Abstract
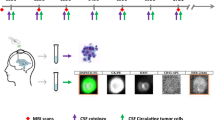
The aim of the present study was to evaluate the predictive value of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) tumor marker levels in patients with breast cancer and carcinomatous meningitis. Serial CSF and serum tumor marker (CEA, CA-15.3, CA-125, and CA-19.9) measurements were performed in five patients with breast cancer developing carcinomatous meningitis in an attempt to correlate these with clinical outcome under treatment. CSF tumor marker levels correlated with response to treatment and outcome in each patient, and, despite achieving negative CSF cytology after therapy in two patients, it heralded disease progression. Given our findings, CSF tumor marker evaluation may provide a reliable means and surrogate end-points of monitoring response of carcinomatous meningitis to treatment. Therefore, large studies to assess the value of CSF tumor marker changes in carcinomatous meningitis are warranted.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Posner JB. Neurologic Complications of Cancer. F.A. Davis: Philadelphia, PA, 1995, pp. 143–168.
Clayton AJ, et al. Incidence of cerebral metastases in patients treated with trastuzumab for metastatic breast cancer. Br J Cancer 2004; 91: 639–643.
Yap BS, Yap HY, Fritsche HA, Blumenschein G, Bodey GP. CSF carcinoembryonic antigen in meningeal carcinomatosis from breast cancer. JAMA 1980; 244: 1601–1603.
Glantz MJ, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid cytology in patients with cancer, minimizing false-negative results. Cancer 1998; 82: 733–739.
Glantz MJ, et al. A randomized controlled trial comparing intrathecal sustained-release cytarabine (DepoCyt) to intrathecal methotrexate in patients with neoplastic meningitis from solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 1999; 5: 3394–3402.
Bagshawe KD, Harland SJ. Immunodiagnosis and monitoring of gonadotrophin-producing metastases in the central nervous system. Cancer 1976; 38: 112–118.
van Oostenbrugge RJ, Hopman AHN, Arends JW, Ramaekers FCS, Twijnstra A. Treatment of leptomeningeal metastases evaluated by interface cytogenetics. J Clin Oncol 2000; 18: 2053–2058.
Stockhammer G, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor in CSF. A biological marker for carcinomatous meningitis. Neurology 2000; 54: 1670–1675.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kosmas, C., Tsavaris, N.B., Soukouli, G. et al. Changes of cerebrospinal fluid tumor marker levels may predict response to treatment and survival of carcinomatous meningitis in patients with advanced breast cancer. Med Oncol 22, 123–128 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1385/MO:22:2:123
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/MO:22:2:123