Abstract
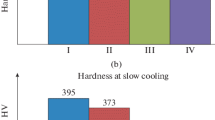
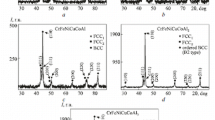
The structural and phase transformations that take place in the cast high-entropy equiatomic alloy AlCrFeCoNiCu after solidification, homogenizing heat treatment, and cooling have been studied. Analytical transmission microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, X-ray energy dispersive spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction analysis were used to conduct the studies. The elastic modulus, nano-, and microhardness have been measured. The alloy decomposition has been found to occur with the precipitation of no less than six nanoscale phases with different morphologies, structures (A2, B2, L12), and chemical compositions. All the nanophases are multicomponent solid solutions enriched with several elements, which indicates the pronounced elemental and phase nanomodulation over the alloy volume.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. L. Bernshtein, Thermomechanical Treatment of Alloys, in 2 vols. (Metallurgiya, Moscow, 1968) [in Russian].
B. A. Kolachev, V. A. Livanov, and V. I. Elagin, Metal Science and Heat Treatment of Non-Ferrous Metals and Alloys (Metallurgiya, Moscow, 1972) [in Russian].
G. V. Kurdyumov, L. M. Utevskii, and R. I. Entin, Transformations in Iron and Steel (Nauka, Moscow, 1977) [in Russian].
I. I. Fridlyander, Aluminum Deformable Structural Alloys (Metallurgiya, Moscow, 1979) [in Russian].
Glezer, A.M. and Molotilov, V.V., Ordering and Deformation of Iron Alloys (Metallurgiya, Moscow, 1984) [in Russian].
V. N. Khachin, V. G. Pushin, and V. V. Kondrat’ev, Titanium Nickelide: Strtucture and Properties (Nauka, Moscow, 1992) [in Russian].
V. G. Pushin, V. V. Kondrat’ev, and V. N. Khachin, Pretransition Phenomena and Martensitic Transformations (Ural. Otd. Ross. Akad. Nauk, Ekaterinburg, 1998) [in Russian].
E. N. Kablov and E. R. Golubovskii, Heat Resistance of Nickel Alloys (Mashinostroenie, Moscow, 1998) [in Russian].
“To 70th anniversary of VIAM: A special issue,” Metal Sci. Heat Treat., No. 7 (2002).
B. A. Greenberg and M. A. Ivanov, Ni3Al and TiAl Intermetallic Compounds: Microstructure and Deformation Behavior (Ural. Otd. Ross. Akad. Nauk, Ekaterinburg, 2002) [in Russian].
V. G. Pushin, S. D. Prokoshkin, R. Z. Valiev, V. Brailovskii, E. Z. Valiev, A. E. Volkov, A. M. Glezer, S. V. Dobatrin, E. F. Dudarev, V. T. Zhu, Yu. G. Zainulin, Yu. R. Kolobov, V.V. Kondratiev, A. V. Korolev, A. I. Korshunov, N. I. Kourov, N. V. Kudrevatykh, A. I. Lotkov, L. L. Meisner, A. A. Popov, N. N. Popov, A. I. Razov, M. A. Khusainov, Yu. I. Chumlyakov, S. V. Andreev, A. A. Baturin, S. P. Belyaev, V. N. Grishkov, D. V. Gunderov, A. P. Dyupin, K. V. Ivanov, V. I. Itin, M. K. Kasymov, O. A. Kashin, I. V. Kireeva, A. I. Kozlov, T. E. Kuntsevich, N. N. Kuranova, N. Yu. Pushina, E. P. Ryklina, A. N. Uksusnikov, I. Yu. Khmelevskaya, A. V. Shelyakov, V. Ya. Shklover, E. V. Shorokhov, and L. I. Yurchenko, Titanium Nickelide Alloys with Shape Memory. Ch. I. Structure, Phase Transformations and Properties (Ural. Otd. Ross. Akad. Nauk, Ekaterinburg, 2006) [in Russian].
V. G. Pushin, “Alloys with a thermomechanical memory: Structure, properties, and application,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 90(Suppl. 1), S68–S95 (2000).
V. Brailovski, I. Yu. Khmelevskaya, S. D. Prokoshkin, V. G. Pushin, E. P. Ryklina, and R. Z. Valiev, “Foundations of heat and thermomechanical treatments and their effect on the structure and properties of titanium nickelide-based alloys,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 97(Suppl.1), S3–S55 (2004).
J. W. Yeh, Y. L. Chen, S. J. Lin, and S. K. Chen, “High-entropy alloys—A new era of exploitation,” Mater. Sci. Forum 560, 1–9 (2007).
C. J. Tong, Y. L. Chen, S. K. Chen, J. W. Yeh, T. T. Shun, C. H. Tsau, S. J. Lin, and S. Y. Chang, “Microstructure characterization of AlxCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy system with multiprincipal elements,” Metall. Mater. Trans. A 36 A, 881–893 (2005).
C. C. Tung, J. W. Yeh, T. T. Shun, S. K. Chen, Y. S. Huang, and H. C. Chen, “On the elemental effect of AlCoArCuFeNi high-entropy alloy system,” Mater. Lett. 61, 1–5 (2007).
X. F. Wang, Y. Zhang, Y. Qiao, and G. L. Chen, “Novel microstructure and properties of multicomponent CoCrCuFeNiTix alloys,” Intermetallics 15, 357–362 (2007).
S. Singh, N. Wanderka, B. S. Murty, U. Glatzel, and J. Banhart, “Decomposition in multi-component AlCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy,” Acta Mater. 59, 182–190 (2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © M.V. Ivchenko, V.G. Pushin, A.N. Uksusnikov, N. Wanderka, 2013, published in Fizika Metallov i Metallovedenie, 2013, Vol. 114, No. 6, pp. 561–568.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ivchenko, M.V., Pushin, V.G., Uksusnikov, A.N. et al. Microstructure features of high-entropy equiatomic cast AlCrFeCoNiCu alloys. Phys. Metals Metallogr. 114, 514–520 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X13060069
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X13060069