Abstract
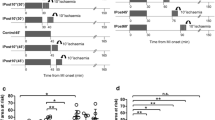
Inhibition of Na+/H+ exchange with amiloride analogues has been shown to provide functional protection during ischemia and reperfusion and to reduce infarct size in isolated rat hearts. In rat hearts, treatment with ethylisopropyl-amiloride (EIPA, a selective Na+/H+ exchange inhibitor) was additive to the protection afforded by ischemic preconditioning. In addition, such compounds have been demonstrated to reduce infarct size in in situ rabbit hearts. The aim of the present study was to determine to what extent preischemic treatment with EIPA could reduce infarct size in an in situ rabbit model of regional ischemia and reperfusion. We also wished to determine if this effect was additive to the infarct reducing effect of ischemic preconditioning. Anaesthetized, open chest rabbits, were subjected to 45 min of regional ischemia and 150 min of reperfusion. The risk zone was determined by fluorescent particles and infarct size was determined by TTC staining. Four groups were investigated: control, ischemic preconditioned (IP) (5 min of ischemia followed by 10 min reperfusion), EIPA (0.65 mg/kg iv given preischemically) and EIPA + IP. The main results expressed as percent infarction of the risk zone ± S.E.M. for the different groups were: control 59.2 ± 3.3% (n = 6), IP 16.3 ± 2.1% (n = 6) (p < 0.001 vs. control), EIPA 16.9 ± 4.1% (n = 5) (p < 0.001 vs. control), EIPA + IP 22.5 ± 9.5% (n = 6) (p < 0.001 vs. control). In conclusion: EIPA, when administered prior to ischemia, caused a reduction in infarct size in the in situ rabbit heart which was similar to that seen with ischemic preconditioning, however, the effect was not additive to ischemic preconditioning.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Murry CE, Jennings RB, Reimer KA: New insights into potential mechanisms of ischemic preconditioning [editorial]. Circ 84: 442–445, 1991
Bugge E, Munch-Ellingsen J, Ytrehus K: Reduced infarct size in the rabbit heart in vivo by ethylisopropyl-amiloride. A role for Na+/H+ exchange. Basic Res Cardiol 91: 203–209, 1996
Ytrehus K, Liu Y, Downey JM: Preconditioning protects ischemic rabbit heart by protein kinase C activation. Am J Physiol 266: H1145–H1152, 1994
Munch-Ellingsen J, Ytrehus K, Bugge E: Blockade of the KATP-channel by glibenclamide aggravates ischemic injury, and counteracts ischemic preconditioning. Basic Res Cardiol 382–388, 1996
Karmazyn M, Moffat MP: Role of Na+/H+ exchange in cardiac physiology and pathophysiology: Mediation of myocardial reperfusion injury by the pH paradox. Cardiovasc Res 27: 915–924, 1993
Duff HJ: Clinical and in vivo antiarrhythmic potential of sodiumhydrogen exchange inhibitors. Cardiovasc Res 29: 189–193, 1995
Frelin C, Vigne P, Lazdunski M: The role of the Na+/H+ exchange system in cardiac cells in relation to the control of the internal Na+ concentration. A molecular basis for the antagonistic effect of ouabain and amiloride on the heart. J Biol Chem 259: 8880–8885, 1984
Tani M, Neely JR: Role of intracellular Na+ in Ca2+ overload and depressed recovery of ventricular function of reperfused ischemic rat hearts. Possible involvement of H+-Na+ and Na+-Ca2+ exchange. Circ Res 65: 1045–1056, 1989
Moffat MP, Karmazyn M: Protective effects of the potent Na/H exchange inhibitor methylisobutyl amiloride against post-ischemic contractile dysfunction in rat and guinea-pig hearts. J Mol Cell Cardiol 25: 959–971, 1993
Scholz W, Albus U, Linz W, Martorana P, Lang HJ, Scholkens BA: Effects of Na+/H+ exchange inhibitors in cardiac ischemia. J Mol Cell Cardiol 24: 731–739, 1992
Kleyman TR, Cragoe EJ: Amiloride and its analogs as tools in the study of ion transport. J Membrane Biol 105: 1–22, 1988
Bugge E, Ytrehus K: Inhibition of sodium-hydrogen exchange reduces infarct size in the isolated rat heart – a protective additive to ischaemic preconditioning. Cardiovasc Res 29: 269–274, 1995
Przyklenk A, Hata K, Kloner RA: The Na+-H+ exchange inhibitor dimethylamiloride blocks preconditioning in the canine model. Circ 94: (abstr) I-424, 1996
Wadsworth S, Wu AM, Spitzer A, Chander A: Protein kinase C in intracellular pH regulation in alveolar type II cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 271: L106–L113, 1996
Liu Y, Ytrehus K, Downey JM: Evidence that translocation of protein kinase C is a key event during ischemic preconditioning of rabbit myocardium. J Mol Cell Cardiol 26: 661–668, 1994
Munch-Ellingsen J, Løkebø JE, Bugge E, Ytrehus K: Dofetilide. Scand J Clin Lab Invest, 1997
Janvier NC, Boyett MR: The role of Na-Ca exchange current in the cardiac action potential. Cardiovasc Res 69–84, 1996
Duff HJ, Lester WM, Rahmberg M: Amiloride. Antiarrhythmic and electrophysiological activity in the dog. Circ 78: 1469–1477, 1988
Gold MR, Strichartz GR: Use-dependent block of atrial sodium current by ethylisopropylamiloride. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 17: 792–799, 1991
Pierce GN, Cole WC, Liu K, Massaeli H, Maddaford TG, Chen YJ, McPherson CD, Jain S, Sontag D: Modulation of cardiac performance by amiloride and several selected derivatives of amiloride. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 265: 1280–1291, 1993
Clark JD, Limbird LE: Na+-H+ exchanger subtypes: A predictive review. Am J Physiol 261: C945–C953, 1991
Gottlieb RA, Gruol DL, Zhu JY, Engler RL: Preconditioning in rabbit cardiomyocytes. J Clin Inv 97: 2391–2398, 1996
Shattock MJ, Bers DM: Rat vs. rabbit ventricle: Ca flux and intracellular Na assessed by ion-selective microelectrodes. Am J Physiol 256: C814–C822, 1989
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Munch-Ellingsen, J., L¢keb¢, J.E., Bugge, E. et al. Equal reduction in infarct size by ethylisopropyl-amiloride pretreatment and ischemic preconditioning in the in situ rabbit heart. Mol Cell Biochem 186, 13–18 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006820509480
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006820509480