Summary
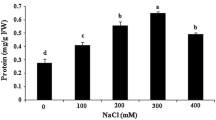
The present study aimed to evaluate the response to salinity of Populus euphratica, which is more salt-resistant than other poplar cultivars, at the cellular level. To this purpose, callus was induced from shoot segments of P. euphratica on Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium supplemented with 0.5 mg l−1 (2.2 μM) 6-benzyladenine (BA) and 0.5 mg l−1 (2.7 μM 1-naphthaleneacetic acid (NAA). Callus was transferred to MS medium supplemented with 0.25 mg l−1 (1.1 μM) BA and 0.5 mg l−1 NAA. The relative growth rate of callus reached a maximum in the presence of 50 mmol l−1 NaCl and growth was inhibited with increasing NaCl concentrations. Examination of the changes of osmotic substances under salt stress showed that accumulation of proline, glycine betaine, and total soluble sugars increased with increasing salt concentrations. The results indicate that the response of the callus of P. euphratica to salt stress is similar to that of the whole plant.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bates, L. S.; Waldren, R. P.; Teare, D. Rapid determination of free proline for water stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207; 1973.
Bohnert, H. J.; Jensen, R. G. Metabolic engineering for increased salt tolerance, the next step. Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 23:661–666; 1996a.
Bohnert, H. J.; Jensen, R. G. Strategies for engineering water stress tolerance in plants. Trends Biotechnol. 14:89–97; 1996b.
Boyer, J. S. Plant productivity and environment. Science 218:443–448; 1982.
Dubois, M.; Gilles, K. A.; Hamilton, J. K.; Rebers, P. A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for the determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 28:350–356; 1956.
Escalada, J. A.; Moss, D. N. Changes in non-structural carbohydrate fractions of developing spring wheat kernels. Crop Sci. 16:627–631; 1976.
Flowers, T. J.; Hajibagueri, M. A.; Clipson, N. C. W. Halophytes. Quart. Rev. Biol. 61:313–337; 1986.
Flowers, T. J.; Troke, P. F.; Yeo, A. R. The mechanism of salt tolerance in halophytes. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 28:89–121; 1977.
Fung, L. E.; Ma, H.; Wang, S. X-ray microanalysis of ion distribution in salt tolerancy and salt intolerant poplar genotypes. J. Beijing For. Univ. 5:23–30; 1996.
Fung, L. E.; Wang, S.; Altman, A.; Hüttermann, A. Effect of NaCl on growth, photosynthesis, ion and water relations of four poplar genotypes. For. Ecol. Manage. 107:135–146; 1998.
Garham, J.; Hughes, L. Y.; Wynjanes, R. G. Low molecular weight carbohydrates in some salt stressed plants. Physiol. Plant. 53:27–33; 1981.
Giridara, K. S.; Madhusudhan, K. V.; Sreenivasulu, N.; Sudhakar, C. Stress responses in two genotypes of mulberry (Morus alba L.) under NaCl salinity. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 38:192–195; 2000.
Greenway, H.; Munns, R. Mechanisms of salt tolerance in nonhalophytes. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 31:149–190; 1980.
Grieve, C. M.; Grattan, S. R. Rapid assay for determination of water soluble quaternary ammonium compounds. Plant Soil. 70:303–307; 1983.
Gu, R.; Jiang, X.; Guo, Z. Organogenesis and plantlet regeneration in vitro of Populus euphratica. Acta Bot. Sin. 41:29–33; 1999.
Hanson, A. D. Compatible solute synthesis and compartmentation in higher plants. In: Osmond, C. B.; Bjorkman, O.; Anderson, D. J., eds. Physiological processes in plant ecology: toward a synthesis with Atriplex. Berlin: Springer-Verlag; 1980:52–60.
Hitz, W. D.; Hanson, A. D. Determination of glycine betaine by pyrolysis-gas chromatography in cereals and grasses. Phytochemistry 19:2371–2374; 1980.
Kavi Kishor, P. B.; Hong, Z.; Miao, G.-H.; Hu, C. A. A.; Verma, D. P. S. Overexpression of D1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase increases proline production and confers osmotolerance in transgenic plants. Plant Physiol. 108:1387–1394; 1995.
Kumar, S. G.; Reddy, A. M.; Sudhakar, C. NaCl effects on proline metabolism in two high yielding genotypes of mulberry (Morus alba L.) with contrasting salt tolerance. Plant Sci. 165:1245–1251; 2003.
Ma, H.; Fung, L.; Wang, S.; Altman, A.; Hüttermann, A. Photosynthetic response of Populus euphratica to salt stress. For. Ecol. Manage. 93:55–61; 1997.
Macleod, A. M.; Orquodale, M. C. Water soluble carbohydrates of seeds of the gramineae. New Phytol. 57:168–182; 1958.
Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15:473–497; 1962.
Nuccio, M. L.; Rhodes, D.; McNeil, S. D.; Hanson, A. D. Metabolic engineering of plants for osmotic stress resistance. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2:128–134; 1999.
Prado, F. E.; Boero, C.; Gallarodo, M.; Gonzalez, J. A. Effect of NaCl on germination, growth and soluble sugar content in Chenopodium quinoa wild seeds. Bot. Bull. Acad. Sin. 41:27–34; 2000.
Prisco, J. T. Alguns aspectos da fisiologia do ‘stress’ salino. Revista Brasil. Bot. 3:85–94; 1980.
Quick, P.; Siegl, G.; Neuhaus, E.; Feil, R.; Sttit, M. Short-term water stress leads to a stimulation of sucrose synthesis by activating sucrose phosphate synthase. Planta 177:535–546; 1989.
Rhodes, D.; Hanson, A. D. Quaternary ammonium and tertiary sulfonium compounds in higher plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 44:357–384; 1993.
Rhodes, D. P.; Rich, J.; Myers, A. C.; Rueter, C. C.; Jamieson, G. C. Determination of betaines by fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry: identification of glycine betaine deficient genotypes of Zea mays. Plant Physiol 84:781–788; 1987.
Wang, W.; Vinocur, B.; Altman, A. Plant responses to drought, salinity and extreme temperatures: towards genetic engineering for stress tolerance. Planta 218:1–14; 2003.
Wang, Z.; Quebedeaux, B.; Stutte, G. W. Partitioning of (14C) glucose into sorbitol and other carbohydrates in apple under water stress. Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 23:245–251; 1996.
Wang, Z.; Stutte, G. W. The role of carbohydrates in active osmotic adjustment in apple under water stress. J. Am. Soc. Hort. Sci. 117:816–823; 1992.
Watanabe, S.; Kojima, K.; Ide, Y.; Sasaki, S. Effects of saline and osmotic stress on proline and sugar accumulation in Populus euphratica in vitro. Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 63:199–206; 2000.
Wei, Q. Euphratica poplar. Preface. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing; 1993: 1–195.
Winter, K. Photosynthesis and water relationships of higher plants in a saline environment. In: Jefferies, R. L.; Davy, A. J., eds. Ecological processes in coastal environments. Oxford: Blackwell Science Publishers; 1979:297–320.
Yokoi, S.; Bressan, R.A.; Hasegawa, P. M. The Japan International Research Center for Agricultural Sciences (JIRCAS) Working Report No. 23. In: Iwanaga, M., ed. Genetic engineering of crop plants for abiotic stress. Salt stress tolerance of plants. Tsukuba: Japan International Research Center for Agricultural Sciences Publishing; 2002:25–33.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, F., Yang, Y.L., He, W.L. et al. Effects of salinity on growth and compatible solutes of callus induced from Populus euphratica . In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Plant 40, 491–494 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1079/IVP2004546
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1079/IVP2004546