Abstract
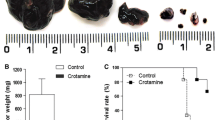
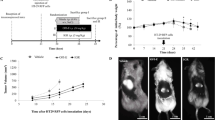
The antitumoral effect of the new lipid A OM 174 was investigated in a model of colon cancer in rats. Peritoneal carcinomatosis were induced in BDIX rats by intraperitoneal injection of syngeneic PROb cancer cells. The treatment started 2 weeks later, when rats had macroscopic peritoneal nodules. An antitumoral effect was first obtained with OM 174 intraperitoneally injected, then an intravenous treatment was developed. When injected 15 times intravenously, at the dose of 1 mg/kg, 2 days apart, OM 174 induced the complete regression of tumors and hemorrhagic ascitis in 90% of the tumor-bearing rats, whereas all the untreated rats died of their tumors. To our knowledge, this treatment is the most effective ever applied to macroscopic tumors. Furthermore, the treatment induced the immunization of rats since the reinjection of PROb tumor cells in OM 174-cured rats did not cause the formation of new tumors while injection of another syngenic colon tumor cells did. Only in treated rats tumors were infiltrated with lymphocytes, macrophages and fibroblasts. The treatment did not increase necrosis but generated apoptotic areas. OM 174 was not directly toxic for tumor cells, and thus the observed effect involved the host-mediated antitumor reaction. Therefore we hypothesize that OM 174 therapy induces tumor cell apoptosis, stimulates the phagocytosis of apoptotic bodies and then activates immune system by antigen presentation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deidier A. Deux dissertations médicinales et chirurgicales, l'une sur la maladie vénérienne, l'autre sur la nature et la curation des tumeurs. Paris: C. M. D'Houry, imprimeur, 1725.
Coley WB. The treatment of inoperable sarcoma with the mixed toxins of erysipelas and bacillus prodigiosus. Am Med Assoc 1898; 31: 389–95.
Shear MJ, Turrner FC. Chemical treatment of tumor. V. Isolation of the hemorrhage-producing fraction from Serratia marcescens (Bacillus prodigiosus) culture filtrate. J Natl Cancer Inst 1943; 4: 81–97.
Engelhard R, Mackensen A, Galanos C, Andreesen R. Biological response to intravenously administered endotoxin in patients with advanced cancer. J Biol Resp Modif 1990; 9: 480–91.
Goto S, Sakai S, Kera J et al. Intradermal administration of lipopolysaccharide in treatment of human cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother 1996; 42: 255–61.
Nowotny A. In search of the active sites in endotoxins. In Nowotny A (ed): Beneficial Effects of Endotoxins. New York: Plenum Press 1983; 1–56.
Jeannin JF, Onier N, Lagadec P et al. Antitumor effect of synthetic derivatives of Lipid A in an experimental model of colon cancer in the rat. Gastroenterology 1991; 101: 726–33.
Galanos C, Lehmann V, Luderritiz O. et al. Endotoxic properties of chemically synthetized lipid A part structures. Comparison of synthetic lipid A precursor and synthetic analogues with biosynthetic lipid A precursor and free lipid A. Eur J Biochem 1984; 140: 221–7.
Imoto M, Kusumoto S, Shiba T et al. Chemical structure of E. coli lipid A. Tetrahedron Lett 1985; 26: 907–8.
Martin F, Caignard A, Jeannin JF et al. Selection by trypsin of two sublines of rat colon cancer cells forming progressive or regressive tumors. Int J Cancer 1983; 32: 623–7.
Lagadec P, Jeannin JF, Reisser D et al. Treatment with endotoxins of peritoneal carcinomatosis induced by colon tumor cells in the rat. Invas Metast 1987; 7: 83–95.
Blondiau C, Lagadec P, Lejeune P et al. Correlation between the capacity to activate macrophages in vitro and the antitutmor activity in vivo of lipopolysaccharides from different bacterial species. Immunobiol 1994; 190: 243–54.
Ribi E, Amano K, Cantrell J et al. Preparation and antitumor activity of nontoxic lipid A. Cancer Immunol Immunother 1982; 12: 91–6.
Qureshi N, Takayama K, Ribi E. Purification and structural determination of nontoxic lipid A obtained from the lipopolysaccharide of Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem 1982; 257: 11808–15.
Kumazawa E, Togho A, Soga T et al. Significant antitumor effect of a synthetic lipid A analogue, DT-5461, on murine syngeneic tumor models. Cancer Immunol Immunother 1992; 35: 307-14.
Sato K, Yoo YC, Mochizuki M et al. Inhibition of tumor-induced angiogenesis by a synthetic lipid A analogue with low endotoxicity, DT-5461. Jpn J Cancer Res 1995; 86: 374–82.
Jimbo T, Akimoto T, Tohgo A. Systemic administration of a synthetic lipid A derivative, DT-5461a, reduces tumor blood flow through endogenous TNF production in hepatic cancer model of VX2 carcinoma in rabbits. Anticancer Res 1996; 16: 359-64.
Nakatsuka M, Kumazawa Y, Ikeda S et al. Antitumor and antimicrobial activities of lipid A-subunit analogue GLA-27. J Clin Lab Immunol 1988; 26: 43–7.
Nakatsuka M, Kumazawa Y, Homma JY et al. Inhibition in mice of experimental metastasis of B16 melanoma by the synthetic Lipid Asubunit analog GLA-60. Int J Immunopharmacol 1991; 13: 11–9.
Yang D, Satoh M, Ueda H et al. Activation of tumor-infiltrating macrophages by a synthetic lipid A analog (ONO-4007) and its implication in antitumor effects. Cancer Immunol Immunother 1994; 38: 287–93.
Matsumoto N, Aze Y, Akimoto A, Fujita T. Restoration of immune responses in tumor-bearing mice by ONO-4007, an antitumor lipid A derivative. Immunopharmacology 1997; 36: 69–78.
Kuramitsu Y, Noshibe M, Ohiro Y et al. A new synthetic lipid A analog, ONO-4007, stimulates the production of tumor necrosis factor-α in tumor tissues, resulting in the rejection of transplanted rat hepatoma cells. Anti-Cancer Drugs 1997; 8: 500–8.
Saiki I, Sato K, Yoo YC et al. Inhibition of tumor-induced angiogenesis by the administration of recombinant interferon-α followed by a synthetic lipid-A subunit analogue (GLA-60). Int J Cancer 1992; 51: 641–5.
Jimbo T, Akimoto T, Tohgo A. Effect of combined administration of a synthetic low-toxicity lipid A derivative, DT 5461a, and indomethacin in various experimental tumor models of colon 26 carcinoma in mice. Cancer Immunol Immunother 1995; 40: 10–6.
Boisteau O, Gautier F, Cordel S et al. Apoptosis induced by sodium butyrate treatment increases immunogenicity of rat colon tumor cell line. Apoptosis 1997; 2: 403–12.
Jeannin JF, Lagadec P, Pelletier D et al. Regression induced by lentinan of peritoneal carcinomatosis in a model of colon cancer in rat. Int J Immunopharmacol 1988; 10: 855–61.
Lejeune P, Reisser D, Onier N et al. Interleukin-8 has antitumor effects in rat which are not associated with PMN cytotoxicity. Cancer Immunol Immunother 1994; 38: 167–70.
Chauffert B, Dimanche-Boitrel MT, Genne P et al. Chimiothérapie expérimentale d'une carcinomatose péritonéale d'origine colique chez le rat. Gastroen Clin Biol 1992; 16: 215–9.
Akimoto T, Kumazawa E, Jimbo T et al. Antitumor effect of DT-5641a, a synthetic low-toxicity lipid A analog, involves endogenous tumor necrosis factor induction subsequent to macrophage activation. Int J Immunopharmacol 1994; 16: 887–93.
Casciola-Rosen LA, Anhalt GJ, Rosen A. DNA-dependent-protein kinase is one of a subset of autoanigens specifically cleaved early during apoptosis. J Exp Med 1995; 182: 1625–34.
Bonnotte B, Favre N, Moutet M et al. Bcl-2-mediated inhibition of apoptosis prevents immunogenicity and restores tumorigenicity of spontaneously regressive tumors. J Immunol 1998; 161: 1433–38.
Onier N, Hilpert S, Reveneau S et al. Expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in tumors in relation with their regression induced by a lipid A in rats. Int J Cancer 1999 (in press).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Onier, N., Hilpert, S., Arnould, L. et al. Cure of colon cancer metastasis in rats with the new lipid A OM 174. Apoptosis of tumor cells and immunization of rats. Clin Exp Metastasis 17, 299–306 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006663017149
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006663017149