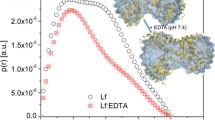
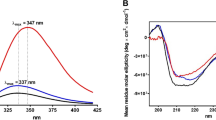
Abstract
Lactoferrin (Lf) has long been recognized as a member of the transferrin family of proteins and an important regulator of the levels of free iron in the body fluids of mammals. Its ability to bind ferric iron with high affinity (KD∼10−20 M) and to retain it to low pH gives the protein bacteriostatic and antioxidant properties. This ability can be well understood in terms of its three dimensional (3D) structure. The molecule is folded into two homologous lobes (N- and C-lobes) with each lobe binding a single Fe3+ ion in a deep cleft between two domains. The iron sites are highly conserved, and highly favorable for iron binding. Iron binding and release are associated with large conformational changes in which the protein adopts either open or closed states. Comparison of available apolactoferrin structures suggests that iron binding is dependent on the dynamics of the open state. What triggers release of the tightly bound iron, however, and why lactoferrin retains iron to much lower pH than its serum homologue, transferrin, has been the subject of much speculation. Comparisons of structural and functional data on lactoferrins and transferrins now suggest that the key factor comes from cooperative interactions between the two lobes of the molecule, mediated by two α-helices.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aisen P, Harris DC. 1989 Physical biochemistry of the transferrins. In: Loehr T, ed. Iron Carriers and Iron Proteins, Vol 5. New York: VCH Publishers: 241-251.
Anderson BF, Baker HM, Dodson EJ, Norris GE, Rumball SV, Waters JM, Baker EN. 1987 The structure of human lactoferrin at 3.2 Å resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84, 1769-1773.
Anderson BF, Baker HM, Norris GE, Rice DW, Baker EN. 1989 Structure of human lactoferrin: Structure analysis and refinement at 2.8 Å resolution. J Mol Biol 209, 711-734.
Anderson BF, Baker HM, Norris GE, Rumball SV, Baker EN. 1990 Apolactoferrin structure demonstrates ligand-induced conformational change in transferrins. Nature 344, 784-787.
Bailey S, Evans RW, Garratt RC, Gorinsky B, Hasnain S, Horsburgh C, Jhoti H, Lindley PF, Mydin A, Sarra R, Watson JL. 1988 Molecular structure of serum transferrin at 3.3 Å resolution. Biochemistry 27, 5804-5812.
Baker EN. 1994 Structure and reactivity of transferrins. Adv Inorg Chem 41, 389-463.
Baker EN and Lindley PF. 1992 New perspectives on the structure and function of transferrins. J Inorg Biochem 47, 147-160.
Baker EN, Rumball SV, Anderson BF. 1987 Transferrins: Insights into structure and function from studies on lactoferrin. Trends Biochem Sci 12, 350-353.
Baker EN, Anderson BF, Baker HM, Faber HR, Smith CA, Sutherland-Smith AJ. 1997 In: Hutchens TW, Lonnerdal B, eds. Lactoferrin: Interactions and Biological Functions. Totowa NJ: Humana Press, 177-191.
Baker EN, Baker HM, Kidd, RD. 2002 Lactoferrin and transferrin: Functional variations on a common structural framework. Biochem Cell Biol 80, 27-34.
Baker HM, He Q-Y, Briggs SK, Mason AB, Baker EN. 2003 Structural and functional consequences of binding site mutations in transferrin: Crystal structures of the Asp63Glu and Arg124Ala mutants of the N-lobe of human transferrin. Biochemistry 42, 7084-7089.
Baldwin DA, Jenny RR, Aisen P. 1984 The effect of human serum transferrin and milk lactoferrin on hydroxyl radical formation from superoxide and hydrogen peroxide. J Biol Chem 259, 13391-13394.
Bali PK, Aisen P. 1991 Receptor-modulated iron release from transferrin: Differential effects on the N-and C-terminal sites. Biochemistry 30, 9947-9952.
Bellamy W, Takase M, Yamauchi K, Wakabayashi H, Kawase K, Tomita M. 1992 Identification of the bactericidal domain of lactoferrin. Biochim Biophys Acta 1121, 130-136.
Bennett RM, Davis J. 1982 Lactoferrin interacts with deoxyribonucleic acid: A preferential reactivity with double-stranded DNA and dissociation of DNA-anti-DNA complexes. J Lab Clin Med 99, 127-138.
Bruns CM, Nowalk AJ, Arvai AS, McTigue MA, Vaughan KG, Mietzner TA, McRee DE. 1997 Structure of Haemophilus influenzae Fe+3-binding protein reveals convergent evolution within a superfamily. Nature Struct Biol 4, 919-924.
Bullen JJ, Rogers HJ, Leigh L. 1972 Iron-binding proteins in milk and resistance to Escherichia coli infections in infants. Brit Med J 1, 69-75.
Day CL, Stowell KM, Baker EN, Tweedie JW. 1992 Studies of the N-terminal half of lactoferrin produced from the cloned cDNA demonstrate that interlobe interactions modulate iron release. J Biol Chem 267, 13857-13862.
Dewan JC, Mikami B, Hirose M, Sacchettini JC. 1993 Structural evidence for a pH-sensitive dilysine trigger in the hen ovotransferrin N-lobe: Implications for transferrin iron release. Biochemistry 32, 11963-11968.
El Hage Chahine J-M, Pakdaman R. 1995. Transferrin, a mechanism for iron release. Eur J Biochem 230, 1102-1110.
Faber HR, Bland T, Day CL, Norris GE, Tweedie JW, Baker EN. 1996 Altered domain closure and iron-binding in transferrins: The crystal structure of the Asp60Ser mutant of the amino-terminal half-molecule of human lactoferrin. J Mol Biol 256, 352-363.
Grossmann JG, Neu M, Pantos E, Schwab FJ, Evans RW, Towns-Andrews E, Lindley PF, Appel H, Thies W-G, Hasnain SS. 1992 X-ray solution scattering reveals conformational changes upon iron uptake in lactoferrin, serum and ovotransferrins. J Mol Biol 225, 811-819.
Groves ML. 1960 The isolation of a red protein from milk. J Am Chem Soc 82, 3345-3350.
Haridas M, Anderson BF, Baker EN. 1995 Structure of human diferric lactoferrin, refined at 2.2 Å resolution. Acta Cryst D51, 629-646.
He J, Furmanski P. 1995 Sequence specificity and transcriptional activation in the binding of lactoferrin to DNA. Nature 373, 721-724.
Jameson GB, Anderson BF, Norris GE, Thomas DH, Baker EN. 1998 Structure of human apolactoferrin at 2.0 Å resolution. Refinement and analysis of ligand-induced conformational change. Acta Cryst D54, 1319-1335.
Jeffrey PD, Bewley MC, MacGillivray RTA, Mason AB, Woodworth RC, Baker EN. 1998 Ligand-induced conformational change in transferrins: Crystal structure of the open form of the N-terminal half-molecule of human transferrin. Biochemistry 40, 13978-13986.
Johansson B. 1960 Isolation of an iron-containing red protein from human milk. Acta Chem Scand 14, 510-512.
Karthikeyan S, Paramasivam M, Yadav S, Srinivasan A, Singh TP. 1999 Structure of buffalo lactoferrin at 2.5 Å resolution using crystals grown at 303K shows different orientations of the N and C lobes. Acta Cryst D55, 1805-1813.
Khan JA, Kumar P, Paramasivam M, Yadav RS, Sahani MS, Sharma S, Srinivasan A, Singh TP. 2001a Camel lactoferrin, a transferrincum-lactoferrin: Crystal structure of camel lactoferrin at 2.6 Å resolution and structural basis of its dual role. J Mol Biol 309, 751-761.
Khan JA, Kumar P, Srinivasan A, Singh TP. 2001b Protein intermediate trapped by the simultaneous crystallization process. J Biol Chem 276, 36817-36823.
Kraulis PJ. 1991 MOLSCRIPT: a program to produce both detailed and schematic plots of protein structures. J Appl Cryst 24, 946-950.
Kurokawa H, Mikami B, Hirose M. 1995 Crystal structure of diferric hen ovotransferrin at 2.4 Å resolution. J Mol Biol 254, 196-207.
Kurokawa H, Dewan JC, Mikami B, Sacchettini JC, Hirose M. 1999 Crystal structure of hen apo-ovotransferrin at 2.4 Å resolution. J Mol Biol 254, 196-207.
MacGillivray RTA, Moore SA, Chen J, Anderson BF, Baker H, Luo Y, Bewley M, Smith CA, Murphy MEP, Wang Y, Mason AB, Woodworth RC, Brayer GD, Baker EN. 1998 Two high resolution structures of the recombinant N-lobe of human transferrin reveal a structural change implicated in iron release. Biochemistry 37, 7919-7928.
Mann DM, Romm E, Migliorini M. 1994 Delineation of a glycosaminoglycan-binding site in the human inflammatory response protein lactoferrin. J Biol Chem 269, 23661-23667.
Mazurier J, Spik G. 1980 Comparative study of the iron-binding properties of human transferrins. Biochim Biophys Acta 629, 399-408.
Merritt EA, Bacon DJ. 1997 Raster3D: photorealistic molecular graphics. Methods Enzymol 277, 505-524.
Metz-Boutigue M-H, Jolles J, Mazurier J, Schoentgen F, Legrand D, Spik G, Montreuil J, Jolles P. 1984 Human lactotransferrin: Amino acid sequence and structural comparisons with other transferrins. Eur J Biochem 145, 659-676.
Montreuil J, Tonnelat J, Mullet S. 1960 Preparation et proprietes de la lactosiderophiline (lactotransferrine) du lait du femme. Biochim Biophys Acta 45, 413-421.
Moore SA, Anderson BF, Groom CR, Haridas M, Baker EN. 1998 Three-dimensional Structure of diferric bovine lactoferrin at 2.8 Å resolution. J Mol Biol 274, 222-236.
Nicholson H, Anderson BF, Bland T, Shewry SC, Tweedie JW, Baker EN. 1997 Mutagenesis of the histidine ligand in human lactoferrin: Iron-binding properties and crystal structure of the His253Met mutant. Biochemistry 36, 341-346.
Nurizzo D, Baker HM, He Q-Y, MacGillivray RTA, Mason AB, Woodworth RC, Baker EN. 2001 Crystal structures and iron release properties of mutants (K206A and K296A) that abolish the dilysine interaction in the N-lobe of human transferrin. Biochemistry 40, 1616-1623.
Octave J-N, Schneider Y-J, Trouet A, Crichton RR. 1983 Iron uptake and utilization by mammalian cells: cellular uptake of transferrin and iron. Trends Biochem Sci 8, 217-220.
Peterson NA, Anderson BF, Jameson GB, Tweedie JW, Baker EN. 2000 Crystal structure and iron-binding properties of the R210K mutant of the N-lobe of human lactoferrin: implications for iron release from transferrins. Biochemistry 39, 6625-6633.
Qiu J, Hendrixson DR, Baker EN, Murphy TF, St Geme III JW, Plaut AG. 1998 Human milk lactoferrin inactivates two putative colonization factors expressed by Haemophilus influenzae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95, 12641-12646.
Sharma, AK, Paramasivan, M, Srinivasan A, Yadav MP, Singh TP. 1999a Three dimensional structure of mare diferric lactoferrin at 2.6 Å resolution. J Mol Biol 289, 303-317.
Sharma, AK, Rajashankar, KR, Yadav MP, Singh, TP. 1999b Crystal structure of mare apo lactoferrin: Structures of the N and C lobes are in the closed form. Acta Cryst D55, 1152-1157.
Singh PK, Parsek MR, Greenberg EP, Welsh MJ. 2002 A component of innate immunity prevents bacterial biofilm development. Nature 417, 552-555.
Suzuki YA, Shin K, Lonnerdal B. 2001 Molecular cloning and functional expression of a human intestinal Lf receptor. Biochemistry 40, 15771-15779.
Van Berkel PHC, Geerts MEJ, van Veen HA, Mericskay M, de Boer HA, Nuijens JH. 1997 N-terminal stretch Arg2, Arg3, Arg4 and Arg5 of human lactoferrin is essential for binding to heparin, bacterial lipopolysaccharide, human lysozyme and DNA. Biochem J 328, 145-151.
Ward PP, Zhou X, Conneely OM. 1996 Cooperative interactions between the amino-and carboxy-terminal lobes contribute to the unique iron-binding stability of lactoferrin. J Biol Chem 271, 12790-12794.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baker, H.M., Baker, E.N. Lactoferrin and Iron: structural and dynamic aspects of binding and release. Biometals 17, 209–216 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BIOM.0000027694.40260.70
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BIOM.0000027694.40260.70