Abstract
Introduction
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) has a poorer prognosis; the factors that contribute to this remain unclear. We hypothesized that TNBC is associated with ABO blood type/Rh factors that account for differences in survival.
Methods
We identified 468 patients with stage I–III TNBC [estrogen receptor (ER)-negative, progesterone receptor (PR)-negative, and HER2 nonamplified]. Patient/tumor characteristics, treatments, and outcomes were obtained. Data were examined for associations with specific ABO blood type/Rh factors. Descriptive statistics and χ 2 analysis were utilized for data summary and comparisons.
Results
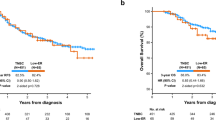
Of 468 TNBC patients, 283 had known ABO blood type [122 (43 %) O, 108 (38 %) A, 39 (14 %) B, and 14 (5 %) AB] and Rh factor [253 (89 %) positive and 30 (11 %) negative]. Mean patient age was 53.7 ± 12.5 years, and median follow-up was 30.2 ± 20.5 months. The incidence of each ABO blood type/Rh factor in our TNBC cohort was not different from the general population or a cohort of ER-positive breast cancers (P > 0.05). Compared with patients with blood type O, there was no difference in breast cancer-specific mortality for type A [hazard ratio (HR) 0.906; 95 % confidence interval (CI) 0.554–1.481], type B (HR 1.534; 95 % CI 0.792–2.972), or type AB (HR 0.488; 95 % CI 0.113–2.106). Compared with women with negative Rh, there was no difference in breast cancer-specific mortality for women with positive Rh (HR 1.161; 95 % CI 0.568–2.374).
Conclusions
TNBC was not associated with a specific ABO blood type or Rh factor. Our results failed to demonstrate an association between ABO blood type/Rh factor and breast cancer mortality in patients with TNBC.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wolpin BM, Chan AT, Hartge P, Chanock SJ, Kraft P, Hunter DJ, et al. ABO blood group and the risk of pancreatic cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2009;101:424–31.
Ben Q, Wang K, Yuan Y, Li Z. Pancreatic cancer incidence and outcome in relation to ABO blood groups among Han Chinese patients: a casecontrol study. Int J Cancer. 2011;128:1179–86.
Pandey M, Gautam A, Shukla VK. ABO and Rh blood groups in patients with cholelithiasis and carcinoma of the gallbladder. BMJ. 1995;310:1639.
Gates MA, Wolpin BM, Cramer DW, Hankinson SE, Tworoger SS. ABO blood group and incidence of epithelial ovarian cancer. Int J Cancer. 2011;128(2):482–6.
Stamatakos M, Kontzoglou K, Safioleas P, Safioleas C, Manti C, Safioleas M. Breast cancer incidence in Greek women in relation to ABO blood groups and Rh factor. Int Semin Surg Oncol. 2009;6:14.
Tryggvadottir L, Tulinius H, Robertson JM: Familial and sporadic breast cancer cases in Iceland: a comparison related to ABO blood groups and risk of bilateral breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 1988;42(4):499–501.
Holdsworth PJ, Thorogood J, Benson EA, Clayden AD. Blood group as a prognostic indicator in breast cancer. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1985;290:671–673.
Dede DS, Aksoy S, Dizdar O, Cerci P, Gullu I, Ozisik Y, Altundag K. Blood ABO groups and risk of breast cancer. Med Oncol. 2009;27:1433.
Gates MA, Xu M, Chen WY, Kraft P, Hankinson SE, Wolpin BM. ABO blood group and breast cancer incidence and survival. Int J Cancer. 2011 Jun 1 [Epub ahead of print].
Klimant E, Glurich I, Mukesh B, Onitilo AA. Blood type, hormone receptor status, HER2/neu status, and survival in breast cancer: a retrospective study exploring relationships in a phenotypically well-defined cohort. Clin Med Res. 2011; 9(3–4):111–8.
Ferguson-Smith MA, Aitken DA, Turleau C, de Grouchy J. Localization of the human ABO: Np-1: AK-1 linkage group by regional assignment of AK-1 to 9q34. Hum Genet. 1976;34:35–43.
Yamamoto F, Clausen H, White T, et al. Molecular genetic basis of the histo-blood group ABO system. Nature. 1990;345:229–33.
Ravn V, Dablesteen E. Tissue distribution of histo-blood group antigens. APMIS. 2000;108:1–28.
Strauchen JA, Bergman SM, Hanson TA. Expression of A and B tissue isoantigens in benign and malignant lesions of the breast. Cancer. 1980;45:2149–55.
Vowden P, Lowe AD, Lennox ES, Bleehen NM. The expression of ABH and Y blood group antigens in benign and malignant breast tissue: the preservation of the H and Y antigens in malignant epithelium. Br J Cancer. 1986;53:313–9.
Ura Y, Dion AS, Williams CJ, Olsen BD, Redfield ES, Ishida M, Herlyn M, Major PP. Quantitative dot blot analyses of blood-group-related antigens in paired normal and malignant human breast tissues. Int J Cancer. 1992;50(1):57–63.
Idikio HA, Manickavel V. A, B, H, and Lewis-a and Lewis-b blood group antigens in human breast cancer: correlation with steroid hormone receptor and disease status. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1993;119:486–92.
Nakagoe T, Fukushima K, Itoyanagi N, Ikuta Y, Oka T, Nagayasu T, Ayabe H, Hara S, Ishikawa H, Minami H. Expression of ABH/Lewis-related antigens as prognostic factors in patients with breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2002;128:257–64.
Rakha EA, El-Sayed ME, Green AR, et al. Prognostic markers in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer. 2007;109(1):25–32.
Dent R, Trudeau M, Pritchard KI, et al. Triple-negative breast cancer: clinical features and patterns of recurrence. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:4429–34.
Carey LA, Perou CM, Livasy CA, et al. Race, breast cancer subtypes, and survival in the Carolina Breast Cancer Study. JAMA. 2006;295:2492–502.
Liedtke C, Mazouni C, Hess KR, et al. Response to neoadjuvant therapy and long-term survival in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(8):1275–81.
Onitilo AA, Engel JM, Greenlee RT, Mukesh BN. Breast cancer subtypes based on ER/PR and Her2 expression: comparison of clinicopathologic features and survival. Clin Med Res. 2009;7:4–13.
Bauer KR, Brown M, Cress RD, Parise CA, Caggiano V. Descriptive analysis of estrogen receptor (ER)-negative, progesterone receptor (PR)-negative, and HER2-negative invasive breast cancer, the so-called triple-negative phenotype: a population-based study from the California cancer registry. Cancer. 2007;109(9):1721–8.
Bertucci F, Finetti P, Cervera N, Esterni B, Hermitte F, Viens P, Birnbaum D. How basal are triple-negative breast cancers? Int J Cancer. 2008;123(1):236–40.
Haffty BG, Yang Q, Reiss M, et al. Locoregional relapse and distant metastasis in conservatively managed triple negative early-stage breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:5652–7.
Tischkowitz M, Brunet JS, Bégin LR, Huntsman DG, Cheang MC, Akslen LA, Nielsen TO, Foulkes WD. Use of immunohistochemical markers can refine prognosis in triple negative breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 2007;7:134.
Corkery B, Crown J, Clynes M, O’Donovan N. Epidermal growth factor receptor as a potential therapeutic target in triple-negative breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2009;20(5):862–7.
Carey LA, Dees EC, Sawyer L, et al. The triple negative paradox: primary tumor chemosensitivity of breast cancer subtypes. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:2329–34.
Aird I, Bentall HH, Roberts JA. A relationship between cancer of stomach and the ABO blood groups. Br Med J. 1953;1:799–801.
Hakomori S. Antigen structure and genetic basis of histo-blood groups A, B and O: their changes associated with human cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999;1473:247–66.
Dabelsteen E. Cell surface carbohydrates as prognostic markers in human carcinomas. J Pathol. 1996;179:358–69.
Lee AK, DeLellis RA, Rosen PP, Saigo PE, Gangi MD, Bagin R, Groshen S, Wolfe HJ. ABH blood group isoantigen expression in breast carcinomas—an immunohistochemical evaluation using monoclonal antibodies. Am J Clin Pathol. 1985;83(3):308–19.
Le Pendu J, Marionneau S, Cailleau-Thomas A, Rocher J, Le Moullac-Vaidye B, Clement M. ABH and Lewis histo-blood group antigens in cancer. APMIS. 2001;109:9–31.
Disclosures
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, J., Gao, F., Klimberg, V.S. et al. ABO Blood Type/Rh Factor and the Incidence and Outcomes for Patients with Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 19, 3159–3164 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-012-2533-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-012-2533-x