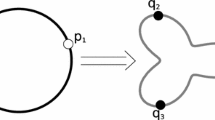
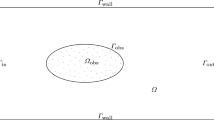
Abstract
The Minkowski problem asks a fundamental question in differential geometry whose answer is not only important in that field but has real world applications as well. We endeavor to construct the shapes that arise from the Minkowski problem by forming a PDE that flows an initial implicitly defined hypersurface to an approximation of the shape under the level set framework. Tools and ideas found in the various applications of level set methods are gathered to generate this PDE. Numerically, its solution is determined by incorporating high order finite difference schemes over the uniform grid available in the framework. Finally, we use our approach in various test cases to generate various shapes arising from different given data in the Minkowski problem.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adalsteinsson, D., and Sethian, J. A. (1995). A fast level set method for propagating interfaces. J. Comput. Phys. 118, 269-277.
Adalsteinsson, D., and Sethian, J. A. (1999). The fast construction of extension velocities in level set methods. J. Comput. Phys. 148, 2-22.
Ambrosio, L., and Soner, H. M. (1996). Level set approach to mean curvature flow in arbitrary codimension. J. Differential Geom. 43, 693-737.
Chen, S., Merriman, B., Osher, S., and Smereka, P. (1997). A simple level set method for solving Stefan problems. J. Comput. Phys. 135, 8-29.
Cheng, L.-T. (2000). The Level Set Method Applied to Geometrically Based Motion, Materials Science, and Image Processing. Ph.D. thesis, University of California, Los Angeles.
Cheng, S. Y., and Yau, S. T. (1976). On the regularity of the solution of the n-dimensional Minkowski problem. Comm. Pure Appl. Math. 29, 495-516.
Chou, K.-S., and Wang, X.-J. (2000). A logarithmic Gauss curvature flow and the Minkowski problem. Ann. Inst. H. Poincaré Anal. Non Lineaire 17(6), 733-751.
Danielsson, P. (1980). Euclidean distance mapping. Computer Graphics and Image Processing 14, 227-248.
do Carmo, M. (1976). Differential Geometry of Curves and Surfaces, Prentice–Hall, Inc. Translated from the Portuguese.
Helmsen, J., Puckett, E., Colella, P., and Dorr, M. (1996). Two new methods for simulating photolithography development in 3D. Proc. SPIE 2726, 253-261.
Jiang, G. S., and Peng, D. (2000). Weighted ENO schemes for Hamilton–Jacobi equations. SIAM J. Scient. Comput. 21(6), 2126-2143.
Kaasalainen, M., Lamberg, L., and Lumme, K. (1992). Interpretation of lightcurves of atmosphereless bodies. 2. Practical aspects of inversion. Astron. Astrophys. 259, 333-340.
Kaasalainen, M., Lamberg, L., Lumme, K., and Bowell, E. (1992). Interpretation of lightcurves of atmosphereless bodies. 1. General theory and new inversion schemes. Astron. Astrophys. 259, 318-332.
Kang, M., Merriman, B., Osher, S., and Smereka, P. (1996). Level Set Approach for the Motion of Soap Bubbles with Curvature Dependent Velocity or Acceleration. CAM Report 96-19, UCLA.
Lamberg, L. (1993). On the Minkowski Problem and the Lightcurve Operator, Ph.D. thesis, University of Helsinki.
Lamberg, L., and Kaasalainen, M. (2001). Numerical solution of the Minkowski problem. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 137(2), 213-227.
Lewy, H. (1938). On differential geometry in the large 1 (Minkowski's Problem). Trans. Amer. Math. Soc. 43(2), 258-270.
Majda, A. (1976). The inverse problem for convex bodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 73(5), 1377-1378.
Nirenberg, L. (1953). The Weyl and Minkowski problems in differential geometry in the large. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 6, 337-394.
Osher, S., and Fedkiw, R. (2001). Level set methods: An overview and some recent results. J. Comput. Phys. 169, 463-502.
Osher, S., and Merriman, B. (1997). The Wulff shape as the asymptotic limit of a growing crystal interface. Asian J. Math. 1(3), 560-571.
Osher, S., and Sethian, J. A. (1988). Fronts propagating with curvature dependent speed: Algorithms based on Hamilton–Jacobi formulations. J. Comput. Phys. 169(1), 12-49.
Osher, S., and Shu, C.-W. (1991). High order essentially non-oscillatory schemes for Hamilton–Jacobi equations. SINUM 28, 907-922.
Peng, D., Merriman, B., Osher, S., Zhao, H. K., and Kang, M. (1999). A PDE-based fast local level set method. J. Comput. Phys. 155(2), 410-438.
Pogorelov, A. V. (1975). The Multidimensional Minkowski Problem, Izdat. “Nauka”, Moscow.
Pogorelov, A. V. (1978). The Multidimensional Minkowski Problem, Wiley.
Rudin, L., Osher, S., and Fatemi, E. (1992). Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms. Physica D 60, 259-268.
Sethian, J. A. (1996). Fast marching level set methods for three dimensional photolithography development. Proc. SPIE 2726, 261-272.
Shu, C.-W., and Osher, S. (1988). Efficient implementation of essentially nonoscillatory shock-capturing schemes. J. Comput. Phys. 77(2), 439-471.
Spiteri, R. J., and Ruuth, S. J. (2002). A new class of optimal high-order strong-stability-preserving time discretization methods. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 40(2): 469-491.
Sussman, M., Smereka, P., and Osher, S. (1994). A level set method for computing solutions to incompressible two-phase flow. J. Comput. Phys. 114, 146-159.
Tsai, Y.-H., Cheng, L.-T., Osher, S., and Zhao, H. K. (2001). Fast sweeping algorithms for a class of Hamilton–Jacobi equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal., to appear.
Tsitsiklis, J. N. (1995). Efficient algorithms for globally optimal trajectories. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control 50, 1528-1538.
Zhao, H. K., Chan, T. F., Merriman, B., and Osher, S. (1996). A variational level set approach to multiphase motion. J. Comput. Phys. 127, 179-195.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, LT. Construction of Shapes Arising from the Minkowski Problem Using a Level Set Approach. Journal of Scientific Computing 19, 123–138 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025343723019
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025343723019