Abstract
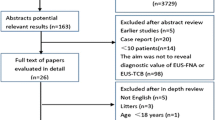
Published data on accuracy of endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) in differentiating T stages of rectal cancers is varied. Study selection criteria were to select only EUS studies confirmed with results of surgical pathology. Articles were searched in Medline and Pubmed. Pooling was conducted by both fixed and random effects models. Initial search identified 3,630 reference articles, of which 42 studies (N = 5,039) met the inclusion criteria and were included in this analysis. The pooled sensitivity and specificity of EUS to determine T1 stage was 87.8% [95% confidence interval (CI) 85.3–90.0%] and 98.3% (95% CI 97.8–98.7%), respectively. For T2 stage, EUS had a pooled sensitivity and specificity of 80.5% (95% CI 77.9–82.9%) and 95.6% (95% CI 94.9–96.3%), respectively. To stage T3 stage, EUS had a pooled sensitivity and specificity of 96.4% (95% CI 95.4–97.2%) and 90.6% (95% CI 89.5–91.7%), respectively. In determining the T4 stage, EUS had a pooled sensitivity of 95.4% (95% CI 92.4–97.5%) and specificity of 98.3% (95% CI 97.8–98.7%). The p value for chi-squared heterogeneity for all the pooled accuracy estimates was > 0.10. We conclude that, as a result of the demonstrated sensitivity and specificity, EUS should be the investigation of choice to T stage rectal cancers. The sensitivity of EUS is higher for advanced disease than for early disease. EUS should be strongly considered for T staging of rectal cancers.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2007. CA Cancer J Clin. 2007;57(1):43–66.
National Cancer Institute. Surveillance epidemiology and end results (SEER). U.S. National Institutes of Health. http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2004/results_merged/sect_06_colon_rectum.pdf. Accessed June 2008.
Atkin WS, Morson BC, Cuzick J. Long-term risk of colorectal cancer after excision of rectosigmoid adenomas. N Engl J Med. 1992;326(10):658–62.
Larsson SC, Orsini N, Wolk A. Diabetes mellitus and risk of colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005;97(22):1679–87.
Giovannucci E, Ascherio A, Rimm EB, Colditz GA, Stampfer MJ, Willett WC. Physical activity, obesity, and risk for colon cancer and adenoma in men. Ann Intern Med. 1995;122(5):327–34.
Cho E, Smith-Warner SA, Ritz J, van den Brandt PA, Colditz GA, Folsom AR, et al. Alcohol intake and colorectal cancer: a pooled analysis of 8 cohort studies. Ann Intern Med. 2004;140(8):603–13.
Paskett ED, Reeves KW, Rohan TE, Allison MA, Williams CD, Messina CR, et al. Association between cigarette smoking and colorectal cancer in the Women’s Health Initiative. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007;99(22):1729–35.
Greene FL, Page DL, Fleming ID, Fritz A, Balch CM, Haller DG, et al. AJCC cancer staging manual (6th ed). New York: Springer-Verlag; 2002.
Rich T, Gunderson LL, Lew R, Galdibini JJ, Cohen AM, Donaldson G. Patterns of recurrence of rectal cancer after potentially curative surgery. Cancer. 1983;52(7):1317–29.
Minsky BD, Mies C, Recht A, Rich TA, Chaffey JT. Resectable adenocarcinoma of the rectosigmoid and rectum: patterns of failure and survival. Cancer. 1988;61(7):1408–16.
Willett CG, Lewandrowski K, Donelly S, Shellito PC, Convery K, Eliseo R, et al. Are there patients with stage I rectal carcinoma at risk for failure after abdominoperineal resection? Cancer. 1992;69(7):1651–5.
Bailey HR, Huval WV, Max E, Smith KW, Butts DR, Zamora LF. Local excision of carcinoma of the rectum for cure. Surgery. 1992;111(5):555–61.
Kodner IJ, Gilley MT, Shemesh EI, Fleshman JW, Fry RD, Myerson RJ. Radiation therapy as definitive treatment for selected invasive rectal cancer. Surgery. 1993;114(4):850–6.
Mendenhall WM, Rout WR, Vauthey JN, Haigh LS, Zlotecki RA, Copeland EM 3rd. Conservative treatment of rectal adenocarcinoma with endocavitary irradiation or wide local excision and postoperative irradiation. J Clin Oncol. 1997;15(10):3241–8.
Maingon P, Guerif S, Darsouni R, Salas S, Barillot I, d’Hombres A, et al. Conservative management of rectal adenocarcinoma by radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1998;40(5):1077–85.
Sleisenger & Fortran’s gastrointestinal and liver disease, 8th ed. Saunders, 2006.
Krook JE, Moertel CG, Gunderson LL, Wieand HS, Collins RT, Beart RW, et al. Effective adjuvant therapy for high-risk rectal carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1991;324:709.
Videtic GM, Fisher BJ, Perera FE, et al. Preoperative radiation with concurrent 5-fluorouracil continuous infusion for locally advanced unresectable rectal cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1998; 42:319.
Guinet C, Buy JN, Ghossain MA, Sezeur A, Mallet A, Bigot JM, et al. Comparison of magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography in the preoperative staging of rectal cancer. Arch Surg. 1990;125(3):385–8.
Rifkin MD, Ehrlich SM, Marks G. Staging of rectal carcinoma: prospective comparison of endorectal US and CT. Radiology. 1989;170(2):319–22.
Hildebrandt U, Klein T, Feifel G, Schwarz HP, Koch B, Schmitt RM. Endosonography of pararectal lymph nodes In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Dis Colon Rectum. 1990;33(10):863–8.
Tio TL, Coene PP, van Delden OM, Tytgat GN. Colorectal carcinoma: preoperative TNM classification with endosonography. Radiology 1991;179(1):165–70.
Kwok H, Bissett IP, Hill GL. Preoperative staging of rectal cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2000;15(1):9–20.
Thaler W, Watzka S, Martin F, La Guardia G, Psenner K, Bonatti G, et al. Preoperative staging of rectal cancer by endoluminal ultrasound vs magnetic resonance imaging Preliminary results of a prospective, comparative study. Dis Colon Rectum. 1994;37(12):1189–93.
Meyenberger C, Huch Boni RA, Bertschinger P, Zala GF, Klotz HP, Krestin GP. Endoscopic ultrasound and endorectal magnetic resonance imaging: a prospective, comparative study for preoperative staging and follow-up of rectal cancer. Endoscopy. 1995;27(7):469–79.
Harewood GC, Wiersema MJ, Nelson H, Maccarty RL, Olson JE, Clain JE, et al. A prospective, blinded assessment of the impact of preoperative staging on the management of rectal cancer. Gastroenterology. 2002;123(1):24–32.
Moher D, Cook DJ, Eastwood S, Olkin I, Rennie D, Stroup DF, for the QUOROM Group. Improving the quality of reports of meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials: the QUOROM statement. Lancet. 1999;354:1896–1900.
Bossuyt PM, Reitsma JB, Bruns DE, Gatsonis CA, Glasziou PP, Irwig LM, et al. Standards for reporting of diagnostic accuracy group Towards complete and accurate reporting of studies of diagnostic accuracy: the STARD initiative The Standards for Reporting of Diagnostic Accuracy Group. Croatian Med J. 2003;44(5):635–8.
Brennan P, Silman A. Statistical methods for assessing observer variability in clinical measures. BMJ. 1992;304:1491–4.
Jadad AR, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Controlled Clin Trials. 1996;17:1–12.
Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, Olkin I, Williamson GD, Rennie D, et al. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting Meta-analysis of observational studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA 2000;283(15):2008–12.
Whiting P, Rutjes AW, Reitsma JB, et al. The development of QUADAS: a tool for the quality assessment of studies of diagnostic accuracy included in systematic reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2003;3:25.
Whiting PF, Weswood ME, Rutjes AW, et al. Evaluation of QUADAS, a tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2006;6:9.
Puli SR, Singh S, Hagedorn CH, Reddy J, Olyaee M. Diagnostic accuracy of EUS for vascular invasion in pancreatic and periampullary cancers: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007;65(6):788–97.
Puli SR, BK Reddy J, Bechtold ML, Antillon M, Ibdah JA. How good is endoscopic ultrasound for TNM staging of gastric cancers? A meta-analysis and systematic review. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14(25):4011–9.
Puli SR, BK Reddy J, Bechtold ML, Ibdah JA, Antillon M. Staging accuracy of esophageal cancer by endoscopic ultrasound: a meta-analysis and systematic review. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14(10):1479–90.
Leemis LM, Trivedi KS. A comparison of approximate interval estimators for the Bernoulli parameter. Am Stat. 1996;50:63–8.
Cox DR. The analysis of binary data. London: Methuen; 1970.
Agresti A. Analysis of ordinal categorical data. New York: Wiley; 1984.
Deeks JJ. Systematic reviews of evaluations of diagnostic and screening tests. In: Egger M, Smith GD, Altman DG, editors. Systematic Reviews in Health Care Meta-analysis in context. London: BMJ Books; 2001.
Harbord RM, Egger M, Sterne JAC. A modified test for small-study effects in meta-analyses of controlled trials with binary endpoints. Stat Med. 2005;25(20):3443–57.
Begg CB, Mazumdar M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics. 1994;50:1088–101.
Sterne JAC, Egger M, Davey-Smith G. Investigating and dealing with publication and other biases in meta-analysis. BMJ. 2001;323: 101–5.
Sterne JAC, Egger M. Funnel plots for detecting bias in meta-analysis: guidelines on choice of axis. J Clin Epidemiol. 2001;54: 1046–55.
Saitoh N, Okui K, Sarashina H, Suzuki M, et al. Evaluation of echographic diagnosis of rectal cancer using intrarectal ultrasonic examination. Dis Colon Rectum. 1986;29(4):234–42.
Waizer A Zitron S, Ben-Baruch D, Baniel J, Wolloch Y, Dintsman M. Comparative study for preoperative staging of rectal cancer. Dis Colon Rectum. 1989;32(1):53–6.
Bali C, Nousias V, Fatouros M, Stefanou D, Kappas AM. Assessment of local stage in rectal cancer using endorectal ultrasonography (EUS). Tech Coloproctol. 2004;8(Suppl 1):S170–3.
AP Zbar. Endorectal ultrasonography in rectal cancer: a preliminary Barbadian experience. West Indian Med J. 2006;55(5).
Sailer M, Leppert R, Kraemer M, et al. The value of endorectal ultrasound in the assessment of adenomas, T1- and T2-carcinomas. Int J Colorectal Dis. 1997;12(4):214–9.10.1007/s003840050092.
Glaser F, Kuntz C, Schlag P, et al. Endorectal ultrasound for control of preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer. Ann Surg. 1993;217(1):64–71.
Maor Y, Nadler M, Barshack I, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound staging of rectal cancer: diagnostic value before and following chemoradiation. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;21:454–8.
Kim JC, Kim HC, Yu CS, et al. Efficacy of 3-dimensional endorectal ultrasonography compared with conventional ultrasonography and computed tomography in preoperative rectal cancer staging. Am J Surg. 2006;192:89–97.
AkasuT, KondoH, MoriyaY, et al. Endorectal ultrasonography and treatment of early stage rectal cancer. World J Surg. 2000;24(9):1061–8.10.1007/s002680010151.
Norton SA, Thomas MG. Staging of rectosigmoid neoplasia with colonoscopic endoluminal ultrasonography. Brit J Surg. 1999;86(7):942–6.
Kaneko K, Boku N, Hosokawa K, et al. Diagnostic utility of endoscopic ultrasonography for preoperative rectal cancer staging estimation. Japan J Clin Oncol. 1996;26(1):30–5.
Adams DR, Blatchford GJ, Lin KM, et al. Use of preoperative ultrasound staging for treatment of rectal cancer. Dis Colon Rectum. 1999;42(2):159–66.
Gualdi GF, Casciani E, Guadalaxara A, et al. Local staging of rectal cancer with transrectal ultrasound and endorectal magnetic resonance imaging: comparison with histologic findings. Dis Colon Rectum. 2000;43(3):338–45.
Hildebrandt U, Feifel G. Preoperative staging of rectal cancer by intrarectal ultrasound. Dis Colon Rectum. 1985;28(1):42–6.
Mackay SG, Pager CK, Joseph D, et al. Assessment of the accuracy of transrectal ultrasonography in anorectal neoplasia. Br J Surg. 2003;90(3):346–50.
Nishimori H, Sasaki K, Hirata K, et al. The value of endoscopic ultrasonography in preoperative evaluation of rectal cancer. Int Surg. 1998;83(2):157–60.
Marone P, Petrulio F, de Bellis M, et al. Role of endoscopic ultrasonography in the staging of rectal cancer: a retrospective study of 63 patients. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2000;30(4):420–4.
Hsieh PS, Changchien CR, Chen JS, et al. Comparing results of preoperative staging of rectal tumor using endorectal ultrasonography and histopathology. Chang Gung Medical J. 2003;26(7):474–8.
Kramann B, Hildebrandt U. Computed tomography versus endosonography in the staging of rectal carcinoma: a comparative study. Int J Colorectal Dis. 1986;1(4):216–8.
Massari M, De Simone M, Cioffi U, et al. Value and limits of endorectal ultrasonography for preoperative staging of rectal carcinoma. Surg Laparosc Endosc. 1998;8(6):438–44.
Boyce GA, Sivak MV, Jr., Lavery IC, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound in the pre-operative staging of rectal carcinoma. Gastrointest Endosc. 1992;38(4):468–71.
Pappalardo G, Reggio D, Frattaroli FM, et al. The value of endoluminal ultrasonography and computed tomography in the staging of rectal cancer: A preliminary study. J Surg Oncol. 1990;43(4):219–22.
Akasu T, Sugihara K, Moriya Y, et al. Limitations and pitfalls of transrectal ultrasonography for staging of rectal cancer. Dis Colon Rectum. 1997;40(Suppl 10):S10–5.
Feifel G, Hildebrandt U, Dhom G. Assessment of depth of invasion in rectal cancer by endosonography. Endoscopy. 1987;19(2):64–7.
Giovannini M, Bories E, Pesenti C, Moutardier V et al. Three- dimensional endorectal ultrasound using a new freehand software program: results in 35 patients with rectal cancer. Endoscopy. 2006;38(4):339–43.
Marusch F, Koch A, Schmidt U, et al. Routine use of transrectal ultrasound in rectal carcinoma: Results of a prospective multicenter study. Endoscopy. 2002;34(5):385–90.
Meyenberger C, Huch Boni RA, Bertschinger P, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound and endorectal magnetic resonance imaging: a prospective, comparative study for preoperative staging and follow-up of rectal cancer. Endoscopy. 1995;27(7):469–79.
Thaler W, Watzka S, Martin F, et al. Preoperative staging of rectal cancer by endoluminal ultrasound vs magnetic resonance imaging Preliminary results of a prospective, comparative study. Dis Colon Rectum. 1994;37(12):1189–93.
Waizer A, Powsner E, Russo I, et al. Prospective comparative study of magnetic resonance imaging versus transrectal ultrasound for preoperative staging and follow-up of rectal cancer Preliminary report. Dis Colon Rectum. 1991;34(12):1068–72.
Herzog U, von FM, Tondelli P, Schuppisser JP. How accurate is endorectal ultrasound in the preoperative staging of rectal cancer? Dis Colon Rectum. 1993;36:127–34.
Nielsen MB, Qvitzau S, Pedersen JF, et al. Endosonography for preoperative staging of rectal tumours. Acta Radiologica. 1996;37(5):799–803.
Sentovich SM, Blatchford GJ, Falk PM, et al. Transrectal ultrasound of rectal tumors. Am J Surg. 1993;166(6):638–41 discussion 641–2.
Romano G, de Rosa P, Vallone G, et al. Intrarectal ultrasound and computed tomography in the pre- and postoperative assessment of patients with rectal cancer. Br J Surg. 1985;72(Suppl):S117–9.
Bianchi P, Ceriani C, Palmisano A, Pompili G, Passoni GR, Rottoli M, et al. A prospective comparison of endorectal ultrasound and pelvic magnetic resonance in the preoperative staging of rectal cancer. Ann Ital Chir. 2006;77:41–6.
Ramana KN, Murthy PV, Rao KP, et al. Transrectal ultrasonography versus computed tomography in staging rectal carcinoma. Indian J Gastroenterol. 1997;16(4):142–3.
Garcia-Aguilar J, Pollack J, Lee SH, Hernandez de Anda E, Mellgren A, Wong WD, et al. Accuracy of endorectal ultrasonography in preoperative staging of rectal tumors. Dis Colon Rectum. 2002;45(1):10–5.
Manger T, Stroh C. Accuracy of endorectal ultrasonography in the preoperative staging of rectal cancer. Tech Coloproctol. 2004;8(Suppl 1):s14–5.
Starck M, Bohe M, Simanaitis M, Valentin L. Rectal endosonography can distinguish benign rectal lesions from invasive early rectal cancers. Colorectal Dis. 2003;5(3):246–50.
Kim JC, Yu CS, Jung HY, Kim HC, Kim SY, Park SK, et al. Source of errors in the evaluation of early rectal cancer by endoluminal ultrasonography. Dis Colon Rectum. 2001;44(9):1302–9.
Osti MF, Padovan FS, Pirolli C, Sbarbati S, Tombolini V, Meli C, et al. Comparison between transrectal ultrasonography and computed tomography with rectal inflation of gas in preoperative staging of lower rectal cancer. Eur Radiol. 1997;7(1):26–30.
Caseiro-Alves F, Goncalo M, Cruz L, Ilharco J, Leite J, Agostinho A, et al. Water enema computed tomography (WE-CT) in the local staging of low colorectal neoplasms: Comparison with transrectal ultrasound. Abdominal Imag. 1998;23(4):370–4.
Norton SA, Thomas MG. Staging of rectosigmoid neoplasia with colonoscopic endoluminal ultrasonography.Br J Surg. 1999;86(7): 942–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Puli, S.R., Bechtold, M.L., Reddy, J.B.K. et al. How Good is Endoscopic Ultrasound in Differentiating Various T Stages of Rectal Cancer? Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Ann Surg Oncol 16, 254–265 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-008-0231-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-008-0231-5