Abstract
The pull-out strength of an axially loaded glued-in rod depends on the joint dimensions. For given materials, stresses into the joint and corresponding resistances are governed by geometric parameters. This paper aims at assessing the influence of each geometric parameter on failure modes which affect the timber element. The most significant ones are the shear failure of the adhesive/timber interface and the tensile failure of timber at the bottom of the hole. Some analytical approaches, supported by a large experimental database taken from referenced literature and checked by finite element simulations, are presented using a linear elastic modelling. Finally a proposal is made for a predictive, versatile, numerical model which requires a minimal experimental programme.
Résumé
La résistance à l’arrachement d’un goujon collé est intimement liée aux dimensions de l’assemblage. Celles-ci déterminent, pour des matériaux donnés, l’intensité des contraintes transmises par l’assemblage et les résistances correspondantes. Le présent article s’emploie à évaluer l’influence des paramètres géométriques sur les modes de rupture affectant l’élément bois: rupture en cisaillement de l’interface adhésif/bois et rupture en traction de l’élément bois. Des approches analytiques, basées sur les vastes travaux expérimentaux de la bibliographie et vérifiées au moyen de simulations numériques éléments finis, sont réalisées en élasticité linéaire. Une méthode de caractérisation, basée sur un modèle numérique paramétrable et sur un protocole expérimental allégé, est finalement proposée.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
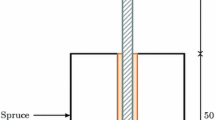
- d r :
-
Rod diameter (mm)
- d h :
-
Hole diameter (mm)
- ℓ:
-
Anchorage length (mm)
- a :
-
Transverse dimension of the beam (mm)
- E r :
-
Young modulus of the rod (MPa)
- E a :
-
Young modulus of the adhesive (MPa)
- E w :
-
Young modulus of the timber (MPa)
- τf :
-
Shear resistance of the glueline (MPa)
- G f :
-
Total fracture energy of the glueline (N/mm)
- t r :
-
Rod thickness in 2D modelling (mm) (see Fig. 9)
- t a :
-
Glue line thickness (mm) (see Fig. 9)
- P f :
-
Joint load carrying capacity (N)
- A r :
-
Rod cross section (mm2)
- A w :
-
Timber cross section (mm2)
- k :
-
Ratio between rod and timber rigidities (E r A r and E w A w)
- η :
-
Distance from the glued-in rod to the timber edge (mm)
- σ :
-
Mean radial tension stress across the adhesive (MPa)
- M :
-
Bending moment (N · mm)
- V :
-
Transverse force (N)
- I w :
-
Inertia of timber (mm4)
- v :
-
deflection (mm)
References
Les cahiers d’IRABOIS (1999) Guide professionnel sur les assemblages: tiges ou goujons collés de grandes dimensions
Gustafsson PJ, Serrano E, Aicher S, Johansson CJ (2001) A strength design equation for glued-in rods. Proceedings of the International RILEM Symposium, Germany, pp 323–332
Feligioni L, Lavisci P, Duchanois G, De Ciechi M, Spinelli P (2003) Influence of glue rheology and joint thickness on the strength of bonded-in rods. Holz als Roh- und Werkstoff61, Springer-Verlag, pp 281–287
Faye C (2004) Durée de vie des assemblages par goujons collés pour du laméllé-collé sous sollicitations mécaniques et hygrothermiques. Rapport final SNCCBLC/CTBA/LRBB
Serrano E (2001) Glued in rods for timber structures – an experimental study of softening behaviour. Mater Struct 34:228–234 (RILEM Publications)
Gustafsson PJ (1987) Analysis of generalized Volkersen joints in terms of non linear fracture mechanics. CIB W18-A, paper 20-18-2
Aicher S (2001) Characteristic axial resistance of threaded rods glued-in spruce dependant on adhesive type – a complementary database for the GIROD project. Otto Graf Institute, University of Stuttgart, Germany
Gardelle V (2005) Mécanique des assemblages et renforts collés en construction bois. Thèse de doctorat, Université Bordeaux 1
Volkersen O (1997) 1938, extrait de “Structural Adhesive Joints in Engineering”, Part 2.2.2. In: Adams RD, Comyn J, Wake WC (eds) Volkersen’s analysis, 2nd edn. Chapman & Hall, pp 18–20
Eurocode 5 (2003) “Design of timber structures”, Part2: Bridges, prEN 1995-2 Second draft
Surleau J (2004) Durée de vie des assemblages par goujons collés sous solicitations mécaniques et hygrothermiques. Thèse de doctorat, Université Bordeaux I
Blass HJ, Laskewitz B (1999) Effect of spacing and edge distance on the axial strength of glued-in rods. CIB W18 Meeting, paper 32-7-12
Gehri E (2001) Ductile behaviour and group effect of glued-in steel rods. Proceedings of the International RILEM Symposium, Germany, pp 333–342
Règles BPEL (1993) 91: Règles techniques de conception et de calcul des ouvrages et constructions en béton précontraint suivant la méthode des états limites. Edition Eyrolles
Hart-Smith LJ (1973) Adhesive-bonded double-lap joints. CR-112235, NASA, Langley Research Center, USA
Bernasconi A (2001) Axially loaded glued-in rods for high capacity joints – behaviour and resistance. Proceedings of the International RILEM Symposium, Germany, pp 323–332
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gardelle, V., Morlier, P. Geometric parameters which affect the short term resistance of an axially loaded glued-in rod. Mater Struct 40, 127–138 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1617/s11527-006-9155-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1617/s11527-006-9155-3