Abstract
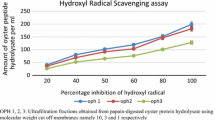
A unique antioxidant peptidoglycan of 6.5 kDa was purified from silk worm (Bombyx mori) pupae. The peptidoglycan was extracted and isolated from the acidified aqueous extract of the homogenized pupae by chloroform/methanol (2:1, v/v), and purified by size-exclusion chromatography and reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC). This separation method allowed an easy and consistent preparation of the peptidoglycan from the high protein load by using only 3 steps of purification. The highly pure peptidoglycan consisted of fucose, glucosamine, galactosamine, glucose, and galactose as constituent sugars when revealed by high-performance anion exchange chromatography (HPAEC) analysis. The amino acid composition analysis showed the presence of acidic and polar amino acids (51.7%), hydrophobic (37.2%), and basic amino acids (9.3%) in the purified peptidoglycan. The IC50 of the purified peptidoglycan was 0.22±0.05 and 0.61±0.09 μg for diphenyl-2-picryl hydrazyl (DPPH) and 2,2′-azinobis-(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS), respectively, as quantified by Ophthalaldehyde (OPA) microplate fluorescent assay.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hasler CM. The changing face of functional foods. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 19: 499S–506S (2000)
Craig TW. Dairy derived food ingredients-functional and nutritional considerations. J. Dairy Sci. 62: 1695–1702 (1979)
Hasler CM. Functional Foods: Benefits, concerns, and challenges-A position paper from the American council on science and health. J. Nutr. 132: 3772–3781 (2002)
Khatun R, Azmal SA, Sarker MSK, Rashid MA, Hussain MA, Miah MY. Effect of silkworm pupae on the growth and egg production performance of Rhode Island red (RIR) pure line. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 4: 718–720 (2005)
Vercruysse L, Smagghe G, Herregods G, Camp JV. ACE inhibitory activity in enzymatic eydrolysates of insect protein. J. Agr. Food Chem. 53: 5207–5211 (2005)
Dean RT, Gieseg S, Davies MJ. Reactive species and their accumulation on radical-damaged proteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 18: 437–441 (1993)
Ooi VE, Liu F. Immunomodulation and anti-cancer activity of polysaccharide-protein complexes. Curr. Med. Chem. 7: 715–729 (2000)
Escribano J, Piqueras A, Medina J, Rubio A, Alvarez-Ortí M, Fernández JA. Production of a cytotoxic proteoglycan using callus culture of saffron corms (Crocus sativus L.). J. Biotechnol. 73: 53–59 (1999)
Rajaganapathi J, Thyagarajan SP, Edward JK. Study on cephalopod’s ink for anti-retroviral activity. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 38: 519–520 (2000)
Sasaki J, Ishita K, Takaya Y, Uchisawa H, Matsue H. Antitumor activity of squid ink. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 43: 455–461 (1997)
Takaya Y, Uchiswa H. An investigation of the antitumor peptidoglycan fraction from squid ink. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 17: 846–851 (1994)
Conlon MJ. Purification of naturally occurring peptides by reversed-phase HPLC. Nat. Protoc. 2: 191–197 (2007)
Goodno CC, Swaisgood HE, Catignani GL. A fluorimetric assay for available lysine in proteins. Anal. Biochem. 115: 203–211 (1981)
Weidekamm E, Wallach DFH, Fluckiger R. A new sensitive, rapid fluorescence technique for the determination of proteins in gel electrophoresis and in solution. Anal. Biochem. 54: 102–114 (1973)
Shimada K, Fujikawa K, Yahara K, Nakamura T. Antioxidative properties of xanthan on the antioxidation of soybean oil in cyclodextrin emulsion. J. Agr. Food Chem. 40: 945–948 (1992)
Re R, Pellegrini N, Proteggente A, Pannala A, Yang M, Rice-Evans C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radical Bio. Med. 26: 1231–1237 (1999)
Curtino JA, Chiodi JC. Delipidization of membrane glycoproteins solubilized in acidified chloroform/methanol. Preparation of N-retinylidene opsin in a water soluble form without-detergent. Biochem. Int. 11: 107–115 (1985)
Rider CC. Analysis of glycosaminoglycans and proteoglycans. Vol. 76, pp. 131–144. In: Glycoanalysis Protocols. Hounsell EF (ed). The Humana Press, Totowa, NJ, USA (1998)
Segrest JP, Jackson RL. Molecular weight determinations of glycoproteins by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in sodium dodecyl sulfate. Methods Enzymol. 27: 54–63 (1972)
Argraves WS, Tran H, Burgess WH, Diekerson K. Fibulin is an extracellular matrix and plasma glycoprotein with repeated domain structure. J. Cell Biol. 111: 3155–3164 (1990)
Takano E, Maki M, Mori H, Hatanaka M, Marti T, Titani K, Kannagi R, Ooi T, Murachi T. Pig heart calpastatin: Identification of repetitive domain structures and anomalous behavior in pelyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry 27: 1964–1972 (1988)
Kirazov LP, Venkov LG, Kirazov EP. Comparison of the Lowry and the Bradford protein assays as applied for protein estimation of membrane-containing fractions. Anal. Biochem. 208: 44–48 (1993)
Congdon RW, Muth GW, Splittgerber AG. The binding interaction of Coomassie blue with proteins. Anal. Biochem. 213: 407–413 (1993)
Lissi EA, Modak B, Torres R, Escobar J, Urzua A. Total antioxidant potential of resinous exudates from Heliotropium species, and a comparison of the ABTS and DPPH methods. Free Radical Res. 30: 471–477 (1999)
Villaño D, Fernández-Pachón MS, Moyá ML, Troncoso AM, García-Parrilla MC. Radical scavenging ability of polyphenolic compounds towards DPPH free radical. Talanta 71: 230–235 (2007)
Pownall TL, Udenigwe CC, Aluko RE. Amino acid composition and antioxidant properties of pea seed (Pisum sativum L.) enzymatic protein hydrolysate fractions. J. Agr. Food Chem. 58: 4712–4718 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Azzouny, R.A., Wang, R. & Yoo, SH. Purification and characterization of a 6.5 kDa antioxidant peptidoglycan purified from silk worm (Bombyx mori) pupae extract. Food Sci Biotechnol 20, 243–249 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-011-0033-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-011-0033-6