Abstract
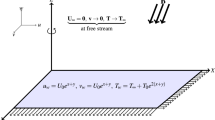
In this paper, magnetic field effects on the forced convection flow of a nanofluid over a stretching surface in the presence of heat generation/absorption are studied. The equations of continuity, momentum and energy are transformed into ordinary differential equations and solved numerically using the fourth-order Runge-Kutta integration scheme featuring the shooting technique. Different types of nanoparticles as copper (Cu), silver (Ag), alumina (Al2O3) and titania (TiO2) with water as their base fluid has been considered. The influence of significant parameters, such as magnetic parameter, volume fraction of the nanoparticles, heat generation/absorption parameter, velocity ratio parameter and temperature index parameter on the flow and heat transfer characteristics are discussed. The results show that the values of temperature profiles increase with increasing heat generation/absorption and volume fraction of the nanoparticles but they decrease with increasing velocity ratio parameter and temperature index parameter. Also, it can be found that selecting silver as nanoparticle leads to the highest heat transfer enhancement.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A 1, A 2, A 3 :
-
Constants parameters
- a :
-
Stretching sheet parameter
- b :
-
Free stream velocity parameter
- C f :
-
Skin friction coefficient
- f :
-
Dimensionless stream function
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity
- M :
-
Magnetic parameter
- Nu :
-
Nusselt number
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number
- q w :
-
Surface heat flux
- Q 0 :
-
Dimensional heat generation or absorption coefficient
- Re x :
-
Local Reynolds number
- T :
-
Fluid temperature
- T ∞ :
-
Ambient temperature
- (u, v):
-
Velocity components in the (x, y) directions, respectively
- (x, y):
-
Cartesian coordinates along x, y axes, respectively
- α :
-
Thermal diffusivity
- η :
-
Similarity parameter
- θ :
-
Similarity function for temperature
- ρ :
-
Density
- ϕ :
-
nanoparticle volume fraction
- μ :
-
Dynamic viscosity
- ν :
-
Kinematic viscosity
- τ w :
-
Wall shear stress
- ψ :
-
Stream function
- λ :
-
Velocity ratio parameter
- w :
-
Condition at the surface
- ∞:
-
Condition at infinity
- nf:
-
Nanofluid
- f :
-
Base fluid
- s :
-
Nano-solid-particles
References
E.M.A. Elbashbeshy, M.A.A. Basid, Appl. Math. Comput. 158, 799 (2004).
A. Chakrabarti, A.S. Gupta, Quart. Appl. Math. 37, 73 (1979).
A.K. Borkakoti, A. Bharali, Q. Appl. Math. 41, 461 (1983).
S. Choi, Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticle, in Developments and Applications of Non-Newtonian Flows, edited by D.A. Siginer, H.P. Wang, Vol. 231 and 66, (1995) pp. 99--105.
M. Sheikholeslami, M. Gorji-Bandpay, D.D. Ganji, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 39, 978 (2012).
Hamid Reza Ashorynejad, Abdulmajeed A. Mohamad, Mohsen Sheikholeslami, Int. J. Thermal Sci. 64, 240 (2013).
Soheil Soleimani, M. Sheikholeslami, D.D. Ganji, M. Gorji-Bandpay, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 39, 565 (2012).
Mohsen Sheikholeslami, Shirley Abelman, IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 14, 561 (2015) DOI:10.1109/TNANO.2015.2416318.
Mohsen Sheikholeslami, Mohammad Mehdi Rashidi, J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng., (2015) DOI:10.1016/j.jtice.2015.03.035.
Mohsen Sheikholeslami, Mofid Gorji Bandpy, Hamid Reza Ashorynejad, Phys. A: Stat. Mech. Appl. 432, 58 (2015).
Mohsen Sheikholeslami Kandelousi, Eur. Phys. J. Plus 129, 248 (2014).
Mohsen Sheikholeslami, Davood Domiri Ganji, Mohammad Mehdi Rashidi, J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 47, 6 (2015).
Mohsen Sheikholeslami Kandelousi, Phys. Lett. A 378, 3331 (2014).
Mohammad Hatami, Mohsen Sheikholeslami, M. Hosseini, Davood Domiri Ganji, J. Mol. Liq. 194, 251 (2014).
M. Sheikholeslami, M.M. Rashidi, Eur. Phys. J. Plus 130, 115 (2015).
T. Hayat, M. Qasim, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 53, 4780 (2010).
Mohsen Sheikholeslami, Mofid Gorji-Bandpy, Davood Domiri Ganji, Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 49, 444 (2015).
M. Hatami, D.D. Ganji, M. Gorji-Bandpy, Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 37, 168 (2014).
Chaoli Zhang, Liancun Zheng, Xinxin Zhang, Goong Chen, Appl. Math. Model. 39, 165 (2015).
M. Sheikholeslami, R. Ellahi, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 89, 799 (2015).
Mohsen Sheikholeslami, Davood Domiri Ganji, Energy 75, 400 (2014).
Mohsen Sheikholeslami, Davood Domiri Ganji, M. Younus Javed, R. Ellahi, J. Magn. & Magn. Mater. 374, 36 (2015).
Mohsen Sheikholeslami, Mofid Gorji-Bandpy, Kuppalapalle Vajravelu, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 80, 16 (2015).
M.M. Rahman, Hakan F. Öztop, Michael Steele, A.G. Naim, Khaled Al-Salem, Talaat A. Ibrahim, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 64, 50 (2015).
M. Sheikholeslami, D.D. Ganji, Sci. Iran. B 21, 203 (2014).
M. Sheikholeslami, M. Gorji-Bandpy, Soheil Soleimani, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 47, 73 (2013).
M. Sheikholeslami, M. Gorji-Bandpy, D.D. Ganji, Energy 60, 501 (2013).
O.D. Makinde, E. Osalusi, Rom. J. Phys. 51, 293 (2006).
N. Masoumi, N. Sohrabi, A. Behzadmehr, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 42, 055501 (2009).
J. Buongiorno, ASME J. Heat Transfer 128, 240 (2006).
R. Prasher, E.P. Phelan, ASME J. Heat Transfer 128, 588 (2006).
H.E. Patel, T. Sundarrajan, T. Pradeep, A. Dasgupta, N. Dasgupta, S.K. Das, Pramana J. Phys. 65, 863 (2005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammadpour, M., Valipour, P., Shambooli, M. et al. Nanofluid flow and forced convection heat transfer over a stretching surface considering heat source. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 130, 155 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2015-15155-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2015-15155-8