Abstract
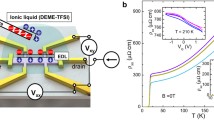
Ultrathin YBa2Cu3O7−x (YBCO) films were grown on SrTiO3 (STO) substrates using the technique of high-pressure oxygen sputtering. Films were then incorporated in a field effect transistor configuration, which facilitated the control of superconductivity by electrostatic charging. While devices using STO as both the substrate and gate dielectric have produced only relatively small shifts in film electrical properties, very large changes can be realized using an electric double layer transistor configuration employing the ionic liquid DEME-TFSI as the dielectric. By depleting holes an electrostatically tuned superconductor insulator transition was studied using a finite size scaling analysis. The breakdown of scaling at the lowest temperatures suggests the presence of a mixed insulator/superconductor phase separating the two ground states. Further depletion of holes resulted in a change of the majority carriers from holes to electrons and the emergence of what appeared to be very weak re-entrant superconductivity. Also by accumulating holes an underdoped film was tuned into the overdoped regime. A two-step mechanism for electrostatic doping was revealed. Hall effect measurements suggested the presence of an electronic phase transition or a change in the Fermi surface as a function of doping near optimal doping.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.G. Bednorz, K.A. Muller, Z. Phys. B: Cond. Matter 64, 189 (1986)
M.K. Wu, et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 58, 908 (1987)
Y. Tokura, H. Takagi, S. Uchida, Nature (London) 337, 345 (1989)
N.P. Armitage, P. Fournier, R.L. Greene, Rev. Mod. Phys. 82, 2421 (2010)
C.H. Ahn, et al., Rev. Mod. Phys. 78, 1185 (2006)
C.H. Ahn, et al., Science 284, 1152 (1999)
H.L.F. von Helmholtz, Ann. Physik 89, 211 (1853)
J.T. Ye, et al., Nature Mater. 9, 125 (2009)
Y. Lee, et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 136809 (2011)
H. Shimotani, et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 082106 (2007)
A.T. Bollinger, et al., Nature (London) 472, 458 (2011)
X. Leng, et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 027001 (2011)
J. Garcia-Barriocanal, et al., Phys. Rev. B 87, 024509 (2013)
W.H. Brattain, C.G.B. Garrett, Bell Syst. Techn. J. 34, 129 (1955)
S.G. Haupt, et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 115, 1196 (1993)
A.S. Dhoot, et al., Adv. Mater. 22, 2529 (2010)
M. Varela, et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 5156 (2001)
M. Varela, et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 3936 (1999)
H.M. Jaeger, et al., Phys. Rev. B 40, 182 (1989)
N. Doiron-Leyraud, et al., Nature (London) 447, 565 (2007)
I.F. Herbut, Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 137004 (2001)
M. Ruhlander, C.M. Soukoulis, Phys. Rev. B 63, 085103 (2001)
D.-H. Lee, Z. Wang, S. Kivelson, Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 4130 (1993)
M. Salluzzo, et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 056810 (2008)
R. Liang, D.A. Bonn, W.N. Hardy, Phys. Rev. B 73, 180505 (2006)
M.R. Presland, et al., Physica C 176, 95 (1991)
J.L. Tallon, et al., Phys. Rev. B 51, 12911 (1995)
X. Leng, et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 067004 (2012)
K. Segawa, Y. Ando, Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 4907 (2001)
F.F. Balakirev, et al., Nature (London) 424, 912 (2003)
F.F. Balakirev, et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 017004 (2009)
J.L. Tallon, et al., Phys. Status Solidi B 215, 531 (1999)
C. Jaudet, et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 187005 (2008)
B. Vignolle, et al., Nature (London) 455, 952 (2008)
D. LeBoeuf, et al., Nature (London) 450, 533 (2007)
M.R. Norman, et al., Nature (London) 392, 157 (1998)
K.M. Shen, et al., Science 307, 901 (2005)
M. Plate, et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 077001 (2005)
M.A. Hossain, et al., Nature Phys. 4, 527 (2008)
M.R. Norman, Physics 3, 86 (2010)
K. Segawa, et al., Nat. Phys. 6, 579 (2010)
T. Nojima, et al., Phys. Rev. B 84, 020502 (2011)
M. Gurvitch, et al., Physica C 153-155, 1369 (1988)
C. Tsuei, A. Gupta, G. Koren, Physica C 161, 415 (1989)
Y. Ando, et al., Phys. Rev. B 61, R14956 (2000)
T.D. Stanescu, P. Phillips, Phys. Rev. B 69, 245104 (2004)
W. Jiang, et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 73, 1291 (1994)
B.G. Orr, H.M. Jaeger, A.M. Goldman, Phys. Rev. B 32, 7586 (1985)
M. Kunchir, et al., Phys. Rev. B 36, 4062 (1987)
A. Gerber, et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 65, 3201 (1990)
W.A. Fertig, et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 38, 987 (1977)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leng, X., Garcia-Barriocanal, J., Kinney, J. et al. Electrostatic tuning of the electrical properties of YBa2Cu3O7−x using an ionic liquid. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 222, 1203–1215 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2013-01915-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2013-01915-y