Abstract
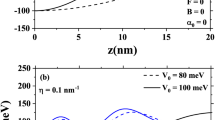
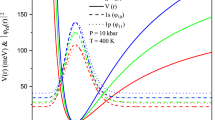
In this work, for the first time, the total refractive index (TRICs) and total absorption coefficients (TACs) of In\(_{x}\)Ga\(_{1-x}\)As/GaAs Mathieu quantum dot (MQD) with hydrogenic impurity under the influence of the external electric field and laser field are probed. Within the framework of the Ehlotzky approximation, considering the Kramers–Henneberger transformation and dipole approximation, the time-dependent in the wave equation is transferred from the kinetic energy operator to the potential energy function. Then, the new Schrödinger equation for the MQD including the hydrogenic impurity under the external electric field and monochromatic linearly polarized laser radiation is solved numerically by employing the tridiagonal matrix method. In order to study the TRICs and TACs of MQD, the iterative method and compact-density-matrix formalism are employed. The influence of structural parameters as well as the external factors on the TRICs and TACs of the MQD is examined. The effects of external electric field, laser field, In-concentration, impurity atom position, the MQD depth and width parameters on the TRICs and TACs are investigated in detail, and functional ranges of relevant parameters are also determined for the purpose. In addition, the alternatives of these parameters to each other are also discussed. It is important for experimental research that all parameter values used are accessible.







Similar content being viewed by others
Code availability
Not applicable.
Data availability statement
The data generated during the current study are accessible. [Authors’ comment: The data would be available on reasonable request.]
Change history
29 November 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-022-03508-7
References
A. Tartakovskii, Quantum Dots Optics, Electron Transport and Future Applications (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2012)
A.D. Yoffe, Semiconductor quantum dots and related systems: electronic, optical, luminescence and related properties of low dimensional systems. Adv. Phys. 50(1), 1 (2001)
M. Nirmal, L. Brus, Luminescence photophysics in semiconductor nanocrystals. Acc. Chem. Res. 32, 407 (1999)
E.H. Sargent, Colloidal quantum dot solar cells. Nat. Photon. 6(3), 133 (2012)
I. Lagraa, B. Soudini, H. Abid, S. Taleb, Study and optimization of structure InAs/InGaAs quantum dot in-a-well long-wave infrared photodetector. Optik 251, 168494 (2022)
A.J. Shields, M.P. O’Sullivan, I. Farrer, D.A. Ritchie, M.L. Leadbeater, N.K. Patel, R.A. Hogg, C.E. Norman, N.J. Curson, M. Pepper, Single photon detection with a quantum dot transistor. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 40, 2058–2064 (2021)
V. Aroutiounian, S. Petrosyan, A. Khachatryan, Quantum dot solar cells. J. Appl. Phys. 89, 2268 (2001)
D.E. Fouskidis, K.E. Zoiros, A. Hatziefremidis, Reconfigurable all-optical logic gates (AND, NOR, NOT, OR) with quantum-dot semiconductor optical amplifier and optical filter. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 27, 7600915 (2021)
S. Ma, Z. Chen, H. Sun, N.K. Dutta, High speed all optical logic gates based on quantum dot semiconductor optical amplifiers. Opt. Express 8, 6417 (2010)
P. Baser, M.K. Bahar, Evaluation of the external electric- and magnetic field-driven Mathieu quantum dot’s optical observables. Physica B 639, 413991 (2022)
J.N.L. Connor, T. Uzer, R.A. Marcus, Eigenvalues of the Schrödinger equation for a periodic potential with nonperiodic boundary conditions: A uniform semiclassical analysis. J. Chem. Phys. 80, 5095 (1984)
H. Panahı, M. Baradaran, S.R. Azızıan, Solutıons of the quası-exactly solvable mathıeu potentıal by the asymptotıc iteratıon method. Romanian Rep. Phys. 68, 56 (2016)
D.S. Jiang, Y.H. Zhang, C. Abraham, K. Syassen, J.B. Xia, K. Ploog, A study of resonant Raman scattering in GaInAs/AlInAs multiple quantum wells. Superlattices Microstruct. 12, 273 (1992)
Y. He, W. Yan, Fabrication and simulation of GaInAs Solar cells using compositionally step-graded AlGaInAs buffers on GaAs substrate. Opt. Quant. Electron. 52, 372 (2020)
W. Gillin, Y.S. Tang, N.J. Whitehead, K.P. Homewood, B.J. Sealy, M.T. Emeny, C.R. Whitehouse, Thermal processing of strained GaInAs/GaAs high hole mobility transistor structures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 56, 1116 (1990)
D. Schlenker, T. Miyamoto, Z. Chen, F. Koyama, Member, IEEE, and K. Iga 1.17- m Highly Strained GaInAs-GaAs Quantum-Well Laser, IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 11, 946, (1999)
C. Thirstrup, Novel electro-optical phase modulator based on GaInAs/InP modulation-doped quantum-well structures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 61, 2641 (1992)
H. Deng, Q. Yang, Z. Wang, X. Guo, H. Shao, X. Li, H. Gong, InGaAs short wavelength infrared detector based on carrier collection effect. Infrared Device and Infrared Technology 12061, 407 (2021)
G. Rezaei, B. Vaseghi, J. Ebrahimi, External electric field effects on the electronic and hydrogenic impurity states in ellipsoidal and semi-ellipsoidal quantum dots. Superlattices Microstruct. 49, 591 (2011)
F. Ungan, M.K. Bahar, Optical specifications of laser-induced Rosen–Morse quantum well. Opt. Mater. 90, 231 (2019)
S. Aktas, A. Bilekkaya, F.K. Boz, S.E. Okan, Electron transmission in symmetric and symmetric double-barrier structures controlled by laser fields. Superlattices Microstruct. 85, 266 (2015)
R.Y. Yan, J. Tang, Z.H. Zhang, Optical properties in GaAs/AlGaAs semiparabolic quantum wells by the finite difference method: combined effects of electric field and magnetic field. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 32, 1850159 (2018)
E.C. Niculescua, L.M. Burileanu, Nonlinear optical absorption in inverse V-shaped quantum wells modulated by high-frequency laser field. Eur. Phys. J. B 74, 117 (2010)
M.J. Karimi, H. Vafaei, Second-order nonlinear optical properties in a strained InGaN/AlGaN quantum well under the intense laser field. Superlattices Microstruct. 78, 1 (2015)
D. Brunne, M. Lafrentz, V.V. Pavlov, R.V. Pisarev, A.V. Rodina, D.R. Yakovlev, M. Bayer, Electric field effect on optical harmonic generation at the exciton resonances in GaAs. Phys. Rev. B 92, 085202 (2015)
A.D. Yoffe, Semiconductor quantum dots and related systems: electronic, optical, luminescence and related properties of low dimensional systems. Adv. Phys. 50, 1 (2001)
C. Xia, Z. Zeng, S. Wei, Electron and impurity states in GaN/AlGaN coupled quantum dots: effects of electric field and hydrostatic pressure. J. Appl. Phys. 108, 054307 (2010)
Gh. Safarpour, M.A. Izadi, E. Niknam, M. Moradi, M.M. Golshan, Simultaneous effects of external electric field and aluminum concentration on the binding energy of a laser-dressed donor impurity in a spherical quantum dot confined at the center of a cylindrical nano-wire. Phys. B 436, 14 (2014)
W. Xie, Y. Chen, Optical absorption and refractive index of a donor impurity in a three-dimensional quantum pseudodot. Superlattices Microstruct. 50, 691 (2011)
E.C. Niculescu, D. Bejan, Off-centre impurity-related nonlinear optical absorption, second and third harmonic generation in a two-dimensional quantum ring under magnetic field. Philos. Mag. 97(24), 2089–2107 (2017)
S. Saha, S. Pal, J. Ganguly, M. Ghosh, Exploring optical refractive index change of impurity doped quantum dots driven by white noise. Superlattices Microstruct. 88, 620 (2015)
A. Mandal, S. Sarkar, A.P. Ghosh, M. Ghosh, Analyzing total optical absorption coefficient of impurity doped quantum dots in presence of noise with special emphasis on electric field, magnetic field and confinement potential. Chem. Phys. 463, 149 (2015)
J. Ganguly, S. Saha, S. Pal, M. Ghosh, Noise-driven optical absorption coefficients of impurity doped quantum dots. Physica E 75, 246 (2016)
J. D. Jackson, Classical Electrodynamics, Third Edition, Wiley, 1999
B.H. Bransden, C.J. Joachain, Physics of Atoms and Molecules (Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, 2003)
W.C. Henneberger, Perturbation method for atoms in intense light beams. Phys. Rev. Lett. 21, 838 (1968)
H.A. Kramers, Collected Scientific Paper, vol. 866 (North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1956)
F.M.S. Lima, M.A. Amato, L.S.F. Olavo, O.A.C. Nunes, A.L.A. Fonseca, E.F. da Silva, Jr., Intense laser field effects on the binding energy of impurities in semiconductors. Phys. Rev. B 75, 073201 (2007)
M. Gavrila, J.Z. Kaminski, Free-free transitions in intense high-frequency laser fields. Phys. Rev. Lett. 52, 613 (1984)
F. Ehlotzky, Scattering phenomena in strong radiation fields II. Can. J. Phys. 63, 907 (1985)
F. Ehlotzky, Positronium decay in intense high frequency laser fields. Phys. Lett. A 126, 524 (1988)
M.K. Bahar, Effects of laser radiation field on energies of hydrogen atom in plasmas. Phys. Plasmas 22, 092709 (2015)
M.K. Bahar, A. Soylu, Laser-driven two-electron quantum dot in plasmas. Phys. Plasmas 25, 062113 (2018)
M.K. Bahar, A. Soylu, Two-electron pseudodot system with laser effect in plasmas. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 47, 1713 (2019)
M. Kalinski, J.H. Eberly, New states of hydrogen in a circularly polarized electromagnetic field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 2420 (1996)
B.N. Datta, Numerical Linear Algebra and Applications, 2nd edn. (SIAM, Philadelphia, 2010)
R.W. Boyd, Nonlinear Optics, 3rd edn. (Rochester, New York, 2007)
K. Kılıç, M.K. Bahar, Optical response of plasma processed quantum dot under the external fields. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 121, e26564 (2021)
S. Paul, J.B. Roy, P.K. Basu, Empirical expressions for the alloy composition and temperature dependence of the band gap and intrinsic carrier density in Ga\(_{x}\)In\(_{1-x}\)As. J. Appl. Phys. 69, 827 (1991)
F. Ungan, M.K. Bahar, M.G. Barseghyan, L.M. Perez, D. Laroze, Effect of intense laser and electric fields on nonlinear optical properties of cylindrical quantum dot with Morse potential. Optik 236, 16662 (2021)
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bahar, M.K., Başer, P. Tuning of nonlinear optical characteristics of Mathieu quantum dot by laser and electric field. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 137, 1138 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-022-03362-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-022-03362-7