Abstract
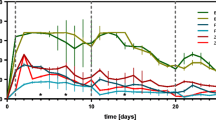
To evaluate the sediment quality of selected sites in the catchment area of the River Neckar, an integrative assessment approach was used to assess the ecological hazard potential of dioxin-like sediment compounds. The approach is based on 7-ethoxyresorufin-O -deethylase (EROD) induction in embryonic chicken liver culture and comprehensive chemical analyses of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (priority PAHs according to the US Environmental Protection Agency). The majority of the sediment extracts exhibited high potencies as EROD-inducers. In one sediment sample, which was influenced by a sewage treatment plant, a very high concentration of 930 ng bioassay 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p -dioxin (TCDD) equivalents (bio-TEQs )/g organic carbon could be determined. However, in none of the samples, more than 6% of the EROD-inducing potency could be explained by the PAHs analyzed chemically. Thus, non-analyzed compounds with EROD-inducing potency were present in the extracts. A fractionation of sediment samples according to pH allowed to localize the major part of EROD-inducing compounds in the neutral fractions. However, a significant portion of the EROD induction could also be explained by the acidic fractions. Following the concept of the Sediment Quality Triad according to Chapman, in situ alterations of macrozoobenthos were examined. A comparison of the results predicted by the EROD assay and chemical analyses with alterations in situ , as measured by means of the saprobic index and the ecotoxicological index according to Carmargo, revealed a high ecological relevance of the results of bioassays and chemical analyses for major sites.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker, R. (1992). Kartierung der Oberflächengewässer. Report. Amt für Umweltschutz und Gesundheitsförderung der Stadt Heidelberg., Heidelberg 213 p.
Berbner, T., Rahman, N. and Braunbeck, T. (1999). Induction of P450 1A and DNA damage in isolated rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss ) hepatocytes by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p -dioxin. Biomarkers 4 , 214–28.
Böhmer, J., Rawer-Jost, C. and Kappus, B. (1999). Ökologische Fließgewässerbewertung, Biologische Grundlagen und Verfahren—Schwerpunkt Makrobenthos. In C. Steinberg, W. Calmano, H. Klapper, R.-D. Wilken (eds). Handbuch Angewandte Limnologie, Loseblattsammlung, 8. Ergänzungslieferung . pp. 1–59 Ecomed. Verlag.
Böhmer, J., Rawer-Jost, C. and Kappus, B. (2000). Ökologische Fließgewässerbewertung, Biologische Grundlagen und Verfahren—Schwerpunkt Makrobenthos, Teil II. In C. Steinberg, W. Calmano, H. Klapper, R.-D. Wilken (eds). Handbuch Angewandte Limnologie, Loseblattsammlung, 9. Ergänzungslieferung . pp. 60–120. Ecomed-Verlag.
Brack, W., Hollert, H., Kind, T., Segner, H. and Schüürmann, G. (1999). Effect-directed identification of EROD-inducing and mutagenic compounds in sediment extracts. Proceedings of the annual meeting of the Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry . USA: Philadelphia.
Brack, W., Hollert, H., Kind, T., Segner, H. and Schüürmann, G. Effect-directed identification of EROD-inducing compounds in sediment extracts.
Brack, W., Segner, H., Möder, M. and Schüürmann, G. (2000). Fixed-effect-level toxicity equivalents—A suitable parameter for assessing ethoxyresorufin-O -deethylase induction potency in complex environmental samples. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 19 , 2493–501.
Braukmann, U. and Pinter, I. (1997). Concepts for an integrated ecological evaluation of running waters—Strategy paper. Acta. Hydrochim. Hydrobiol. 25 , 113–27.
Braukmann, U. and Vobis, H. (1998). LfU Baden-Württemberg, Gewässergütekarte Baden-Württemberg.
Brunström, B., Broman, D. and Näf, C. (1991). Toxicity and EROD-inducing potency of 24 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in chick embryos. Arch. Toxicol. 65 , 485–89.
Brunström, B., Engwall, M., Hjelm, K., Lindqvist, L. and Zebühr, Y. (1995). EROD induction in cultured chick embryo liver: a sensitive bioassay for dioxin-like environmental pollutants. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 14 , 837–42.
Brunström, B., Halldin, K. (1998). EROD induction by environmental contaminants in avian embryo livers. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C. 121 , 213–19.
Bucheli, T.D. and Fent, K. (1995). Induction of cytochrome P450 as a biomarker for environmental contamination in aquatic ecosystems. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 00 , 201–68.
Carmargo, J.A. (1990). Performance of a new ecotoxicological index to assess environmental impacts on freshwater communities. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 44 , 529–34.
Chapman, P.M. (1990). The sediment quality triad approach to determining pollution-induced degradation. Sci. Tot. Environ. 97/98 , 815–25.
Chapman, P.M. (1996). Presentation and interpretation of sediment quality triad data. Ecotoxicology 5 , 327–39.
Chapman, P.M. (2000). The sediment quality triad: then, now and tomorrow. Int. J. Environ. Poll. 13 , 351–56.
Clemons, J.H., Myers, C.R., Lee, L.E.J., Dixon, D.G. and Bols, N.C. (1998). Induction of cytochrome P4501A by binary mixtures of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p -dioxin (TCDD) in liver cell lines from rat and trout. Aquat. Toxicol. 43 , 179–94.
DelValls, T.A., Forja, J.M. and Gómez-Parra, A. (1998). Integrative assessment of sediment quality in two littoral ecosystems from the gulf of Cádiz, Spain. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 17 , 1073–84.
Di Toro, D.M., Zarba, C.S., Hansen, D.J., Berry, W.J., Swartz, R.C., Cowan, C.E., Pavlou, S.P., Allen, H.E., Thomas, N.A. and Paquin, P.R. (1991). Technical basis for establishing sediment quality criteria for nonionic organic chemicals using equilibrium partitioning. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 10 , 1541–83.
Engwall, M., Broman, D., Dencker, L., Näf, C., Zebühr, Y. and Brunström, B. (1997a). Toxic potencies of extracts of sediment and settling particulate matter collected in the recipient of a bleached pulp mill effluent before and after abandoning chlorine bleaching. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 16 , 1187–94.
Engwall, M., Broman, D., Ishaq, R., Näf, C., Zebühr, Y. and Brunström, B. (1996). Toxic potencies of lipophilic extracts from sediments and settling particulate matter (SPM) collected in a PCB contaminated river system. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 15 , 213–22.
Engwall, M., Broman, D., Naf, C., Zebuhr, Y. and Brunstrom, B. (1997b). Dioxin-like compounds in HPLC-fractionated extracts of marine samples from the east and west coast of Sweden: Bioassay-and instrumentally-derived TCDD equivalents. Mar. Poll. Bull. 34 , 1032–40.
Engwall, M., Brunström, B. and Jakobsson, E. (1994). Ethoxyresorufin o-deethylase (EROD) and aryl-hydrocarbon hydroxylase (AHH)-inducing potency and lethality of chlorinated naphthalenes in chicken (Gallus domesticus ) and eider duck (Somateria mollissima ) embryos. Arch. Toxicol. 68 , 37–42.
Engwall, M., Brunstrom, B., Naf, C. and Hjelm, K. (1999). Levels of dioxin-like compounds in sewage sludge determined with a bioassay based on EROD induction in chicken embryo liver cultures. Chemosphere 38 , 2327–43.
Engwall, M., Naf, C., Broman, D. and Brunstrom, B. (1998). Biological and chemical determination of contaminant levels in settling particulate matter and sediments—A Swedish river system before, during, and after dredging of PCB-contaminated lake sediments. Ambio. 27 , 403–10.
Erdinger, L., Höpker, K.-A., Dörr, I., Fried, M. and Dürr, M. (1997). Genotoxische organische Verbindungen in der Außenluft Identität, Transformation und ökotoxikologische Bedeutung, Veröff PAÖ Publication Series. Landesanstalt für Umweltschutz Karlsruhe, Vol. 24, 215 pp. Karlsruhe.
Förstner, U. and Müller, G. (1974). Schwermetalle in Flüssen und Seen . Heidelberg: Spinger-Verlag.
Froelich, P.N. (1980). Analysis of organic carbon in marine sediment. Limnol. Oceanogr. 25 , 564–72.
Goksøyr, A. and Husøy, A.M. (1998). Immunochemical approaches to studies of CYPIA localization and induction by xenobiotics in fish. In T. Braunbeck, D.E. Hinton, and B. Streit (eds). Fish Ecotoxicology Experimentia Supplement Vol. 86, pp. 165–202. Basel: Birkhäuser.
Gustafsson, E., Brunstrom, B. and Nilsson, U. (1994). Lethality and EROD-inducing potency of chlorinated chrysene in chick embryos. Chemosphere 29 , 2301–8.
Haglund, P., Alsberg, T., Bergman, A. and Jansson, B. (1987). Analysis of halogenated polycyclic aromatic-hydrocarbons in urban air, snow and automobile exhaust. Chemosphere 16 , 2441–50.
Hahn, M.E. and Karchner, S.I. (1995). Evolutionary conservation of the vertebrate Ah (dioxin) receptor: amplification and sequencing of the PAS domain of a teleost Ah receptor cDNA. Biochem J. 310 , 383–7.
Hahn, M.E. and Stegeman, J.J. (1992). Phylogenetic distribution of the Ah receptor in non-mammalian species: implication for dioxin toxicity and receptor evolution. Chemosphere 25 , 931–7.
Ho, K.T.Y. and Quinn, J.G. (1993). Physical and chemical parameters of sediment extraction and fractionation that influence toxicity as evaluated by Microtox. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 12 , 615–25.
Hollert, H., Dürr, M., Erdinger, L. and Braunbeck, T. (2000). Cytotoxicity of settling particulate matter (SPM) and sediments of the Neckar river (Germany) during a winter flood. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 19 , 528–34.
Hollert, H., Heise, S., Pudenz, S., Brüggemann, R., Ahlf, W. and Braunbeck, T. (2002). Application of a sediment quality triad and different statistical approaches (Hasse diagrams and fuzzy logic) for the comparative evaluation of small streams. Ecotoxicology, 11 , 323–36.
Huuskonen, S.E. (1999). Environmental monitoring of lipophilic compounds with PLHC-1 fish cells and fish. Faculty of Natural and Environmental Science . Kuopio, Kuopio.
Kern, U. and Westrich, B. (1995). Sediment contamination by heavy metals in a lock regulated section of the river Neckar. Mar. Freshwater Res. 46 , 101–6.
Kleman, M. and Gustafsson, J.A. (1996). Interactions of procarcinogenic heterocyclic amines and indolocarbazoles with the dioxin receptor. Biol. Chem. 377 , 741–62.
Kwon, C.S., Grose, K.R., Riby, J., Chen, Y.H. and Bjeldanes, L.F. (1994). In-vivo production and enzyme-inducing activity of indole[3,2-b] carbazole. J. Agricult. Food. Chem. 42 , 2536–40.
Lee, L.E.J., Clemons, J.H., Bechtel, D.G., Caldwell, S.J., Han, H.-B., Pasitschniak-Arts, M., Mosser, D.D. and Bols, N.C. (1993). Development and characterization of rainbow trout liver line expressing cytochrome P450-dependent mono-oxygenase activity. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 9 , 279–94.
LfU-(Environmental Protection, Agency), Baden-Württemberg, (1992). Biologisch-ökologische Gewässeruntersuchung-Arbeitsanleitung, Handbuch Wasser 2 Karlsruhe.
Lundstedt, S., van Bavel, B., Haglund, P., Tysklind, M. and Oberg, L. (2000). Pressurised liquid extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from contaminated soils. J. Chromatogr. A 883 , 151–62.
Müller, G. and Gastner, M. (1971). The “Karbonatbombe”, a simple device for the determination of carbonate content in sediments, soils and other materials. Neues Jahrbuch für Mineralogie 00 , 466–9.
Nilsson, U.L. and Ostman, C.E. (1993). Chlorinated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Method of analysis and their occurrence in urban air. Environ. Sci. Technol. 27 , 1826–31.
Oehme, M., Mano, S. and Mikalsen, A. (1987). Formation and presence of polyhalogenated and polycyclic compounds in the emissions of small and large-scale municipal waste incinerators. Chemosphere 16 , 143–53.
Östman, C. and Nilsson, U. (1992). Coupled LC-GC-MS for online cleanup, separation, and identification of chlorinated polycyclic aromatic-hydrocarbons at picogram levels in urban air. J. High. Resolut. Chrom. 15 , 745–50.
Otto, D., Lindström-Seppä, P. and Sen, C. (1994). Cytochrome P450—dependent enzymes and oxidant-mediated responses in rainbow trout exposed to contaminated sediments. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety 27 , 265–80.
Pinter, I. (1986). Auswirkung der Abwassersanierungsmassnahmen auf den Gütezustand des Neckars, In G. Müller (ed.), Neckar-Umwelt-Symposium 22–23 , pp. 64–70. Oktober Heidelberg, Heidelberg.
Poland, A. and Knutson, J.C. (1982). 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and related halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons: examination of the mechanism of toxicity. Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 22 , 517–54.
Schrenk, D., Riebniger, D., Till, M., Vetter, S. and Fiedler, H.P. (1999). Tryptanthrins and other tryptophan-derived agonists of the dioxin receptor. Tryptophan Serotonin Melatonin . 467 , 403–8.
Toftgård, R., Franzén, B., Gustafsson, J.Å. and Löfroth, G. (1985). Characterization of TCDD-receptor ligands present in extracts of urban particulate matter. Environ. Int. 11 , 369–74.
van der Weiden, M.E.J., Celander, M., Seinen, W., van den Berg, M., Goksøyer, A. and Förlin, L. (1993). Induction of cytochrome P450 1A in fish treated with 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p -dioxin or chemically contaminated sediment. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 12 , 989–99.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hollert, H., Dürr, M., Olsman, H. et al. Biological and Chemical Determination of Dioxin-like Compounds in Sediments by Means of a Sediment Triad Approach in the Catchment Area of the River Neckar. Ecotoxicology 11, 323–336 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020549103898
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020549103898