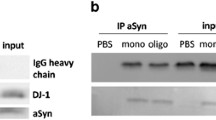
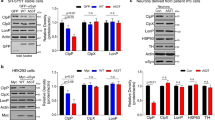
Abstract
α-synuclein, a presynaptic protein, was found to be the major component in the Lewy bodies (LB) in both inherited and sporadic Parkinson’s disease (PD). Furthermore, rare mutations of α-synuclein cause autosomal-dominant PD. However, it is unknown how α-synuclein is involved in the pathogenesis of nigral degeneration in PD. In this study, we examine the protein-protein interactions of wild-type and mutant (A53T) α-synuclein with adult human brain cDNA expression library using the yeast two-hybrid technique. We found that both normal and mutant α-synuclein specifically interact with the mitochondrial complex IV enzyme, cytochrome C oxidase (COX). Wild-type and mutant α-synuclein genes were further fused with c-Myc tag and translated in rabbit reticulocyte lysate. Using anti-c-Myc antibody, we demonstrated that both wild-type and mutant α-synuclein, coimmunoprecipitated with COX. We also showed that potassium cyanide, a selective COX inhibitor, synergistically enhanced the sensitivity of SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells to dopamine-induced cell death. In conclusion, we found specific protein-protein interactions of α-synuclein, a major LB protein, to COX, a key enzyme of the mitochondrial respiratory system. This interaction suggests that α-synuclein aggregation may contribute to enhance the mitochondrial dysfunction, which might be a key factor in the pathogenesis of PD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abeliovich A., Schmitz Y., Farinas I., Choi-Lundberg D., Ho W. H., Castillo P. E., et al. (2000) Mice lacking α-synuclein display functional deficits in the nigrostriatal dopamine system. Neuron 25, 239–252.
Alves-Rodrigues A., Gregori L., and Figueiredo-Pereira M. E. (1998) Ubiquitin, cellular inclusions and their role in neurodegeneration. Trends Neurosci. 21, 516–520.
Baba M., Nakajo S., Tu P. H., Tomita T., Nakaya K., Lee V. M., et al. (1998) Aggregation of α-synuclein in Lewy bodies of sporadic Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Am. J. Pathol. 152, 879–884.
Barzilai A., Zilkha-Falb R., Daily D., Stern N., Offen D., Ziv I., et al. (2000) The molecular mechanism of dopamine-induced apoptosis: identification and characterization of genes that mediate dopamine toxicity. J. Neural Transm. Suppl. 60, 59–76.
Bennet C. M., Bishop J. F., Leng Y., Chock B., Chase T. N., and Mouradian M. (1999) Degradation of α-synuclein by proteasome. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 33855–33858.
Burke P. A. and Poyton R. O. (1998) Structure/function of oxygen-regulated isoforms in cytochrome c oxidase. J. Exp. Biol. 201, 1163–1175.
Casali C., Bonifati V., Santorelli F. M., Casari G., Fortini D., Patrignani A., et al. (2001) Mitochondrial myopathy, parkinsonism, and multiple mtDNA deletions in a Sephardic Jewish family. Neurology 56, 802–805.
Cheng G., Cleary A. M., Ye Z. S., Hong D. I., Lederman S., and Baltimore D. (1995) Involvement of CRAF1, a relative of TRAF, in CD40 signaling. Science 267, 1494–1498.
Cohen G., Farooqui R., and Kesler N. (1997) Parkinson disease: a new link between monoamine oxidase and mitochondrial electron flow. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 4890–4894.
Conway K. A., Harper J. D., and Lansbury P. T. (1998) Accelerated in vitro fibril formation by a mutant alpha-synuclein linked to early-onset Parkinson disease. Nat. Med. 4, 1318–1320.
Davidson W. S., Jonas A., Clayton D. F., and George J. M. (1998) Stabilization of alpha-synuclein secondary structure upon binding to synthetic membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 9443–9449.
El-Agnaf O. M., Jakes R., Curran M. D., Middleton D., Ingenito R., Bianchi E., et al. (1998) Aggregates from mutant and wild-type alpha-synuclein proteins and NAC peptide induce apoptotic cell death in human neuroblastoma cells by formation of beta-sheet and amyloid-like filaments. FEBS Lett. 440, 71–75.
Engelender S., Kaminsky Z., Guo X., Sharp A. H., Amaravi R. K., Kleiderlein J. J., et al. (1999) Synphilin-1 associates with α-synuclein and promotes the formation of cytosolic inclusions. Nat. Genet. 22, 110–114.
Feldman J. M. and Feldman M. D. (1990) Sequelae of attempted suicide by cyanide ingestion: a case report. Int. J. Psychiatry Med. 20, 173–179.
Filloux F. and Townsend J. J. (1993) Pre- and postsynaptic neurotoxic effects of dopamine demonstrated by intrastriatal injection. Exp. Neurol. 119, 79–88.
Forno L. S. (1996) Neuropathology of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 55, 259–272.
Ghee M., Fournier A., and Mallet J. (2000) Rat alpha-synuclein interact with tat binding protein 1, a component of the 26S proteasomal complex. J. Neurochem. 75, 2221–2224.
Grandas F., Artieda J., and Obeso J. A. (1989) Clinical and CT scan findings in a case of cyanide intoxication. Mov. Disord. 4, 188–193.
Gu M., Cooper J. M., Taanman J. W., and Schapira A. H. (1998) Mitochondrial DNA transmission of the mitochondrial defect in Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 44, 177–186.
Hashimoto M., Takeda A., Hsu L. J., Takenouchi T., and Masliah E. (1999) Role of cytochrome c as a stimulator of α-synuclein aggregation in Lewy body disease. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 28849–28852.
Ho S. N., Hunt H. D., Horton R. M., Pullen J. K., and Pease L. R. (1989) Site-directed mutagenesis by overlap extension using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene 77, 51–59.
Hsu L. J., Sagara Y., Arroyo A., Rockenstein E., Sisk A., Mallory M., et al. (2000) alpha-synuclein promote mitochondrial deficit and oxidative stress. Am. J. Pathol. 157, 401–410.
Iwai A., Masliah E., Yoshimoto M., Ge N., Flanagan L., de Silva H. A., et al. (1995) The precursor protein of non-A beta component of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid is a presynaptic protein of the central nervous system. Neuron. 14, 467–475.
Jenco J. M., Rawlingson A., Daniels B., and Morris A. J. (1998) Regulation of phospholipase D2: selective inhibition of mammalian phospholipase Disoenzymes by alpha- and beta-synuclein. Biochemistry 37, 4901–4909.
Kahle P. J., Neumann M., Ozmen L., Muller V., Jacobsen H., Schindzielorz A., et al. (2000) Subcellular localization of wild-type and Parkinson’s disease-associated mutant alpha-synuclein in human and transgenic mouse brain. J. Neurosci. 20, 6365–6373.
Kanda S., Bishop J. F., Eglitis M. A., Yang Y., and Mouradian M. M. (2000) Enhanced vulnerability to oxidative stress by alpha-synuclein mutations and c-terminal truncation. Neuroscience 97, 279–284.
Ko L., Mehta N. D., Farrer M., Easson C., Hussey J., Yen S., et al. (2000) Sensitization of neuronal cells to oxidative stress with mutated human alpha-synuclein. J. Neurochem. 75, 2546–2554.
Kruger R., Kuhn W., Muller T., Woitalla D., Graeber M., Kosel S., et al. (1998) Ala30Pro mutation in the gene encoding α-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Genet. 18, 106–108.
Lantos P. L. and Papp M. I. (1994) Cellular pathology of multiple system atrophy. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 57, 129–133.
Lee F. J., Liu F., Pristupa Z. B., and Niznik H. B. (2001) Direct binding and functional coupling of alpha-synuclein to the dopamine transporters accelerate dopamine-induced apoptosis. FASEB J. 15, 916–926.
Masliah E., Rockenstein E., Veinbergs I., Mallory M., Hashimoto M., Takeda A., et al. (2000) Dopaminergic loss and inclusion body formation in alpha-synuclein mice: implications for neurodegenerative disorders. Science 287, 1265–1269.
Mezey E., Dehejia A., Harta G., Papp M. I., Polymeropoulos M. H., and Brownstein M. J. (1998) Alpha synuclein in neurodegenerative disorders: murderer or accomplice? Nature Med. 4, 755–757.
Mizuno Y., Ikebe S., Hattori N., Nakagawa-Hattori Y., Mochizuki H., Tanaka M., and Ozawa T. (1995) Role of mitochondria in the etiology and pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1271, 265–274.
Narhi L., Wood S. J., Steavenson S., Jiang Y., Wu G. M., Anafi D., et al. (1999) Both familial PD mutations accelerate α-synuclein aggregation. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 9843–9846.
Offen D., Strenin H., Ziv I., Melamed E., and Hochman A. (1996) Prevention of dopamine-induced cell death by thiol antioxidants: possible implications for treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Neurol. 141, 32–39.
Offen D., Ziv I., Gorodin S., Glater E., Hochman A., and Melamed E. (1997) Dopamine-melanin induces apoptosis in PC12 cells: Possible implications for the etiology of Parkinson’s disease. Neurochem. Int. 141, 32–39.
Ostrerova N., Petrucelli L., Farrer M., Mehta N., Choi P., Hardy J., and Wolozin B. (1999) alpha-Synuclein shares physical and functional homology with 14-3-3 proteins. J. Neurosci. 19, 5782–5791.
Polymeropoulos M. H., Lavedan C., Leory E., Ide S. E., Dehejia A., Dutra A., Pike B., et al. (1997) Mutation in the α-Synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s Disease. Science 276, 2045–2047.
Rosenberg N. L., Myers J. A., and Martin W. R. (1989) Cyanide-induced parkinsonism: clinical, MRI, and 6-fluorodopa PET studies. Neurology 39, 142–144.
Sato T., Irie S., and Reed J. C. (1995) A novel member of the TRAF family of putative signal transducing proteins binds to the cytosolic domain of CD40. FEBS Lett. 358, 113–118.
Schapira A. H., Cooper J. M., Dexter D., Clark J. B., Jenner P., and Marsden C. D. (1990) Mitochondrial complex I deficiency in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurochem. 54, 823–827.
Schapira A. H., Gu M., Taanman J. W., Tabrizi S. J., Seaton T., Cleeter M., and Cooper J. M. (1998) Mitochondria in the etiology and pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 44, S89-S98.
Sian J., Dexter D. T., Lees A. J., Daniel S., Jenner P., and Marsden C. D. (1994) Glutathione-related enzymes in brain in Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 36, 356–361.
Simantov R., Blinder E., Ratovitski T., Tauber M., Gabbay M., and Porat S. (1996) Dopamine-induced apoptosis in human neuronal cells: inhibition by nucleic acids antisense to the dopamine transporter. Neuroscience 74, 39–50.
Spillantini M. G., Crowther R. A., Jakes R., Hasegawa M., and Goedert M. (1998) alpha-Synuclein in filamentous inclusions of Lewy bodies from Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 6469–6473.
Spillantini M. G., Schmidt M. L., Lee V. M., Trojanowski J. Q., Jakes R., and Goedert M. (1997) Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 388, 839–840.
Tabrizi S. J., Orth M., Wilkinson J. M., Taanman J. W., Warner T. T., Cooper J. M., and Schapira A. H. (2000) Expression of mutant alpha-synuclein causes increased susceptibility to dopamine toxicity. Hum. Mol. Genet. 9, 2683–2689.
Tanaka Y., Engelender S., Igarashi S., Rao R. K., Wanner T., Tanzi R. E., et al. (2001) Inducible expression of mutant alpha-synuclein decreases proteasome activity and increases sensitivity to mitochondria-dependent apoptosis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 10, 919–926.
Trimmer P. A., Swerdlow R. H., Parks J. K., Keeney P., Bennett J. P. Jr, Miller S. W., et al. (2000) Abnormal mitochondrial morphology in sporadic Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease cybrid cell lines. Exp. Neurol. 162, 37–50.
Tu P. H., Galvin J. E., Baba M., Giasson B., Tomita T., Leight S., et al. (1998) Glial cytoplasmic inclusions in white matter oligodendrocytes of multiple system atrophy brains contain insoluble alpha-synuclein. Ann. Neurol. 44, 415–422.
Turnbull S., Tabner B. J., El-Agnaf O. M., Moore S., Davies Y., and Allsop D. (2001) alpha-synuclein implicated in Parkinson’s disease catalyses the formation of hydrogen peroxide in vitro. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 30, 1163–1170.
Ueda K., Fukushima H., Masliah E., Xia Y., Iwai A., Yoshimoto M., et al. (1993) Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding an unrecognized component of amyloid in Alzheimer disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 11282–11286.
Uitti R. J., Rajput A. H., Ashenhurst E. M., and Rozdilsky B. (1985) Cyanide-induced parkinsonism: a clinicopathologic report. Neurology 35, 921–925.
van der Putten H., Wiederhold K. H., Probst A., Barbieri S., Mistl C., Danner S., et al. (2000) Neuropathology in mice expressing human alpha-synuclein. J. Neurosci. 20, 6021–6029.
Weinreb P. H., Zhen W., Poon A. W., Conway K. A., and Lansbury P. T. Jr. (1996) NACP, a protein implicated in Alzheimer’s disease and learning, is natively unfolded. Biochemistry 35, 13709–13715.
Zhou W., Hurlbert M. S., Schaack J., Prasad K. N., and Freed C. R. (2000) Overexpression of human alpha-synuclein causes dopamine neuron death in rat primary culture and immortalized mesencephalon-derived cells. Brain Res. 866, 33–43.
Ziv I., Barzilai A., Offen D., Stein R., Achiron A., and Melamed E. (1996) Dopamine-induced, genotoxic activation of programmed cell death. A role in nigrostriatal neuronal degeneration in Parkinson’s disease? Adv. Neurol. 69, 229–233.
Ziv I., Melamed E., Nardi N., Luria D., Achiron A., Offen D., and Barzilai A. (1994) Dopamine induces apoptosis-like cell death in cultured chick sympathetic neurons—a possible novel pathogenetic mechanism in Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 170, 136–140.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elkon, H., Don, J., Melamed, E. et al. Mutant and wild-type α-synuclein interact with mitochondrial cytochrome C oxidase. J Mol Neurosci 18, 229–238 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:18:3:229
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:18:3:229