li, Z., Zhan, W., Wang, Z., Zhu, B., He, Y., Peng, J., Cai, S., and Ma, J. (2006) Inhibition of PRL-3 gene expression in gastric cancer cell line SGC7901 via microRNA suppressed reduces peritoneal metastasis, Biochem Biophys Res Commun 348, 229–237.
Weiler, J., Hunziker, J., and Hall, J. (2006) Anti-miRNA oligonucleotides (AMOs): ammunition to target miRNAs implicated in human disease? Gene Ther 13(6), 496–502.
Wahlestedt, C., Salmi, P., Good, L., Kela, J., Johnsson, T., Hokfelt, T., Broberger, C., Porreca, F., Lai, J., Ren, K., Ossipov, M., Koshkin, A., Jakobsen, N., Skouv, J., Oerum, H., Jacobsen, M. H., and Wengel, J. (2000) Potent and nontoxic antisense oligonucleotides containing locked nucleic acids, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97, 5633–5638.
Chan, J. A., Krichevsky, A. M., and Kosik, K. S. (2005) MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells, Cancer Res 65, 6029–6033.
Si, M. L., Zhu, S., Wu, H., Lu, Z., Wu, F., and Mo, Y. Y. (2006) miR-21-mediated tumor growth, Oncogene 26(19), 2799–2803.
Moriyama, T., Ohuchida, K., Mizumoto, K., Yu, J., Sato, N., Nabae, T., Takahata, S., Toma, H., Nagai, E., and Tanaka, M. (2009) MicroRNA-21 modulates biological functions of pancreatic cancer cells including their proliferation, invasion, and chemoresistance, Mol Cancer Ther 8(5), 1067–1074.
Meng, F., Henson, R., Lang, M., Wehbe, H., Maheshwari, S., Mendell, J. T., Jiang, J., Schmittgen, T. D., and Patel, T. (2006) Involvement of human micro-RNA in growth and response to chemotherapy in human cholangiocarcinoma cell lines, Gastroenterology 130, 2113–2129.
Corsten, M. F., Miranda, R., Kasmieh, R., Krichevsky, A. M., Weissleder, R., and Shah, K. (2007) MicroRNA-21 knockdown disrupts glioma growth in vivo and displays synergistic cytotoxicity with neural precursor cell delivered S-TRAIL in human gliomas, Cancer Res 67, 8994–9000.
Ebert, M. S., Neilson, J. R., and Sharp, P. A. (2007) MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells, Nat Methods 4, 721–726.
Lu, Y., Xiao, J., Lin, H., Bai, Y., Luo, X., Wang, Z., and Yang, B. (2009) A single anti-microRNA antisense oligodeoxyribonucleotide (AMO) targeting multiple microRNAs offers an improved approach for microRNA interference, Nucleic Acids Res 37, e24.
Abujarour, R., and Ding, S. (2009) Induced pluripotent stem cells free of exogenous reprogramming factors, Genome Biol 10, 220.
Gumireddy, K., Young, D. D., Xiong, X., Hogenesch, J. B., Huang, Q., and Deiters, A. (2008) Small-molecule inhibitors of microrna miR-21 function, Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 47, 7482–7484.
Rossi, L., Bonmassar, E., and Faraoni, I. (2007) Modification of miR gene expression pattern in human colon cancer cells following exposure to 5-fluorouracil in vitro, Pharmacol Res 56, 248–253.
Bhat-Nakshatri, P., Wang, G., Collins, N. R., Thomson, M. J., Geistlinger, T. R., Carroll, J. S., Brown, M., Hammond, S., Srour, E. F., Liu, Y., and Nakshatri, H. (2009) Estradiol-regulated microRNAs control estradiol response in breast cancer cells, Nucleic Acids Res 37, 4850–4861.
Wickramasinghe, N. S., Manavalan, T. T., Dougherty, S. M., Riggs, K. A., Li, Y., and Klinge, C. M. (2009) Estradiol downregulates miR-21 expression and increases miR-21 target gene expression in MCF-7 breast cancer cells, Nucleic Acids Res 37, 2584–2595.
Deiters, A. (2010) Small molecule modifiers of the microRNA and RNA interference pathway, AAPS J 12(1), 51–60.
Krutzfeldt, J., Rajewsky, N., Braich, R., Rajeev, K. G., Tuschl, T., Manoharan, M., and Stoffel, M. (2005) Silencing of microRNAs in vivo with ‘antagomirs’, Nature 438, 685–689.
Wolfrum, C., Shi, S., Jayaprakash, K. N., Jayaraman, M., Wang, G., Pandey, R. K., Rajeev, K. G., Nakayama, T., Charrise, K., Ndungo, E. M., Zimmermann, T., Koteliansky, V., Manoharan, M., and Stoffel, M. (2007) Mechanisms and optimization of in vivo delivery of lipophilic siRNAs, Nat Biotechnol 25, 1149–1157.
Elmen, J., Lindow, M., Schutz, S., Lawrence, M., Petri, A., Obad, S., Lindholm, M., Hedtjarn, M., Hansen, H. F., Berger, U., Gullans, S., Kearney, P., Sarnow, P., Straarup, E. M., and Kauppinen, S. (2008) LNA-mediated microRNA silencing in non-human primates, Nature 452, 896–899.
Elmen, J., Lindow, M., Silahtaroglu, A., Bak, M., Christensen, M., Lind-Thomsen, A., Hedtjarn, M., Hansen, J. B., Hansen, H. F., Straarup, E. M., McCullagh, K., Kearney, P., and Kauppinen, S. (2008) Antagonism of microRNA-122 in mice by systemically administered LNA-antimiR leads to up-regulation of a large set of predicted target mRNAs in the liver, Nucleic Acids Res 36, 1153–1162.
Kota, J., Chivukula, R. R., O’Donnell, K. A., Wentzel, E. A., Montgomery, C. L., Hwang, H. W., Chang, T. C., Vivekanandan, P., Torbenson, M., Clark, K. R., Mendell, J. R., and Mendell, J. T. (2009) Therapeutic microRNA delivery suppresses tumorigenesis in a murine liver cancer model, Cell 137, 1005–1017.
Takahashi, K., and Yamanaka, S. (2006) Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors, Cell 126, 663–676.
Yu, J., Vodyanik, M. A., Smuga-Otto, K., Antosiewicz-Bourget, J., Frane, J. L., Tian, S., Nie, J., Jonsdottir, G. A., Ruotti, V., Stewart, R., Slukvin, II, and Thomson, J. A. (2007) Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from human somatic cells, Science 318, 1917–1920.
Judson, R. L., Babiarz, J. E., Venere, M., and Blelloch, R. (2009) Embryonic stem cell-specific microRNAs promote induced pluripotency, Nat Biotechnol 27, 459–461.
Lin, S. L., Chang, D. C., Chang-Lin, S., Lin, C. H., Wu, D. T., Chen, D. T., and Ying, S. Y. (2008) Mir-302 reprograms human skin cancer cells into a pluripotent ES-cell-like state, RNA 14, 2115–2124.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Wu, W. (2011). Modulation of MicroRNAs for Potential Cancer Therapeutics. In: Wu, W. (eds) MicroRNA and Cancer. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 676. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60761-863-8_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60761-863-8_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, Totowa, NJ
Print ISBN: 978-1-60761-862-1
Online ISBN: 978-1-60761-863-8
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols